What Are The Characteristics Of Matter
Juapaving
Mar 13, 2025 · 6 min read
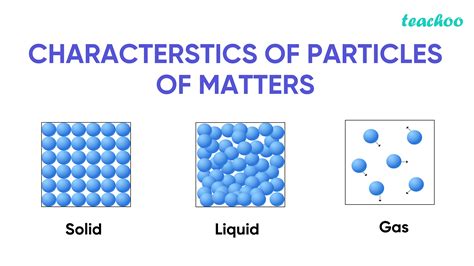
Table of Contents
What Are the Characteristics of Matter? A Deep Dive into the Building Blocks of Our Universe
Matter, the physical substance that makes up everything we can see and touch, is a fascinating subject of study. From the smallest subatomic particles to the largest celestial bodies, understanding the characteristics of matter is crucial to grasping the workings of the universe. This comprehensive guide delves into the defining properties of matter, exploring its various forms, behaviors, and the fundamental laws that govern it.
The Fundamental Characteristics of Matter
Matter is characterized by several key properties that distinguish it from other forms of energy. These include:
1. Mass and Weight: A Fundamental Distinction
Mass is a measure of the amount of matter in an object. It remains constant regardless of location. Weight, on the other hand, is a measure of the force of gravity acting on an object's mass. This means your weight changes depending on the gravitational pull – you'd weigh less on the Moon than on Earth because the Moon's gravity is weaker. While related, mass and weight are distinct concepts crucial in understanding matter's behavior.
2. Volume and Density: Defining Physical Space
Volume refers to the amount of three-dimensional space occupied by matter. It's often expressed in cubic units (e.g., cubic centimeters or liters). Density, a crucial characteristic, relates mass and volume. It's the mass of a substance per unit volume. A high-density object, like gold, packs a lot of mass into a small volume, while a low-density object, like a balloon filled with helium, has a small mass spread over a large volume. Density plays a significant role in determining buoyancy and the behavior of materials in different environments.
3. States of Matter: Solid, Liquid, Gas, and Beyond
Matter exists in various states, commonly known as solid, liquid, and gas. However, the picture is far more complex.
-
Solids: Solids have a definite shape and volume. Their particles are tightly packed and have strong intermolecular forces, resulting in a rigid structure. Examples include rocks, ice, and wood.
-
Liquids: Liquids have a definite volume but take the shape of their container. Their particles are more loosely packed than in solids, allowing for movement and flow. Examples include water, oil, and mercury.
-
Gases: Gases have neither a definite shape nor volume. Their particles are widely dispersed and move freely, easily compressed or expanded. Examples include air, oxygen, and carbon dioxide.
Beyond these three common states, there are other exotic states:
-
Plasma: A highly energized state of matter where electrons are stripped from atoms, forming ions. It's the most abundant state of matter in the universe, found in stars and lightning.
-
Bose-Einstein Condensate: A state achieved at extremely low temperatures where atoms behave as a single quantum entity.
-
Superfluids: Liquids exhibiting zero viscosity, flowing without resistance.
Understanding the transitions between these states (e.g., melting, boiling, freezing) is crucial for numerous applications in science and engineering.
4. Physical and Chemical Properties: Identifying and Characterizing Matter
Matter is characterized by both physical and chemical properties:
-
Physical Properties: These are characteristics that can be observed or measured without changing the substance's chemical composition. Examples include color, odor, density, melting point, boiling point, and conductivity.
-
Chemical Properties: These describe how a substance reacts with other substances. They indicate the potential for chemical change. Examples include flammability, reactivity with acids, and the ability to oxidize. Observing chemical properties often requires a chemical reaction, fundamentally altering the substance's composition.
5. Atomic Structure and Composition: The Building Blocks of Matter
All matter is made up of atoms, the fundamental units of chemical elements. Atoms themselves consist of subatomic particles:
-
Protons: Positively charged particles found in the nucleus.
-
Neutrons: Neutrally charged particles found in the nucleus.
-
Electrons: Negatively charged particles orbiting the nucleus.
The number of protons in an atom's nucleus determines its atomic number and identifies the element. Isotopes of an element have the same number of protons but different numbers of neutrons. The arrangement of electrons determines an atom's chemical behavior and its ability to form bonds with other atoms.
6. Chemical Reactions and Transformations: Altering Matter's Composition
Chemical reactions involve the rearrangement of atoms to form new substances. These reactions are governed by the principles of conservation of mass and energy, meaning that matter is neither created nor destroyed in a chemical reaction; it simply changes form. Understanding chemical reactions is crucial for fields such as chemistry, biology, and materials science.
Exploring Specific Characteristics of Matter in Detail
Let's delve deeper into some specific characteristics:
7. Compressibility and Expansion: The Effects of Pressure and Temperature
The compressibility of matter refers to its ability to be squeezed into a smaller volume. Gases are highly compressible, while liquids and solids are much less so. Expansion, the opposite, describes the increase in volume due to increased temperature or decreased pressure. Gases expand significantly with increasing temperature, while solids and liquids expand to a lesser extent. Understanding compressibility and expansion is vital in various engineering and industrial applications.
8. Thermal Conductivity: The Transfer of Heat
Thermal conductivity measures a substance's ability to transfer heat. Materials with high thermal conductivity, like metals, readily transfer heat, while materials with low thermal conductivity, like wood or plastic, are good insulators. This property is crucial in designing efficient heating and cooling systems.
9. Electrical Conductivity: The Flow of Electrical Current
Electrical conductivity describes a substance's ability to conduct electricity. Metals are excellent conductors, while nonmetals are generally poor conductors (insulators). Semiconductors exhibit intermediate conductivity, a property exploited in electronics.
10. Magnetic Properties: Attraction and Repulsion
Certain materials exhibit magnetic properties, meaning they can be attracted or repelled by magnets. Ferromagnetic materials, such as iron, nickel, and cobalt, are strongly attracted to magnets and can be magnetized themselves. Paramagnetic materials are weakly attracted, while diamagnetic materials are weakly repelled. Understanding magnetic properties is crucial in various technologies, including electric motors and data storage.
The Importance of Understanding Matter's Characteristics
The characteristics of matter are fundamental to understanding the physical world around us. This knowledge is crucial in various fields:
-
Material Science: Designing new materials with specific properties for various applications (e.g., stronger, lighter, more conductive materials).
-
Chemistry: Understanding chemical reactions and the behavior of different substances.
-
Physics: Exploring the fundamental laws governing matter and energy.
-
Biology: Studying the composition and functions of living organisms.
-
Engineering: Designing and building structures and machines that utilize the properties of matter.
-
Medicine: Developing new drugs and treatments based on the interaction of matter at a molecular level.
In Conclusion:
The study of matter is a vast and intricate field. From the simplest atoms to the most complex molecules and materials, the characteristics of matter shape our world. Understanding these properties allows us to unlock the potential of the material world and develop new technologies that improve our lives. Further exploration into the nuances of specific properties of matter will continue to unveil new insights and applications in countless fields.
Latest Posts
Latest Posts
-
Write The Prime Factorization Of 15
Mar 13, 2025
-
How Many Sex Chromosomes Are In A Human Gamete
Mar 13, 2025
-
Reaction Of Ammonia With Sulfuric Acid
Mar 13, 2025
-
Which Of The Following Is A Multiple Of 5
Mar 13, 2025
-
Force Of Gravitation Between Earth And Sun
Mar 13, 2025
Related Post
Thank you for visiting our website which covers about What Are The Characteristics Of Matter . We hope the information provided has been useful to you. Feel free to contact us if you have any questions or need further assistance. See you next time and don't miss to bookmark.
