What Are The Advantages Of Ac Over Dc
Juapaving
Mar 22, 2025 · 5 min read
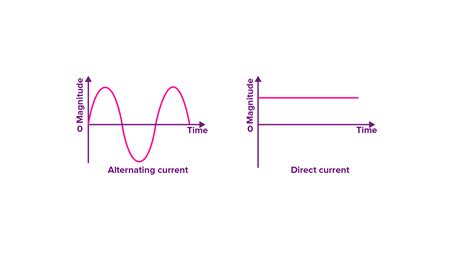
Table of Contents
What Are the Advantages of AC Over DC?
The ongoing debate between alternating current (AC) and direct current (DC) is a cornerstone of electrical engineering history. While DC boasts simplicity, AC reigns supreme in large-scale power transmission and distribution. This comprehensive article delves into the key advantages of AC over DC, exploring the technical nuances and practical implications that solidify AC's dominance in modern power grids.
The Transformation of Power: Why AC Won the "Current Wars"
The "War of the Currents" in the late 19th century pitted Thomas Edison's DC system against George Westinghouse's AC system. While Edison championed DC's perceived safety and simplicity, Westinghouse's AC system ultimately prevailed due to its inherent advantages in long-distance power transmission. These advantages are still relevant today and continue to shape our electrical infrastructure.
1. Efficient Long-Distance Transmission: The Transformer's Role
The most significant advantage of AC over DC is its ability to be easily transformed to higher or lower voltages using transformers. This is crucial for efficient long-distance power transmission.
-
High Voltage Transmission: Power loss during transmission is proportional to the square of the current. By stepping up the voltage using a transformer at the generating station, the current is significantly reduced, minimizing energy loss over long distances. This is impossible to achieve efficiently with DC without complex and expensive technologies.
-
Low Voltage Distribution: Once the electricity reaches a city or town, the high voltage is stepped down using transformers to a safer and more usable voltage for homes and businesses. This ability to efficiently change voltage is a fundamental reason why AC dominates power grids.
-
Cost-Effectiveness: The relative simplicity and low cost of transformers compared to other voltage conversion methods in DC systems make AC transmission far more economical for large-scale power distribution.
2. Simple and Cost-Effective Generation
Generating AC power is relatively simpler and less expensive than generating DC power at large scales. Alternators, the machines that generate AC power, are more robust and require less maintenance compared to DC generators, which often involve complex commutator systems prone to wear and tear. The simplicity of alternator design translates to lower manufacturing costs and easier maintenance, making it a more economical choice for large-scale power generation.
3. Ease of Use and Control in Modern Power Grids
AC's inherent properties lend themselves well to the sophisticated control systems necessary for modern power grids.
-
Synchronization: Multiple AC generators can be easily synchronized to work together in a power plant, providing redundancy and scalability. Synchronizing DC generators is far more complex and challenging.
-
Power Factor Correction: AC systems allow for power factor correction, which optimizes the efficiency of power usage. This technique minimizes the reactive power component, reducing energy loss and improving the overall efficiency of the electrical system. Power factor correction is far more challenging in DC systems.
-
Integration with Existing Infrastructure: The massive existing AC infrastructure worldwide, from power plants to transmission lines and distribution networks, makes shifting to a predominantly DC system a practically impossible and economically unsustainable endeavor. Upgrading and adapting the current AC infrastructure is far more cost-effective than replacing it entirely.
Addressing Misconceptions about AC vs. DC
Several common misconceptions surround the AC/DC debate, often stemming from a simplified understanding of electrical engineering principles. Let's address some of these:
1. The Myth of AC's "Dangerous" Nature
While high-voltage AC can certainly be dangerous, so can high-voltage DC. The safety concerns associated with electricity are primarily related to voltage levels and not the type of current. Appropriate safety measures, regardless of whether the electricity is AC or DC, are crucial to prevent accidents.
2. The Oversimplification of DC's Simplicity
While DC is inherently simpler in its unidirectional flow, generating, controlling, and efficiently transmitting high-power DC over long distances are significantly more complex and expensive than their AC counterparts. The apparent simplicity of DC is often overshadowed by the technical challenges in large-scale applications.
3. Ignoring the Technological Advancements in DC
While AC currently dominates, significant advancements in high-voltage DC (HVDC) technology are emerging. HVDC transmission is becoming increasingly viable for specific applications, particularly in long undersea cable installations and large-scale renewable energy integration. However, even with these advancements, AC remains the more cost-effective and widely applicable solution for most scenarios.
The Future of AC and DC in Power Systems
The future of power systems is likely to involve a sophisticated blend of both AC and DC technologies. While AC will continue to be the backbone of most power grids, HVDC will likely play an increasingly significant role in specific applications where its advantages outweigh the costs. This integration of AC and DC technologies will optimize efficiency, reliability, and scalability in power transmission and distribution networks.
HVDC's Emerging Role: Specific Applications and Advantages
HVDC technology is making inroads, particularly in long-distance underwater cable transmission, where AC experiences significant signal attenuation. HVDC also offers advantages in integrating renewable energy sources like wind and solar farms located far from load centers. The ability to easily convert DC power from these sources to AC for distribution is a key driver of HVDC's adoption.
The Continued Dominance of AC: A Robust and Cost-Effective Solution
Despite the advancements in HVDC, AC's inherent advantages in terms of cost-effectiveness, ease of transformation, and integration with existing infrastructure will ensure its continued dominance in large-scale power systems for the foreseeable future. The massive investment in existing AC infrastructure makes a complete switch to DC impractical and economically infeasible.
Conclusion: A Symbiotic Relationship
The discussion of AC versus DC isn't about choosing a clear winner. Instead, it highlights the complementary nature of these two technologies. AC's strengths in long-distance transmission and cost-effectiveness solidify its position in the bulk power system. HVDC’s strengths in specific applications, such as long undersea cables and renewable energy integration, will lead to its increased adoption. The future of power systems lies in a synergistic approach, leveraging the unique advantages of both AC and DC technologies to create a more efficient, reliable, and sustainable energy infrastructure. This symbiotic relationship will drive innovation and further improve the effectiveness of our global power grid. The "War of the Currents" may be over, but the evolution of power transmission continues, with both AC and DC technologies playing vital roles in shaping the future of energy.
Latest Posts
Latest Posts
-
Which Planet Revolves Around The Sun The Fastest
Mar 23, 2025
-
Least Common Multiple Of 3 4 And 8
Mar 23, 2025
-
Lowest Common Multiple Of 24 And 28
Mar 23, 2025
-
Is 90 Minutes An Hour And A Half
Mar 23, 2025
-
What Is Larger 3 8 Or 1 2
Mar 23, 2025
Related Post
Thank you for visiting our website which covers about What Are The Advantages Of Ac Over Dc . We hope the information provided has been useful to you. Feel free to contact us if you have any questions or need further assistance. See you next time and don't miss to bookmark.
