What Are Lightning Conductors Made Of
Juapaving
Mar 19, 2025 · 6 min read
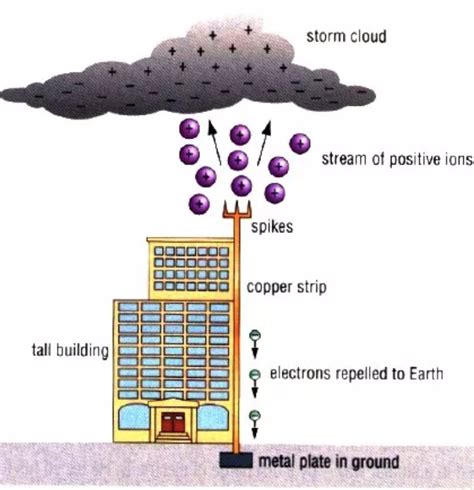
Table of Contents
What are Lightning Conductors Made Of? A Deep Dive into Materials and Design
Lightning strikes are terrifying and powerful natural events, capable of causing significant damage to property and even loss of life. For centuries, humanity has sought ways to mitigate this risk, and the lightning conductor, also known as a lightning rod, remains a cornerstone of lightning protection systems. But what exactly are lightning conductors made of, and why are those specific materials chosen? This article will delve deep into the materials science and engineering behind these life-saving devices.
The Primary Material: Copper
The most common material used in the construction of lightning conductors is copper. Its prevalence stems from a unique combination of properties that make it ideally suited for this demanding application:
Superior Conductivity:
Copper boasts exceptionally high electrical conductivity. This is paramount because the primary function of a lightning conductor is to provide a low-resistance pathway for the immense electrical current of a lightning strike to safely travel to the ground. The lower the resistance, the less heat is generated, minimizing the risk of the conductor itself overheating and failing. This superior conductivity helps prevent dangerous voltage surges and potential fires.
Durability and Longevity:
Copper is known for its excellent durability and corrosion resistance. Exposure to the elements, including rain, wind, and UV radiation, is inevitable for a lightning conductor. Copper's inherent resistance to corrosion ensures the long-term effectiveness of the system, minimizing the need for frequent replacements and maintenance. This translates to cost savings and increased peace of mind over the lifespan of the structure it protects.
Workability and Malleability:
Copper is relatively easy to work with. It's highly malleable and ductile, meaning it can be easily shaped and formed into the desired configurations for installation. This flexibility allows for the creation of complex lightning conductor systems tailored to the specific geometry of buildings and structures. The ease of installation contributes to lower labor costs and faster project completion times.
Cost-Effectiveness:
While not the cheapest metal available, copper offers a compelling balance of performance and cost. Its longevity minimizes the need for frequent replacements, ultimately making it a cost-effective solution in the long run compared to materials requiring more frequent maintenance.
Other Materials Used in Lightning Conductors:
While copper is the dominant material, other metals sometimes find use in various components of lightning protection systems:
Aluminum:
Aluminum is another metal frequently employed, particularly in situations where weight reduction is a critical factor, such as on tall structures or in applications where weight is a significant concern. While aluminum's conductivity isn't quite as high as copper's, its lighter weight can be a substantial advantage in certain installations. However, aluminum's susceptibility to corrosion in specific environmental conditions needs to be carefully considered, often requiring specialized coatings or alloys.
Galvanized Steel:
Galvanized steel (steel coated with zinc) is sometimes used, particularly in less demanding applications or where cost is a primary driver. The zinc coating offers some protection against corrosion, but the conductivity of steel is significantly lower than that of copper or aluminum, making it less ideal for high-current lightning strikes. Its use is often limited to grounding systems rather than the main conductor itself.
Stainless Steel:
Stainless steel offers excellent corrosion resistance and reasonable conductivity. It is sometimes utilized in specific components of lightning protection systems, especially in marine environments or where extremely high corrosion resistance is needed. However, its higher cost often limits its widespread adoption compared to copper.
The Importance of Grounding:
The effectiveness of a lightning conductor hinges not only on the material of the conductor itself but also on the grounding system. The conductor’s role is to safely channel the current to the earth, and a properly designed grounding system is crucial for dissipating this immense electrical energy without causing damage.
The grounding system typically consists of:
- Grounding rods: These are driven deep into the earth to provide a low-resistance path to ground. Copper or galvanized steel are common materials for these rods.
- Grounding wires: These connect the lightning conductor to the grounding rods, ensuring a continuous and low-resistance path for the current. Copper is usually the preferred material for these wires due to its superior conductivity.
- Grounding connections: These ensure a secure and reliable connection between the conductor, grounding wires, and grounding rods. Proper bonding and clamping are vital to avoid creating high-resistance points that could compromise the system's safety.
The quality of the grounding system is paramount in preventing voltage surges, which can damage electrical equipment and pose significant fire hazards.
Design Considerations:
The design of a lightning conductor system is not merely a matter of selecting the right material. Several critical factors influence the effectiveness and safety of the system:
- Height: The conductor should extend above the highest point of the structure to be protected. The taller the conductor, the greater the probability of intercepting a lightning strike.
- Air Termination: The top of the conductor, often pointed or shaped to optimize lightning interception, is known as the air termination. Its design is crucial for the effective capture of lightning strikes.
- Down Conductors: These are the vertical conductors that carry the current from the air termination to the grounding system. Multiple down conductors are often used to distribute the current and further reduce the risk of overheating.
- Grounding Grid: In large structures, a grounding grid helps spread the current over a larger area, minimizing the potential for damage.
Maintenance and Inspection:
Even with high-quality materials and proper design, regular inspection and maintenance are essential to ensure the continued effectiveness of a lightning protection system. Corrosion, damage from impacts, and loose connections can compromise the system's performance over time. Regular checks and appropriate maintenance can prolong the lifespan of the system and guarantee its effectiveness.
Conclusion:
The choice of material for a lightning conductor is a crucial design decision. While copper remains the preferred material due to its superior conductivity, durability, and workability, other materials like aluminum, galvanized steel, and stainless steel can play roles in specific applications based on factors like cost, weight considerations, and environmental conditions. The effectiveness of a lightning protection system, however, goes far beyond the mere selection of the conductor material. Careful consideration of the entire system, including the grounding system and design elements, is necessary to ensure optimal protection against the destructive power of lightning. Regular inspection and maintenance further contribute to the long-term safety and reliability of these crucial life-saving installations. Understanding the materials and the complete system design is essential for anyone seeking to protect their property and loved ones from the devastating effects of lightning strikes.
Latest Posts
Latest Posts
-
How Many Feet Is 25 Inches
Mar 19, 2025
-
How Many Months Are In Three Years
Mar 19, 2025
-
What Is The Additive Inverse Of
Mar 19, 2025
-
Does Liquid Have A Definite Volume
Mar 19, 2025
-
How Many Feet Is 40 M
Mar 19, 2025
Related Post
Thank you for visiting our website which covers about What Are Lightning Conductors Made Of . We hope the information provided has been useful to you. Feel free to contact us if you have any questions or need further assistance. See you next time and don't miss to bookmark.
