The Division Of The Cytoplasm Is Called
Juapaving
Mar 15, 2025 · 5 min read
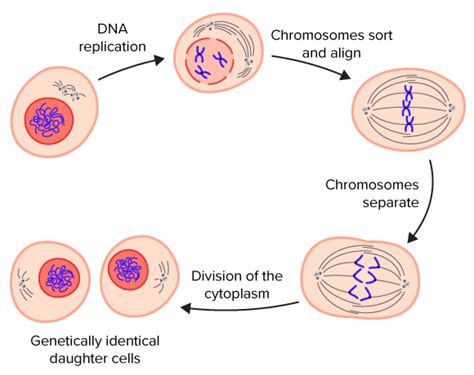
Table of Contents
The Division of the Cytoplasm is Called Cytokinesis: A Deep Dive into Cell Division
The process of cell division is a fundamental aspect of life, enabling growth, repair, and reproduction in all living organisms. While the meticulous separation of chromosomes during mitosis or meiosis is often the focus of discussion, the division of the cytoplasm, a process known as cytokinesis, is equally crucial for successful cell division. This article will delve deep into the intricacies of cytokinesis, exploring its mechanisms, variations across different cell types, and its significance in maintaining cellular integrity and organismal health.
Understanding Cytokinesis: The Final Act of Cell Division
Cytokinesis, literally meaning "cell movement," is the final stage of cell division, following the completion of nuclear division (karyokinesis). It involves the physical partitioning of the cytoplasm, resulting in two distinct daughter cells, each inheriting a complete set of organelles and cytoplasmic components. Unlike karyokinesis, which is largely conserved across species, cytokinesis displays significant variations depending on the organism and cell type. However, the core principle remains the same: the even distribution of cytoplasmic contents to ensure the viability and functionality of the new cells.
The Significance of Cytokinesis
The precise division of the cytoplasm during cytokinesis is not merely a cosmetic conclusion to cell division; it plays a vital role in:
-
Maintaining Cellular Integrity: An uneven distribution of cytoplasmic components could lead to daughter cells with compromised function or viability. Proper cytokinesis ensures each daughter cell receives the necessary resources to survive and function independently.
-
Preventing Polyploidy: Failure of cytokinesis results in a single cell with duplicated chromosomes—a condition called polyploidy. This can disrupt cellular processes and contribute to genomic instability, potentially leading to cancerous growth or cell death.
-
Organismal Development and Growth: Accurate cytokinesis is critical for embryonic development and tissue growth. Defects in this process can result in developmental abnormalities and organ malformations.
-
Tissue Homeostasis: The regulated division and cytokinesis of cells maintain tissue homeostasis, ensuring a balance between cell proliferation and cell death. Disruptions in this delicate balance can contribute to various diseases.
The Mechanisms of Cytokinesis: A Comparative Overview
The mechanisms of cytokinesis differ significantly between animal and plant cells, reflecting the fundamental structural differences between these cell types.
Cytokinesis in Animal Cells: The Cleavage Furrow
In animal cells, cytokinesis is characterized by the formation of a cleavage furrow. This is a contractile ring composed primarily of actin filaments and myosin II motor proteins, which assembles beneath the plasma membrane at the cell's equator. The contraction of this ring constricts the cell, pinching it into two separate daughter cells.
The Actin-Myosin Ring: A Molecular Engine
The actin-myosin ring acts as a molecular motor, generating the force needed to constrict the cell. Myosin II motor proteins interact with actin filaments, causing them to slide past each other and generate contractile force. This process is regulated by various signaling molecules, ensuring coordinated and timely contraction.
Membrane Invagination and Abscission
As the contractile ring constricts, the plasma membrane invaginates, forming a deep furrow that progressively deepens until the cell is completely divided. The final step, called abscission, involves the severing of the connection between the two daughter cells. This process involves intricate membrane fusion and trafficking events.
Cytokinesis in Plant Cells: The Cell Plate
Plant cells, with their rigid cell walls, cannot undergo cytokinesis through the formation of a cleavage furrow. Instead, they employ a distinct mechanism involving the formation of a cell plate.
The Phragmoplast: A Microtubule-Based Scaffold
The cell plate begins to form in the center of the cell, within a structure called the phragmoplast. This is a complex array of microtubules and associated proteins that acts as a scaffold for the assembly of the new cell wall.
Vesicle Fusion and Cell Wall Synthesis
Numerous vesicles containing cell wall materials, such as cellulose and pectin, are transported to the phragmoplast and fuse together to form the expanding cell plate. As the cell plate grows outwards, it eventually fuses with the existing parental cell wall, creating two distinct daughter cells, each enclosed within its own cell wall.
Variations in Cytokinesis: Adapting to Diverse Cell Types
While the fundamental principles of cytokinesis remain the same, specific aspects of the process can vary considerably depending on cell type and organism.
Asymmetric Cytokinesis: Unequal Distribution of Cytoplasmic Components
In some cases, cytokinesis results in the formation of two daughter cells with unequal cytoplasmic content. This is known as asymmetric cytokinesis, and it plays a crucial role in cell differentiation and tissue development. For example, during stem cell division, one daughter cell remains a stem cell, while the other differentiates into a specialized cell type. This unequal distribution of cytoplasmic determinants contributes to the specialized fate of each daughter cell.
Cytokinesis in Multicellular Organisms: Coordination and Regulation
In multicellular organisms, cytokinesis is tightly regulated and coordinated with other cellular processes. This ensures that cell division contributes to the overall organization and function of the organism. Signaling pathways and cell-cell interactions play crucial roles in coordinating cytokinesis across different cells and tissues. Defects in this coordination can lead to developmental abnormalities and disease.
Cytokinesis and Disease: When Things Go Wrong
Errors in cytokinesis can have significant consequences for cellular health and organismal development.
Polyploidy and Cancer: A Dangerous Connection
Failure of cytokinesis can lead to polyploidy, a state in which cells have more than two complete sets of chromosomes. Polyploidy is often associated with genomic instability and increased risk of cancer. Many cancer cells exhibit defects in cytokinesis, contributing to their uncontrolled proliferation.
Developmental Abnormalities: The Impact of Cytokinesis Errors
Errors in cytokinesis during development can cause serious developmental abnormalities. For example, defects in cytokinesis can lead to malformations in organs and tissues. These defects can range from mild to severe, depending on the timing and severity of the cytokinesis error.
Conclusion: The Unsung Hero of Cell Division
Cytokinesis, though often overshadowed by the more visually striking events of karyokinesis, is an indispensable stage of cell division. Its precise mechanisms, variations across different cell types, and vital role in maintaining cellular integrity highlight its significance in all aspects of life, from single-celled organisms to complex multicellular life forms. Future research into the molecular intricacies of cytokinesis will undoubtedly reveal more about its regulatory mechanisms, its role in various diseases, and its potential as a therapeutic target. Understanding this critical process is key to unlocking a deeper understanding of cell biology and its implications for human health.
Latest Posts
Latest Posts
-
Do Viruses Belong To One Of The Domains Of Life
Mar 17, 2025
-
The C Shape Of The Tracheal Cartilages Is Important Because
Mar 17, 2025
-
Least Common Multiple Of 5 6 7
Mar 17, 2025
-
How Do You Find The Inverse Of A Relation
Mar 17, 2025
-
Does Cold Air Go Up Or Down
Mar 17, 2025
Related Post
Thank you for visiting our website which covers about The Division Of The Cytoplasm Is Called . We hope the information provided has been useful to you. Feel free to contact us if you have any questions or need further assistance. See you next time and don't miss to bookmark.
