The Function Of The Dartos And Cremaster Muscles Is To
Juapaving
Mar 20, 2025 · 6 min read
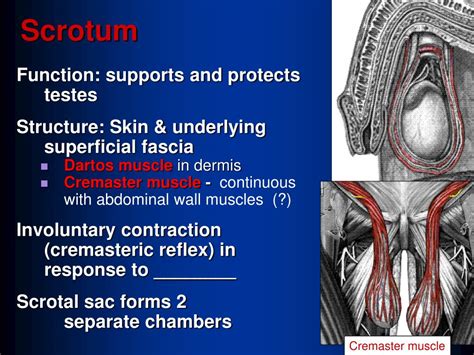
Table of Contents
The Function of the Dartos and Cremaster Muscles Is to… Regulate Testicular Temperature
The human male reproductive system is a marvel of biological engineering, and a crucial element of its success lies in maintaining the testes at a temperature slightly lower than core body temperature. This seemingly minor detail is vital for optimal sperm production, a process known as spermatogenesis. Achieving and maintaining this temperature difference is primarily the responsibility of two muscles: the dartos and cremaster muscles. Their coordinated actions are crucial for male fertility and overall reproductive health. Let's delve into the intricate functions of these often-overlooked muscles.
Understanding the Importance of Testicular Temperature
Before exploring the muscular mechanisms, it's essential to understand why maintaining a lower testicular temperature is so critical. Spermatogenesis, the process of sperm formation, is exquisitely sensitive to temperature fluctuations. While the core body temperature of approximately 98.6°F (37°C) is ideal for many bodily functions, it's too high for healthy sperm development. Elevated temperatures can lead to:
- Decreased Sperm Production: High temperatures can impair the normal development and maturation of sperm cells, resulting in a lower sperm count (oligospermia) or even the absence of sperm (azoospermia).
- Reduced Sperm Motility: Heat stress can negatively affect the motility, or movement, of sperm, hindering their ability to reach and fertilize an egg.
- Abnormal Sperm Morphology: Exposure to excessive heat can lead to structural abnormalities in sperm, further reducing their chances of successful fertilization.
- Infertility: In severe cases, prolonged exposure to elevated temperatures can cause irreversible damage, leading to infertility.
Therefore, the body employs several mechanisms to keep the testes cool, and the dartos and cremaster muscles play a central role in this thermoregulation.
The Dartos Muscle: The Skin's Protector
The dartos muscle is a thin layer of smooth muscle found within the superficial fascia of the scrotum. Unlike skeletal muscles, which are under voluntary control, the dartos muscle is involuntary, meaning its contractions are not consciously controlled. Its primary function is to regulate scrotal skin temperature through changes in its tension.
Dartos Muscle Contraction and Relaxation: A Temperature-Sensitive Response
When the temperature surrounding the scrotum drops, the dartos muscle contracts. This contraction causes the scrotal skin to wrinkle and become tighter, reducing the surface area exposed to the cold. This decreased surface area minimizes heat loss and helps to maintain testicular temperature. Think of it like pulling in your shoulders on a cold day to conserve body heat.
Conversely, when the temperature surrounding the scrotum rises, the dartos muscle relaxes. This relaxation causes the scrotal skin to become smoother and more relaxed, increasing the surface area exposed to the environment. This increased surface area facilitates heat dissipation through convection, radiation, and evaporation, helping to cool the testes.
Beyond Temperature Regulation: The Dartos Muscle's Role in Support
While its primary function is thermoregulation, the dartos muscle also plays a secondary role in supporting the testes and maintaining their position within the scrotum. Its contractile properties contribute to the overall structural integrity of the scrotum.
The Cremaster Muscle: The Testes' Shifter
The cremaster muscle is a paired muscle, meaning there's one on each side of the scrotum. It’s composed of striated muscle fibers originating from the internal oblique muscle of the abdominal wall. It encircles the spermatic cord and extends down to envelop the testes. Unlike the dartos muscle, the cremaster muscle is partially under voluntary control, although its primary function is involuntary and reflexive.
Cremasteric Reflex: A Quick Response to Temperature Changes
The cremaster muscle's most significant function is its involvement in the cremasteric reflex. This reflex is triggered by a decrease in scrotal temperature or by lightly stroking the inner thigh. When the reflex is activated, the cremaster muscle contracts, pulling the testes closer to the body's warmth. This movement helps to conserve heat and protect the testes from cold temperatures.
Cremaster Muscle and Temperature Regulation: A Dynamic System
The cremaster muscle's action is complementary to that of the dartos muscle. While the dartos muscle primarily affects the scrotal skin, the cremaster muscle adjusts the position of the testes themselves, providing an additional layer of temperature control. By drawing the testes closer to the body, the cremaster muscle reduces their exposure to cold air and minimizes heat loss. When temperatures rise, it relaxes, allowing the testes to hang lower and benefit from increased cooling.
Other Potential Functions: Beyond Thermoregulation
Although thermoregulation is the cremaster muscle's primary function, research suggests potential additional roles. Some studies indicate it might contribute to the protection of the testes from trauma. Its contractile action might help to cushion them from impact, reducing the risk of injury.
The Interplay of Dartos and Cremaster Muscles: A Coordinated Effort
The dartos and cremaster muscles don't operate in isolation. Instead, they work in a coordinated manner to maintain optimal testicular temperature. The dartos muscle adjusts the scrotal skin's surface area, while the cremaster muscle modifies the position of the testes, creating a dynamic system capable of responding to a wide range of temperature fluctuations. Their combined actions ensure that the testes remain within the ideal temperature range for optimal sperm production.
Clinical Implications: When Thermoregulation Fails
When the mechanisms controlled by the dartos and cremaster muscles malfunction, various problems can arise. Conditions such as cryptorchidism (undescended testes), where one or both testes fail to descend into the scrotum, can lead to significantly elevated testicular temperatures, resulting in reduced fertility. Similarly, conditions affecting the scrotal blood supply or nerve function can impair thermoregulation, leading to similar problems.
Factors Affecting Testicular Temperature Beyond Muscle Function
While the dartos and cremaster muscles are key players in thermoregulation, other factors also influence testicular temperature:
- Clothing: Tight-fitting clothing can restrict blood flow and heat dissipation, leading to increased testicular temperatures.
- Environmental Temperature: Exposure to excessive heat, such as from saunas or hot tubs, can negatively impact sperm production.
- Obesity: Excess abdominal fat can insulate the scrotum, hindering heat dissipation.
- Scrotal Trauma: Injuries to the scrotum can compromise the integrity of the dartos and cremaster muscles, and compromise their functionality.
Maintaining Optimal Testicular Temperature: Practical Considerations
Maintaining optimal testicular temperature is crucial for male fertility. Here are some practical tips:
- Wear loose-fitting underwear: Avoid tight underwear that can restrict blood flow and increase testicular temperature. Loose boxers are generally recommended over tight-fitting briefs.
- Avoid prolonged exposure to heat: Limit time spent in hot tubs, saunas, and other high-temperature environments.
- Maintain a healthy weight: Obesity can increase testicular temperature; maintaining a healthy weight is important for overall health and reproductive function.
- Protect the scrotum from trauma: Take precautions to avoid injuries to the scrotum.
Conclusion: The Crucial Role of Dartos and Cremaster Muscles
The dartos and cremaster muscles are essential components of the male reproductive system. Their coordinated actions to regulate testicular temperature are vital for maintaining sperm production, motility, and morphology. Understanding their function and the factors affecting testicular temperature highlights the importance of lifestyle choices and healthcare practices in promoting male fertility and overall reproductive health. By paying attention to factors like clothing choices, environmental temperature exposure, and maintaining a healthy weight, men can actively contribute to maintaining optimal testicular temperature and preserving their reproductive health. Any concerns regarding testicular health or fertility should be addressed promptly with a healthcare professional.
Latest Posts
Latest Posts
-
What Is Group Of Fish Called
Mar 21, 2025
-
Label The Parts Of A Animal Cell
Mar 21, 2025
-
How Many Ml In 1 75 Ltr
Mar 21, 2025
-
Words With Ad At The Beginning
Mar 21, 2025
-
32 32 32 Divided By 7
Mar 21, 2025
Related Post
Thank you for visiting our website which covers about The Function Of The Dartos And Cremaster Muscles Is To . We hope the information provided has been useful to you. Feel free to contact us if you have any questions or need further assistance. See you next time and don't miss to bookmark.
