Write The Prime Factorization Of 15
Juapaving
Mar 13, 2025 · 6 min read
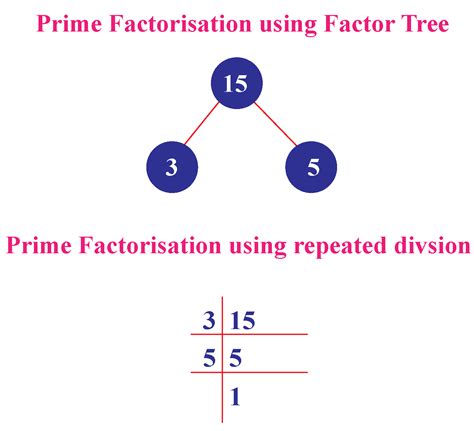
Table of Contents
The Prime Factorization of 15: A Deep Dive into Number Theory
The seemingly simple question, "What is the prime factorization of 15?" opens a door to a fascinating world of number theory, a branch of mathematics brimming with elegant concepts and surprising applications. While the answer itself is straightforward, exploring the process and the underlying principles reveals much about the fundamental building blocks of numbers. This article will not only provide the prime factorization of 15 but also delve into the broader context of prime numbers, factorization, and their significance in mathematics and beyond.
Understanding Prime Numbers
Before tackling the factorization of 15, let's solidify our understanding of prime numbers. A prime number is a natural number greater than 1 that has no positive divisors other than 1 and itself. This seemingly simple definition belies the profound complexity and mystery surrounding these numbers. Prime numbers are the fundamental building blocks of all other natural numbers, meaning that every natural number greater than 1 can be expressed as a unique product of prime numbers. This is known as the Fundamental Theorem of Arithmetic.
Some examples of prime numbers are 2, 3, 5, 7, 11, 13, and so on. Notice that 2 is the only even prime number; all other even numbers are divisible by 2. The distribution of prime numbers across the number line is irregular and unpredictable, a fact that has captivated mathematicians for centuries. The search for larger and larger prime numbers continues to this day, with advancements in computing power constantly pushing the boundaries of discovery. The largest known prime number currently holds the record, but the search for even bigger ones is an ongoing pursuit.
What is Prime Factorization?
Prime factorization, also known as prime decomposition, is the process of finding the prime numbers that, when multiplied together, result in a given number. This process is unique for every number; each number has only one set of prime factors, regardless of the order in which they are presented. This uniqueness is crucial in various mathematical applications.
For example, the prime factorization of 12 is 2 x 2 x 3, often written as 2² x 3. This means that the prime numbers 2 and 3, when multiplied together (with 2 appearing twice), produce the number 12. Similarly, the prime factorization of 18 is 2 x 3 x 3, or 2 x 3².
Finding the Prime Factorization of 15
Now, let's address the question at hand: what is the prime factorization of 15?
The number 15 is relatively small, making the process straightforward. We can begin by identifying the smallest prime number that divides 15. That number is 3. Dividing 15 by 3 gives us 5. Since 5 is itself a prime number, we have found the prime factors of 15.
Therefore, the prime factorization of 15 is 3 x 5.
This simple factorization might seem trivial, but it illustrates the fundamental principle that underlies the factorization of much larger numbers. The process always involves dividing by the smallest prime number possible and continuing until all remaining factors are prime.
Methods for Finding Prime Factorization
While the factorization of 15 is simple, larger numbers require more systematic approaches. Here are some common methods:
1. Factor Tree Method
The factor tree method is a visual approach that helps break down a number into its prime factors. You start by finding any two factors of the number, and then continue factoring each factor until all factors are prime.
For example, let's find the prime factorization of 24 using the factor tree method:
24
/ \
2 12
/ \
2 6
/ \
2 3
The prime factorization of 24 is therefore 2 x 2 x 2 x 3, or 2³ x 3.
2. Division Method
The division method involves repeatedly dividing a number by its smallest prime factor until you reach 1. The prime factors are the numbers used in the divisions.
Let's factor 36 using the division method:
- 36 ÷ 2 = 18
- 18 ÷ 2 = 9
- 9 ÷ 3 = 3
- 3 ÷ 3 = 1
The prime factorization of 36 is therefore 2 x 2 x 3 x 3, or 2² x 3².
3. Using Algorithms (for very large numbers)
For extremely large numbers, algorithms are necessary. These are sophisticated computer programs designed to efficiently find the prime factors of numbers that would be impossible to factor by hand. These algorithms are crucial in cryptography, where the difficulty of factoring large numbers forms the basis of many encryption systems. The RSA algorithm, widely used in secure online communications, relies heavily on the difficulty of factoring large semiprime numbers (numbers that are the product of two prime numbers).
Applications of Prime Factorization
The concept of prime factorization might seem purely theoretical, but it has numerous practical applications in various fields:
1. Cryptography
As mentioned earlier, prime factorization plays a crucial role in modern cryptography. The security of many encryption systems relies on the difficulty of factoring very large numbers into their prime components. The larger the numbers, the more computationally intensive the factorization becomes, making it practically impossible to break the encryption within a reasonable timeframe.
2. Coding Theory
In coding theory, prime numbers and their properties are essential for designing error-correcting codes. These codes are used to detect and correct errors that might occur during data transmission or storage.
3. Number Theory Research
Prime factorization is a fundamental tool in number theory research. Many unsolved problems in number theory, such as the Riemann Hypothesis, are intricately linked to the distribution and properties of prime numbers.
4. Computer Science
Prime numbers are used in hash table algorithms and other data structures in computer science to efficiently manage and retrieve data. The unique properties of prime numbers are exploited to reduce collisions and improve the performance of these structures.
The Ongoing Mystery of Prime Numbers
Despite centuries of study, prime numbers continue to hold many unsolved mysteries. The distribution of prime numbers remains a significant area of research, with many open questions yet to be answered. The Riemann Hypothesis, one of the most important unsolved problems in mathematics, deals with the distribution of prime numbers and has profound implications for our understanding of number theory. The search for patterns and relationships within the seemingly random distribution of primes continues to captivate mathematicians and computer scientists alike.
Conclusion: Beyond the Simple Factorization of 15
While the prime factorization of 15 – 3 x 5 – is a simple calculation, the underlying principles and broader applications extend far beyond this basic example. The concept of prime factorization is a cornerstone of number theory, with implications that ripple through various branches of mathematics, computer science, and cryptography. The ongoing quest to understand prime numbers better highlights the enduring beauty and complexity of this fundamental mathematical concept. The seemingly simple act of finding the prime factors of a number like 15 opens a window into a vast and intricate world of mathematical exploration.
Latest Posts
Latest Posts
-
How Many Centimeters Are In 50 Millimeters
May 09, 2025
-
Describe The Epithelium Found In The Uterine Tube
May 09, 2025
-
What Animal Lay Eggs And Is Not A Bird
May 09, 2025
-
Label The Anatomy Of The Male
May 09, 2025
-
Electrical Resistivity Of A Given Metallic Wire Depends Upon
May 09, 2025
Related Post
Thank you for visiting our website which covers about Write The Prime Factorization Of 15 . We hope the information provided has been useful to you. Feel free to contact us if you have any questions or need further assistance. See you next time and don't miss to bookmark.