What Are Characteristics Of Covalent Compounds
Juapaving
Mar 22, 2025 · 6 min read
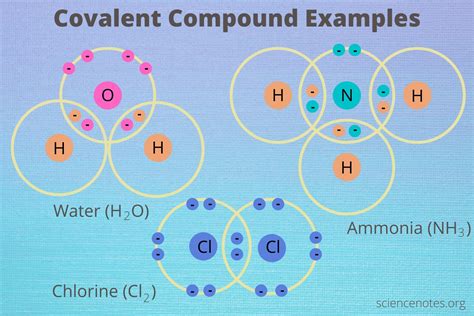
Table of Contents
What are the Characteristics of Covalent Compounds?
Covalent compounds, also known as molecular compounds, are formed when atoms share electrons to achieve a stable electron configuration. Understanding their characteristics is crucial for comprehending their behavior in various chemical reactions and applications. This comprehensive guide delves into the key properties of covalent compounds, exploring their structure, bonding, and resulting physical and chemical attributes.
Defining Covalent Bonding
Before diving into the characteristics, let's establish a firm understanding of the fundamental concept: covalent bonding. This type of bonding occurs when two or more non-metal atoms share one or more pairs of electrons. This sharing allows each atom to achieve a full outer electron shell, mirroring the stability of noble gases. The shared electron pair forms a covalent bond, represented by a single line (-) in chemical formulas. Double bonds (=) and triple bonds (≡) represent the sharing of two and three pairs of electrons, respectively.
The Role of Electronegativity
Electronegativity, the ability of an atom to attract electrons in a chemical bond, plays a significant role in determining the nature of the covalent bond. When atoms with similar electronegativities bond, they share electrons relatively equally, resulting in a nonpolar covalent bond. Examples include bonds between identical atoms (e.g., H₂ , O₂) or atoms with very similar electronegativities (e.g., C-H bonds in methane).
Conversely, when atoms with significantly different electronegativities bond, the electrons are shared unequally. This results in a polar covalent bond, where one atom carries a partial negative charge (δ-) and the other a partial positive charge (δ+). Water (H₂O) is a prime example, with oxygen being more electronegative than hydrogen, leading to a polar covalent bond.
Physical Properties of Covalent Compounds
The physical properties of covalent compounds are directly influenced by the strength and type of covalent bonds present, as well as intermolecular forces. These properties often differ significantly from those of ionic compounds.
1. Low Melting and Boiling Points:
Covalent compounds generally have low melting and boiling points. This is because the intermolecular forces (forces of attraction between molecules) holding covalent molecules together are relatively weak compared to the strong electrostatic forces in ionic compounds. These weak intermolecular forces – such as London Dispersion Forces, dipole-dipole interactions, and hydrogen bonding – require less energy to overcome, resulting in lower melting and boiling points.
2. Poor Electrical Conductivity:
In their solid, liquid, or dissolved states, most covalent compounds are poor conductors of electricity. This is because covalent compounds generally do not have freely moving charged particles (ions or electrons) to carry an electric current. Unlike ionic compounds which dissociate into ions in solution, covalent compounds usually remain as neutral molecules. However, there are exceptions: some covalent compounds, especially in their molten or aqueous states, can exhibit some degree of electrical conductivity. This is often due to the presence of polar molecules, which can temporarily ionize, allowing for limited charge transfer.
3. Solubility:
The solubility of covalent compounds varies greatly depending on the polarity of the molecule and the solvent. Polar covalent compounds tend to dissolve in polar solvents (like water), while nonpolar covalent compounds tend to dissolve in nonpolar solvents (like oil). This principle is often summarized as "like dissolves like".
4. Volatility:
Many covalent compounds are volatile, meaning they readily change from a liquid or solid state to a gaseous state at relatively low temperatures. This volatility is a consequence of the weak intermolecular forces. The molecules can easily overcome these forces and escape into the gaseous phase.
5. Hardness and Brittleness:
Covalent compounds can exhibit varying degrees of hardness and brittleness. Some, like diamond (a giant covalent structure), are extremely hard due to the strong covalent bonds extending throughout a rigid three-dimensional network. Others are relatively soft and brittle because their molecules are held together by weak intermolecular forces.
Chemical Properties of Covalent Compounds
The chemical properties of covalent compounds are determined by the nature of the covalent bonds and the atoms involved.
1. Reactivity:
The reactivity of covalent compounds is highly variable and depends on several factors, including the strength of the bonds, the presence of functional groups, and the electronegativity differences between the atoms. Some covalent compounds are very reactive, readily participating in various chemical reactions. Others are quite inert, resisting chemical changes.
2. Combustion:
Many covalent compounds, particularly those containing carbon and hydrogen (hydrocarbons), are combustible, meaning they react readily with oxygen to produce carbon dioxide, water, and heat. This combustion reaction is a characteristic of many organic compounds.
3. Reaction with Acids and Bases:
The reactions of covalent compounds with acids and bases vary considerably. Some covalent compounds may react with strong acids or bases to undergo hydrolysis (a reaction with water) or other types of chemical changes. Others remain unreactive under these conditions.
4. Formation of Polymeric Structures:
Covalent bonding plays a crucial role in the formation of large, complex molecules called polymers. Polymers consist of repeating structural units, often linked together through strong covalent bonds. These polymers can have diverse properties and numerous applications, spanning from plastics and fibers to biological molecules like proteins and DNA.
Examples of Covalent Compounds and their Applications
Covalent compounds are ubiquitous, playing crucial roles in various aspects of our lives. Here are some notable examples:
-
Water (H₂O): Essential for life, water acts as a solvent, participates in biochemical reactions, and plays a vital role in regulating temperature.
-
Carbon Dioxide (CO₂): A greenhouse gas, crucial for photosynthesis and also used in carbonated drinks.
-
Glucose (C₆H₁₂O₆): A simple sugar, a fundamental source of energy for living organisms.
-
Methane (CH₄): A major component of natural gas, used as a fuel.
-
Silicon Dioxide (SiO₂): The primary component of sand and quartz, used in glass and ceramics.
-
Polymers (Plastics, Rubbers, Fibers): A vast array of materials with diverse applications, from packaging to clothing to medical devices.
Distinguishing Covalent from Ionic Compounds
It’s important to be able to distinguish between covalent and ionic compounds. While their properties differ significantly, some subtleties exist. Key differentiators include:
-
Bonding: Covalent compounds are formed through the sharing of electrons, while ionic compounds are formed by the transfer of electrons.
-
Melting/Boiling Points: Covalent compounds generally have lower melting and boiling points than ionic compounds.
-
Electrical Conductivity: Covalent compounds are typically poor conductors of electricity, while ionic compounds (when molten or dissolved) are good conductors.
-
Solubility: Solubility patterns differ; "like dissolves like" applies strongly to covalent compounds.
Conclusion:
The characteristics of covalent compounds are a direct result of the nature of covalent bonding – the sharing of electrons between non-metal atoms. Their properties, ranging from low melting points and poor electrical conductivity to diverse reactivity and the formation of complex polymers, make them essential in numerous applications, shaping our world in countless ways. Understanding these characteristics is fundamental to appreciating the vast diversity and importance of covalent compounds in chemistry and beyond. Further investigation into specific types of covalent compounds and their respective properties can provide even deeper insights into their behavior and applications.
Latest Posts
Latest Posts
-
What Is The Lcm Of 7 And 5
Mar 22, 2025
-
One Inch Is Equal To 2 54 Centimeters
Mar 22, 2025
-
Is 1 2 Greater Than 1
Mar 22, 2025
-
What Is The Lcm Of 32 And 48
Mar 22, 2025
-
5 Letter Word Starts With Tha
Mar 22, 2025
Related Post
Thank you for visiting our website which covers about What Are Characteristics Of Covalent Compounds . We hope the information provided has been useful to you. Feel free to contact us if you have any questions or need further assistance. See you next time and don't miss to bookmark.
