What Are All Of The Factors Of 33
Juapaving
Mar 19, 2025 · 6 min read
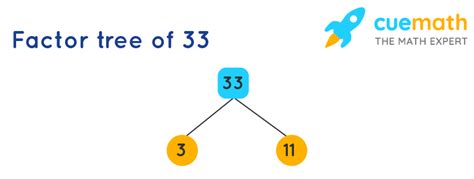
Table of Contents
What Are All of the Factors of 33? A Deep Dive into Prime Factorization and Divisibility
Finding the factors of a number might seem like a simple arithmetic task, but understanding the process reveals fundamental concepts in number theory. This article will explore the factors of 33, delving into the methods used to identify them, their significance in mathematics, and how this seemingly straightforward problem relates to more advanced mathematical ideas.
Understanding Factors and Divisibility
Before we tackle the factors of 33, let's define what a factor is. A factor (or divisor) of a number is a whole number that divides the number exactly, leaving no remainder. In simpler terms, if you divide a number by its factor, the result is another whole number.
Divisibility is the property of one number being divisible by another. For example, 33 is divisible by 3 because 33/3 = 11 (a whole number). Understanding divisibility rules can significantly speed up the process of finding factors.
Finding the Factors of 33: A Step-by-Step Approach
There are several ways to find the factors of 33:
1. The Brute-Force Method: Testing Divisibility
The simplest method is to systematically test each whole number starting from 1 to see if it divides 33 without leaving a remainder.
- 1: 33 ÷ 1 = 33 (1 is a factor)
- 2: 33 ÷ 2 = 16.5 (2 is not a factor)
- 3: 33 ÷ 3 = 11 (3 is a factor)
- 4: 33 ÷ 4 = 8.25 (4 is not a factor)
- 5: 33 ÷ 5 = 6.6 (5 is not a factor)
- 6: 33 ÷ 6 = 5.5 (6 is not a factor)
- 7: 33 ÷ 7 ≈ 4.71 (7 is not a factor)
- 8: 33 ÷ 8 ≈ 4.125 (8 is not a factor)
- 9: 33 ÷ 9 ≈ 3.67 (9 is not a factor)
- 10: 33 ÷ 10 = 3.3 (10 is not a factor)
- 11: 33 ÷ 11 = 3 (11 is a factor)
- 12: 33 ÷ 12 ≈ 2.75 (12 is not a factor)
We can stop here because any factor greater than the square root of 33 (approximately 5.74) will have a corresponding factor smaller than the square root. Therefore, we've found all the factors.
2. Using Prime Factorization
Prime factorization is a more elegant and efficient method for finding factors, especially for larger numbers. A prime number is a whole number greater than 1 that has only two factors: 1 and itself (e.g., 2, 3, 5, 7, 11...). The prime factorization of a number is its expression as a product of prime numbers.
To find the prime factorization of 33:
- We start by dividing 33 by the smallest prime number, 2. Since 33 is not divisible by 2, we move to the next prime number.
- 33 is divisible by 3: 33 ÷ 3 = 11.
- 11 is itself a prime number.
Therefore, the prime factorization of 33 is 3 x 11.
Once we have the prime factorization, we can easily find all the factors. The factors are all the possible combinations of the prime factors and 1:
- 1
- 3
- 11
- 3 x 11 = 33
So, the factors of 33 are 1, 3, 11, and 33.
Properties of the Factors of 33
The factors of 33 exhibit several interesting properties:
- They are all integers: Factors are always whole numbers.
- They include 1 and the number itself: Every number has 1 and itself as factors.
- They are relatively few in number: 33 has only four factors, which is relatively low compared to some numbers. This is partly due to it being a product of two small prime numbers.
- They are related through multiplication: Each factor can be obtained by multiplying other factors (e.g., 3 x 11 = 33).
- They help determine the number of divisors: The number of factors is directly related to the prime factorization. Since 33 = 3¹ x 11¹, the number of divisors is (1+1)(1+1) = 4. This formula works for any number whose prime factorization is known.
The Significance of Factors in Mathematics
The concept of factors is fundamental to various areas of mathematics:
- Number Theory: Factors are crucial for understanding the structure of numbers, prime factorization, and concepts like greatest common divisors (GCD) and least common multiples (LCM).
- Algebra: Factoring polynomials involves finding expressions that multiply to give a given polynomial. This is analogous to finding the factors of a number.
- Cryptography: Prime factorization is essential in modern cryptography. The difficulty of factoring large numbers into their prime factors underpins the security of many encryption systems.
- Modular Arithmetic: Factors play a significant role in understanding congruences and modular arithmetic, which have applications in various fields, including computer science and coding theory.
Applications of Factorization Beyond Mathematics
Understanding factors and factorization extends beyond the realm of pure mathematics and finds practical applications in many areas:
- Division problems: Finding factors helps solve division problems efficiently. If we know the factors of a number, we can quickly determine if it's divisible by other numbers.
- Geometry: Factors are used in geometrical calculations involving areas and volumes. For example, finding the dimensions of a rectangle with a specific area often involves factoring.
- Data analysis: Factors can be used in data analysis to identify patterns and relationships within datasets.
- Computer Science: Factoring algorithms are vital in various computer science applications such as cryptography and database management.
Advanced Concepts Related to Factors of 33
Exploring the factors of 33 opens doors to more advanced mathematical concepts:
- Perfect Numbers: A perfect number is a positive integer that is equal to the sum of its proper divisors (divisors excluding the number itself). 33 is not a perfect number, but understanding factors helps in identifying potential candidates for perfect numbers.
- Abundant and Deficient Numbers: A number is abundant if the sum of its proper divisors is greater than the number itself; it's deficient if the sum is less than the number. Again, the ability to find all factors is crucial for classifying numbers based on these properties.
- Highly Composite Numbers: A highly composite number is a positive integer with more divisors than any smaller positive integer. Understanding factor counts helps determine which numbers are highly composite.
- Divisor Function: The divisor function (σ(n)) counts the number of divisors of a positive integer n. For 33, σ(33) = 4. This function is extensively studied in number theory.
Conclusion: The Unassuming Power of Factors
While finding the factors of 33 might appear trivial, it provides a valuable gateway to understanding deeper concepts in number theory and their broader applications. The simple act of identifying 1, 3, 11, and 33 as the factors of 33 unveils fundamental principles that underpin various mathematical fields and have practical implications across numerous disciplines. By exploring this seemingly basic problem, we gain a deeper appreciation for the power and beauty of mathematics. The seemingly simple act of factoring numbers forms the bedrock for more complex mathematical investigations and real-world applications. The seemingly straightforward factors of 33, therefore, are much more significant than they initially appear.
Latest Posts
Latest Posts
-
What Type Of Bond Is Kcl
Mar 19, 2025
-
Nucleic Acids Are Polymers Of Blank
Mar 19, 2025
-
Ias Exam Qualification And Age Limit
Mar 19, 2025
-
Simplify The Square Root Of 243
Mar 19, 2025
-
What Is The Net Gain Of Atp During Glycolysis
Mar 19, 2025
Related Post
Thank you for visiting our website which covers about What Are All Of The Factors Of 33 . We hope the information provided has been useful to you. Feel free to contact us if you have any questions or need further assistance. See you next time and don't miss to bookmark.
