Two Angles Whose Sum Is 90
Juapaving
Mar 15, 2025 · 5 min read
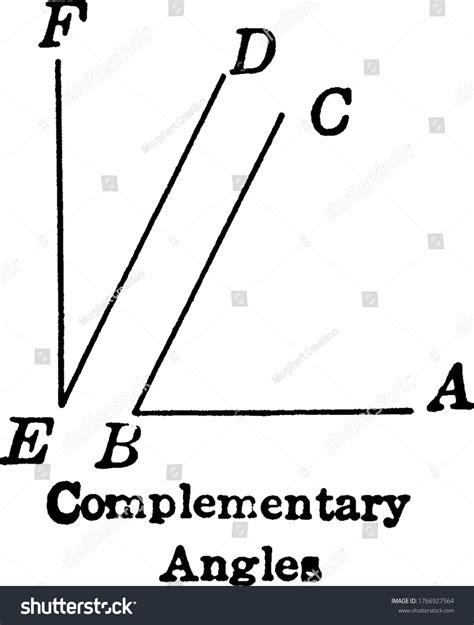
Table of Contents
Two Angles Whose Sum is 90: A Deep Dive into Complementary Angles
Complementary angles are a fundamental concept in geometry, forming the bedrock for understanding many other geometric relationships. This comprehensive guide will explore complementary angles in detail, covering their definition, properties, applications, and how they relate to other angle types. We'll delve into practical examples and problem-solving techniques, ensuring you gain a thorough understanding of this crucial geometric concept.
Defining Complementary Angles
Two angles are considered complementary if their sum is exactly 90 degrees (90°). This is a crucial definition to remember. It's important to note that complementary angles don't necessarily have to be adjacent (next to each other); they simply need to add up to 90°.
Key takeaway: The defining characteristic of complementary angles is their sum equaling 90°.
Examples of Complementary Angles:
- 30° and 60°: 30° + 60° = 90°
- 45° and 45°: 45° + 45° = 90° (These are also known as equal complementary angles).
- 15° and 75°: 15° + 75° = 90°
- 22.5° and 67.5°: 22.5° + 67.5° = 90°
Identifying Complementary Angles in Diagrams
Identifying complementary angles in diagrams requires careful observation. Look for angles that appear to add up to a right angle (90°). A right angle is often indicated by a small square in the corner of the angle. However, remember that complementary angles don't have to be adjacent. They can be separate angles within a larger diagram.
Tips for identifying complementary angles:
- Look for right angles: Right angles are a strong indicator of potential complementary pairs.
- Add the angles: Carefully calculate the sum of angles that appear to be related.
- Consider all possibilities: Don't overlook possibilities where angles are non-adjacent.
Complementary Angles and Other Angle Types
Complementary angles are closely related to other types of angles, particularly:
- Right Angles: A right angle measures exactly 90°. Complementary angles, by definition, add up to a right angle.
- Supplementary Angles: Supplementary angles are two angles whose sum is 180°. They are distinct from complementary angles, which add up to 90°.
- Acute Angles: An acute angle is an angle that measures less than 90°. Complementary angles are always acute angles.
- Obtuse Angles: An obtuse angle is an angle that measures greater than 90° but less than 180°. A complementary angle pair cannot contain an obtuse angle.
Solving Problems Involving Complementary Angles
Many geometry problems involve finding the measure of a missing angle given that it forms a complementary pair with a known angle. Here's a step-by-step approach:
- Identify the known angle: Determine the measure of the angle that is given.
- Apply the definition of complementary angles: Remember that the sum of complementary angles is 90°.
- Set up an equation: Create an equation where the known angle plus the unknown angle (let's call it 'x') equals 90°.
- Solve for the unknown angle: Use algebraic techniques to solve for 'x', which represents the measure of the missing complementary angle.
Example Problem:
One angle is 35°. Find its complementary angle.
Solution:
- Known angle: 35°
- Equation: 35° + x = 90°
- Solve: x = 90° - 35° = 55°
- Answer: The complementary angle is 55°.
Applications of Complementary Angles
Complementary angles find application in various areas, including:
- Engineering and Architecture: Complementary angles are crucial in structural design, ensuring stability and proper construction. For example, the angles in a right-angled triangle are often complementary or related to complementary angles in construction planning.
- Navigation: Understanding complementary angles is essential in navigation, particularly when using bearings and calculating angles relative to a fixed point or direction.
- Computer Graphics: In computer graphics, complementary angles play a role in creating accurate 3D models and animations. The precise positioning and rendering of objects rely on accurate angle calculations, including the understanding of complementary angles.
- Trigonometry: Complementary angles have a significant role in trigonometric identities, allowing for simplifications and efficient problem-solving in more complex geometric applications. The co-functions of complementary angles (sine and cosine, tangent and cotangent) are key to understanding these identities.
Advanced Concepts and Extensions
While the basic concept of complementary angles is straightforward, more advanced concepts build upon this foundation:
- Complementary angles in triangles: In right-angled triangles, the two acute angles are always complementary. This relationship is fundamental to understanding trigonometric ratios.
- Complementary angles and trigonometric identities: Trigonometric identities, such as sin(90° - x) = cos(x) and tan(90° - x) = cot(x), are directly derived from the properties of complementary angles. These identities are essential for solving more complex trigonometric problems.
- Complementary angles in coordinate geometry: Understanding complementary angles is vital when working with slopes and angles in coordinate geometry. For example, perpendicular lines have slopes that are negative reciprocals, a relationship directly linked to complementary angles.
Practical Exercises and Further Exploration
To solidify your understanding, try these exercises:
- Find the complement of a 28° angle.
- Two angles are complementary. One angle is twice the other. Find the measures of both angles.
- In a right-angled triangle, one acute angle is 40°. Find the measure of the other acute angle.
- Draw a diagram showing two non-adjacent complementary angles.
- Research and explain the relationship between complementary angles and the sine and cosine functions.
By working through these exercises and delving deeper into the advanced concepts, you'll build a solid grasp of complementary angles and their significance in various mathematical and real-world applications. This understanding will provide a strong foundation for further exploration in geometry and related fields. Remember that consistent practice is key to mastering this fundamental geometric concept and unlocking its broader applications.
Latest Posts
Latest Posts
-
Least Common Multiple Of 5 6 7
Mar 17, 2025
-
How Do You Find The Inverse Of A Relation
Mar 17, 2025
-
Does Cold Air Go Up Or Down
Mar 17, 2025
-
Least Common Multiple Of 20 And 3
Mar 17, 2025
-
Function Of The Motor End Plate
Mar 17, 2025
Related Post
Thank you for visiting our website which covers about Two Angles Whose Sum Is 90 . We hope the information provided has been useful to you. Feel free to contact us if you have any questions or need further assistance. See you next time and don't miss to bookmark.
