What Are The Common Factors Of 14 And 28
Juapaving
Mar 20, 2025 · 5 min read
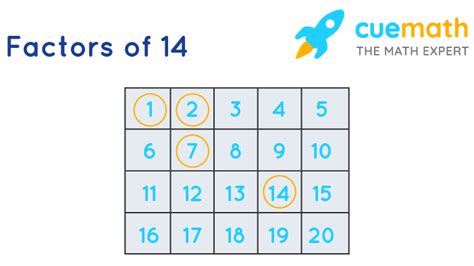
Table of Contents
What Are the Common Factors of 14 and 28? A Deep Dive into Number Theory
Finding the common factors of two numbers might seem like a simple task, especially with smaller numbers like 14 and 28. However, understanding the underlying concepts reveals a fascinating glimpse into the world of number theory, with implications extending far beyond basic arithmetic. This article will explore not only the common factors of 14 and 28 but also delve into the broader mathematical principles involved, including prime factorization, greatest common divisor (GCD), and least common multiple (LCM). We'll also touch upon practical applications of these concepts.
Understanding Factors
Before we tackle the specifics of 14 and 28, let's establish a firm understanding of what factors are. A factor of a number is a whole number that divides that number without leaving a remainder. For instance, the factors of 12 are 1, 2, 3, 4, 6, and 12 because each of these numbers divides 12 evenly.
Finding Factors of 14
Let's find the factors of 14:
- 1: 14 divided by 1 equals 14
- 2: 14 divided by 2 equals 7
- 7: 14 divided by 7 equals 2
- 14: 14 divided by 14 equals 1
Therefore, the factors of 14 are 1, 2, 7, and 14.
Finding Factors of 28
Now, let's determine the factors of 28:
- 1: 28 divided by 1 equals 28
- 2: 28 divided by 2 equals 14
- 4: 28 divided by 4 equals 7
- 7: 28 divided by 7 equals 4
- 14: 28 divided by 14 equals 2
- 28: 28 divided by 28 equals 1
Thus, the factors of 28 are 1, 2, 4, 7, 14, and 28.
Identifying Common Factors
The common factors of 14 and 28 are the numbers that appear in both lists of factors. Comparing the factor lists above, we see that the common factors of 14 and 28 are:
- 1
- 2
- 7
- 14
Therefore, 1, 2, 7, and 14 are the common factors of 14 and 28.
Prime Factorization: A Deeper Look
Prime factorization provides a powerful method for finding common factors. A prime number is a whole number greater than 1 that has only two divisors: 1 and itself (e.g., 2, 3, 5, 7, 11). Prime factorization is the process of expressing a number as a product of its prime factors.
Prime Factorization of 14
14 can be factored as 2 x 7. Both 2 and 7 are prime numbers.
Prime Factorization of 28
28 can be factored as 2 x 2 x 7, or 2² x 7. Again, 2 and 7 are prime numbers.
Using Prime Factorization to Find Common Factors
By examining the prime factorizations of 14 and 28, we can easily identify the common factors. Both numbers share a factor of 2 and a factor of 7. Any combination of these prime factors will also be a common factor. Therefore:
- 2 is a common factor (present in both factorizations)
- 7 is a common factor (present in both factorizations)
- 2 x 7 = 14 is a common factor (both numbers contain at least one 2 and one 7)
- 1 is always a common factor of any two numbers.
This method reinforces our earlier finding that 1, 2, 7, and 14 are the common factors of 14 and 28.
Greatest Common Divisor (GCD)
The greatest common divisor (GCD), also known as the highest common factor (HCF), is the largest number that divides both numbers without leaving a remainder. In the case of 14 and 28, the GCD is 14. This is easily seen from our list of common factors; 14 is the largest of them.
Methods for Finding the GCD
Several methods exist for determining the GCD, including:
- Listing factors: This is the method we used initially, listing all factors and selecting the greatest common one.
- Prime factorization: By comparing the prime factorizations, we identify the common prime factors and multiply them to find the GCD.
- Euclidean algorithm: This is a more efficient algorithm, particularly for larger numbers. It involves repeatedly applying the division algorithm until the remainder is 0. The last non-zero remainder is the GCD.
Least Common Multiple (LCM)
While we've focused on common factors, understanding the least common multiple (LCM) provides a complete picture of the relationship between two numbers. The LCM is the smallest positive number that is a multiple of both numbers.
Finding the LCM of 14 and 28
To find the LCM of 14 and 28, we can list the multiples of each number:
Multiples of 14: 14, 28, 42, 56, 70... Multiples of 28: 28, 56, 84, 112...
The smallest number that appears in both lists is 28. Therefore, the LCM of 14 and 28 is 28.
Using Prime Factorization to Find the LCM
Prime factorization offers an alternative approach to finding the LCM. We use the prime factorizations of 14 (2 x 7) and 28 (2² x 7):
- Identify the highest power of each prime factor present in either factorization: 2² and 7.
- Multiply these highest powers together: 2² x 7 = 28.
This confirms that the LCM of 14 and 28 is 28.
Applications of Common Factors and GCD
The concepts of common factors and the GCD have numerous applications across various fields:
- Simplifying fractions: Finding the GCD allows us to simplify fractions to their lowest terms. For example, the fraction 28/14 simplifies to 2/1 (or simply 2) because the GCD of 28 and 14 is 14.
- Solving problems involving ratios and proportions: Understanding common factors is crucial for working with ratios and proportions.
- Geometry and measurement: GCD is used in calculating the dimensions of objects or finding the largest possible square tile that can be used to completely cover a rectangular area.
- Cryptography: Number theory concepts, including GCD, are fundamental to modern cryptography algorithms.
- Computer science: Algorithms related to GCD and LCM are used in various computer science applications, such as scheduling and resource management.
Conclusion
Determining the common factors of 14 and 28, while seemingly straightforward, provides a valuable entry point into the fascinating world of number theory. The exploration of prime factorization, GCD, and LCM illuminates the rich interconnectedness of mathematical concepts and highlights their practical applications across diverse fields. Understanding these concepts not only enhances mathematical skills but also fosters a deeper appreciation for the elegance and power of mathematics. The seemingly simple act of finding common factors opens a door to a wealth of mathematical understanding and problem-solving capabilities.
Latest Posts
Latest Posts
-
What Is The Lcm Of 7 And 8
Mar 20, 2025
-
What Electrical Charge Does Dna Have
Mar 20, 2025
-
Is Water An Element Or Compound
Mar 20, 2025
-
Lcm Of 4 6 And 8
Mar 20, 2025
-
Is Sugar A Mixture Or A Pure Substance
Mar 20, 2025
Related Post
Thank you for visiting our website which covers about What Are The Common Factors Of 14 And 28 . We hope the information provided has been useful to you. Feel free to contact us if you have any questions or need further assistance. See you next time and don't miss to bookmark.
