What Are The Common Factors Of 18 And 36
Juapaving
Mar 16, 2025 · 6 min read
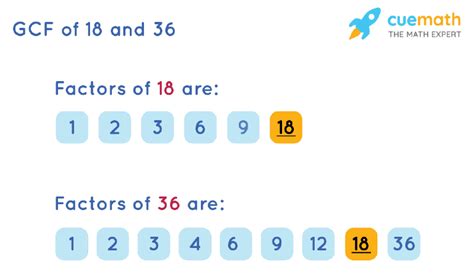
Table of Contents
What are the Common Factors of 18 and 36? A Deep Dive into Number Theory
Finding the common factors of two numbers might seem like a simple task, especially for smaller numbers like 18 and 36. However, understanding the underlying principles behind this seemingly basic concept opens the door to a fascinating world of number theory, with implications far beyond elementary arithmetic. This article will not only answer the question of what the common factors of 18 and 36 are but will also explore the broader mathematical concepts involved, providing a detailed explanation suitable for a diverse audience, from students just beginning to explore factors and multiples to those looking for a deeper understanding of number theory.
Understanding Factors and Multiples
Before we delve into finding the common factors of 18 and 36, let's define some key terms:
-
Factors: Factors of a number are whole numbers that divide evenly into that number without leaving a remainder. For example, the factors of 12 are 1, 2, 3, 4, 6, and 12.
-
Multiples: Multiples of a number are the results of multiplying that number by any whole number. For example, the multiples of 3 are 3, 6, 9, 12, 15, and so on.
-
Common Factors: Common factors are the factors that two or more numbers share. These are the numbers that divide evenly into all the numbers in question.
Finding the Factors of 18 and 36
To find the common factors of 18 and 36, we first need to list all the factors of each number individually.
Factors of 18:
1, 2, 3, 6, 9, 18
Factors of 36:
1, 2, 3, 4, 6, 9, 12, 18, 36
Identifying the Common Factors
Now, let's compare the two lists to identify the numbers that appear in both:
1, 2, 3, 6, 9, and 18.
Therefore, the common factors of 18 and 36 are 1, 2, 3, 6, 9, and 18.
Prime Factorization: A Powerful Tool
A more systematic approach to finding common factors involves prime factorization. Prime factorization is the process of expressing a number as the product of its prime factors. A prime number is a whole number greater than 1 that has only two factors: 1 and itself.
Prime Factorization of 18:
18 = 2 x 3 x 3 = 2 x 3²
Prime Factorization of 36:
36 = 2 x 2 x 3 x 3 = 2² x 3²
By expressing each number as a product of its prime factors, we can easily identify the common factors. The common factors are the prime factors that appear in both factorizations, raised to the lowest power they appear in either factorization. In this case, both 18 and 36 share two prime factors: 2 and 3.
- Common prime factor 2: The lowest power of 2 in either factorization is 2<sup>1</sup> (or simply 2).
- Common prime factor 3: The lowest power of 3 in either factorization is 3<sup>2</sup> (or 9).
To find all the common factors, we combine these common prime factors in all possible ways:
- 2<sup>0</sup> x 3<sup>0</sup> = 1
- 2<sup>1</sup> x 3<sup>0</sup> = 2
- 2<sup>0</sup> x 3<sup>1</sup> = 3
- 2<sup>1</sup> x 3<sup>1</sup> = 6
- 2<sup>0</sup> x 3<sup>2</sup> = 9
- 2<sup>1</sup> x 3<sup>2</sup> = 18
This method confirms that the common factors of 18 and 36 are 1, 2, 3, 6, 9, and 18.
Greatest Common Factor (GCF)
Among the common factors, there is always one that is the largest. This is known as the Greatest Common Factor (GCF), also sometimes called the Highest Common Factor (HCF). In the case of 18 and 36, the GCF is 18. The GCF is a crucial concept in various mathematical applications, including simplifying fractions and solving algebraic equations.
Real-World Applications of Common Factors and GCF
The concept of common factors and the GCF isn't just an abstract mathematical exercise; it has practical applications in various areas:
-
Simplifying Fractions: Finding the GCF is essential when simplifying fractions to their lowest terms. For example, the fraction 36/18 can be simplified by dividing both the numerator and the denominator by their GCF, which is 18, resulting in the simplified fraction 2/1 or simply 2.
-
Dividing Objects Equally: Imagine you have 36 apples and 18 oranges, and you want to distribute them equally among several baskets, such that each basket contains the same number of apples and the same number of oranges. The GCF (18) tells you that you can create a maximum of 18 baskets, each containing 2 apples and 1 orange.
-
Geometric Problems: The GCF is used in geometric problems involving dividing shapes into smaller, identical shapes.
-
Scheduling and Timing: In scheduling tasks or planning events with different time intervals, finding common factors helps determine the next time when events will coincide.
Beyond the Basics: Exploring Further Concepts
The exploration of common factors opens up pathways to several more advanced mathematical concepts:
-
Least Common Multiple (LCM): While we've focused on common factors, the Least Common Multiple (LCM) is the smallest positive integer that is a multiple of two or more numbers. The LCM and GCF are related through the formula: LCM(a, b) * GCF(a, b) = a * b, where 'a' and 'b' are the two numbers.
-
Euclidean Algorithm: This efficient algorithm provides a method for finding the GCF of two numbers without needing to list all their factors. It's particularly useful for larger numbers where listing factors becomes cumbersome.
-
Modular Arithmetic: The concept of factors and multiples plays a fundamental role in modular arithmetic, a branch of number theory that deals with remainders after division. Understanding common factors is vital in solving congruence equations.
-
Cryptography: Prime factorization, a closely related concept, forms the basis of many modern cryptographic systems, securing online transactions and communications. The difficulty of factoring large numbers into their prime components is the foundation of the security of these systems.
Conclusion: The Importance of Understanding Common Factors
Understanding common factors, including how to find them using both listing and prime factorization, and recognizing their importance in finding the GCF, provides a solid foundation in number theory. These concepts aren't just abstract mathematical ideas; they have practical implications across various fields, demonstrating their relevance beyond the classroom. The journey from simply identifying common factors to grasping the intricacies of prime factorization and the Euclidean algorithm showcases the power and beauty of mathematical exploration. The seemingly simple question of "What are the common factors of 18 and 36?" thus becomes a gateway to a rich understanding of a fundamental aspect of mathematics.
Latest Posts
Latest Posts
-
Do Viruses Belong To One Of The Domains Of Life
Mar 17, 2025
-
The C Shape Of The Tracheal Cartilages Is Important Because
Mar 17, 2025
-
Least Common Multiple Of 5 6 7
Mar 17, 2025
-
How Do You Find The Inverse Of A Relation
Mar 17, 2025
-
Does Cold Air Go Up Or Down
Mar 17, 2025
Related Post
Thank you for visiting our website which covers about What Are The Common Factors Of 18 And 36 . We hope the information provided has been useful to you. Feel free to contact us if you have any questions or need further assistance. See you next time and don't miss to bookmark.
