The Law Conservation Of Energy States That
Juapaving
Mar 06, 2025 · 6 min read
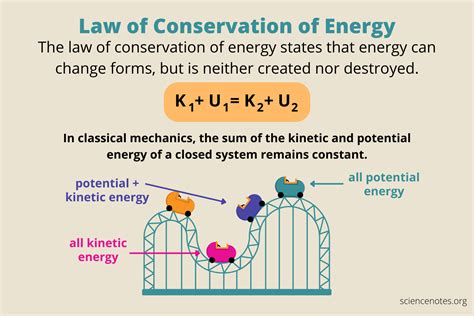
Table of Contents
The Law of Conservation of Energy: A Comprehensive Exploration
The law of conservation of energy is a fundamental principle in physics stating that energy cannot be created or destroyed, only transformed from one form to another. This seemingly simple statement underpins our understanding of the universe, from the smallest subatomic particles to the largest celestial bodies. This article will delve deep into this crucial law, exploring its various facets, implications, and applications.
Understanding the Core Principle
At its heart, the law of conservation of energy dictates that within an isolated system, the total energy remains constant over time. An isolated system is one that doesn't exchange energy with its surroundings. This means that while energy might change forms – from potential energy to kinetic energy, for example – the total amount of energy within the system remains the same.
This principle is not just a theoretical concept; it's a cornerstone of numerous scientific fields and technological advancements. It allows us to predict and understand the behavior of systems ranging from simple machines to complex biological processes.
Examples of Energy Transformation
Let's illustrate the law with some relatable examples:
-
A Rollercoaster: At the top of the hill, the rollercoaster possesses maximum potential energy (due to its height). As it descends, this potential energy is converted into kinetic energy (energy of motion). At the bottom of the hill, kinetic energy is at its peak, and the cycle repeats as it climbs the next hill. Ignoring friction and air resistance (which represent energy loss to the surroundings, making the system not truly isolated), the total energy (potential + kinetic) remains constant throughout the ride.
-
Burning a Candle: When a candle burns, the chemical potential energy stored within the wax is transformed into heat and light energy. While the forms of energy change, the total amount of energy in the system (candle + surrounding air) remains constant. Again, this is an idealized scenario; in reality, some energy is lost as heat to the surroundings.
-
Photosynthesis: Plants use solar energy (light energy) to convert carbon dioxide and water into glucose (chemical energy) and oxygen. This process demonstrates the transformation of radiant energy into chemical energy.
Different Forms of Energy
To fully appreciate the law of conservation of energy, we need to recognize the various forms energy can take:
-
Kinetic Energy: The energy of motion. A moving car, a flying bird, even the vibrating molecules in a warm object all possess kinetic energy. It's directly proportional to the object's mass and the square of its velocity.
-
Potential Energy: Stored energy due to an object's position or configuration. A book held above the ground has gravitational potential energy, ready to be converted into kinetic energy when it falls. A stretched spring possesses elastic potential energy. Chemical potential energy is stored in the bonds of molecules. Nuclear potential energy is stored within the nucleus of atoms.
-
Thermal Energy (Heat): The total kinetic energy of the particles within a substance. Temperature is a measure of the average kinetic energy of these particles.
-
Radiant Energy (Light): Energy that travels in the form of electromagnetic waves, including visible light, infrared radiation, and ultraviolet radiation.
-
Electrical Energy: Energy associated with the flow of electric charge.
-
Sound Energy: Energy that travels in the form of sound waves.
-
Chemical Energy: Energy stored in the chemical bonds of molecules. This energy is released during chemical reactions, such as combustion or digestion.
-
Nuclear Energy: Energy stored within the nucleus of an atom. This energy is released during nuclear reactions, such as nuclear fission and fusion.
These forms are interchangeable; energy can transform from one form to another, but the total energy remains constant within an isolated system.
The First Law of Thermodynamics
The law of conservation of energy is fundamentally linked to the First Law of Thermodynamics. This law states that the change in internal energy of a system is equal to the heat added to the system minus the work done by the system. Mathematically, it's expressed as:
ΔU = Q - W
Where:
- ΔU is the change in internal energy
- Q is the heat added to the system
- W is the work done by the system
This law essentially reiterates the conservation of energy, highlighting the relationship between internal energy, heat transfer, and work. It emphasizes that energy is neither created nor destroyed, but rather transferred or transformed.
Limitations and Considerations
While the law of conservation of energy is incredibly powerful, it's important to acknowledge its limitations:
-
Non-isolated systems: The law strictly applies only to isolated systems. In reality, most systems interact with their surroundings, exchanging energy in the form of heat, work, or radiation. In these cases, the total energy within the system might change.
-
Mass-energy equivalence: Einstein's famous equation, E=mc², demonstrates the equivalence of energy and mass. This means that mass can be converted into energy and vice versa. This necessitates a more comprehensive view of energy conservation, acknowledging that the total mass-energy of a system remains constant. This is particularly relevant in nuclear reactions where a small amount of mass is converted into a significant amount of energy.
Applications of the Law of Conservation of Energy
The principle of energy conservation has far-reaching applications across diverse fields:
-
Engineering: Engineers utilize this principle in designing efficient machines and systems, aiming to minimize energy loss and maximize energy conversion. This is crucial in areas like power generation, transportation, and manufacturing.
-
Environmental Science: Understanding energy flows in ecosystems is critical for environmental modeling and sustainability efforts. This includes studying energy transfer through food chains and assessing the environmental impact of various energy sources.
-
Medicine: Metabolic processes in living organisms are governed by the conservation of energy. Understanding energy balance is vital in studying nutrition, exercise physiology, and disease processes.
-
Physics: The law forms the basis of many branches of physics, including mechanics, thermodynamics, and electromagnetism. It's essential in developing and testing physical theories.
The Importance of Energy Efficiency
Understanding the law of conservation of energy underscores the importance of energy efficiency. Since energy cannot be created, it's crucial to utilize existing energy resources wisely and minimize energy waste. Strategies for improving energy efficiency include:
-
Improving insulation in buildings: This reduces heat loss and reduces the energy required for heating and cooling.
-
Developing more fuel-efficient vehicles: This reduces the amount of fuel needed for transportation.
-
Using energy-efficient appliances: This lowers energy consumption in homes and businesses.
-
Investing in renewable energy sources: This reduces reliance on fossil fuels and minimizes environmental impact.
Conclusion
The law of conservation of energy is a cornerstone of physics and has profound implications across various scientific and technological domains. While seemingly simple, its implications are far-reaching, guiding our understanding of the universe and informing our efforts to create a more sustainable future. By recognizing the diverse forms energy can take and the importance of energy efficiency, we can leverage this fundamental principle to develop innovative solutions and address global challenges. The continued exploration and application of this principle will undoubtedly shape scientific advancements and technological innovations for generations to come. It remains a testament to the elegance and power of fundamental physical laws in explaining the intricate workings of our world. Furthermore, its importance in fostering responsible energy usage and promoting sustainable practices cannot be overstated, ensuring a healthier planet for future generations. Continuous research and technological advancements based on this principle will continue to pave the way for a more efficient and sustainable future.
Latest Posts
Latest Posts
-
Is 23 A Composite Or Prime Number
Mar 06, 2025
-
Consecutive Angles In A Parallelogram Are
Mar 06, 2025
-
Is Root 72 A Rational Number
Mar 06, 2025
-
What Is The Prime Factorization Of 15
Mar 06, 2025
-
A Heat Flux Of 4000 J S Is To Be Passed
Mar 06, 2025
Related Post
Thank you for visiting our website which covers about The Law Conservation Of Energy States That . We hope the information provided has been useful to you. Feel free to contact us if you have any questions or need further assistance. See you next time and don't miss to bookmark.
