Sum Of Exterior Angles Of A Hexagon
Juapaving
Mar 20, 2025 · 6 min read
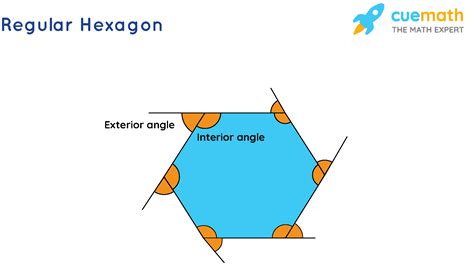
Table of Contents
The Sum of Exterior Angles of a Hexagon: A Deep Dive
The sum of exterior angles of any polygon, including a hexagon, is a fundamental concept in geometry. Understanding this concept is crucial for solving various geometric problems and building a strong foundation in mathematics. This comprehensive guide will explore the sum of exterior angles of a hexagon, providing a detailed explanation, practical examples, and related concepts to solidify your understanding.
Understanding Polygons and Their Angles
Before diving into the specifics of hexagons, let's establish a clear understanding of polygons and their angles. A polygon is a closed two-dimensional figure formed by connecting a finite number of straight line segments. These segments are called the sides of the polygon. Polygons are classified based on the number of sides they have:
- Triangle: 3 sides
- Quadrilateral: 4 sides
- Pentagon: 5 sides
- Hexagon: 6 sides
- Heptagon: 7 sides
- Octagon: 8 sides
- and so on...
Each polygon has interior angles – the angles formed inside the polygon by its sides. It also possesses exterior angles. An exterior angle is formed by extending one side of the polygon and measuring the angle between the extension and the adjacent side. For each interior angle, there's a corresponding exterior angle. Importantly, the interior and exterior angle at a given vertex are supplementary; meaning they add up to 180 degrees.
The Sum of Exterior Angles: A General Rule
A remarkable property of polygons is that the sum of their exterior angles is always 360 degrees, regardless of the number of sides. This rule holds true for all polygons, from triangles to complex polygons with hundreds of sides. This consistent property simplifies many geometric calculations. This is a powerful and consistent rule across all polygons.
This fact can be intuitively understood. Imagine walking around the perimeter of a polygon. At each vertex, you turn through the exterior angle. After completing a full circuit of the polygon, you will have rotated a total of 360 degrees to return to your starting point, facing the same direction. This rotation represents the sum of the exterior angles.
Focusing on Hexagons
A hexagon is a six-sided polygon. Applying the general rule of exterior angles, the sum of the exterior angles of any hexagon is also 360 degrees. This is true whether the hexagon is regular (all sides and angles are equal) or irregular (sides and angles vary). The rule remains consistent. This simplification simplifies many geometric calculations concerning hexagons.
Let's consider a regular hexagon. Each interior angle of a regular hexagon measures 120 degrees (calculated using the formula (n-2) * 180 / n, where n is the number of sides). Since each interior and exterior angle are supplementary, each exterior angle of a regular hexagon measures 180 - 120 = 60 degrees. Multiplying this by the six exterior angles, we get 6 * 60 = 360 degrees. This confirms the general rule.
Calculating Interior Angles of a Hexagon
Understanding interior angles is essential to grasp the relationship with exterior angles. For a regular hexagon, as mentioned above, each interior angle is 120 degrees. But for irregular hexagons, the interior angles will vary. However, the sum of the interior angles of any hexagon can be calculated using the formula:
(n - 2) * 180°
Where 'n' is the number of sides (in this case, 6 for a hexagon). Substituting, we get:
(6 - 2) * 180° = 720°
Therefore, the sum of the interior angles of any hexagon is 720 degrees. This formula applies to all polygons, making it a crucial tool in geometric problem-solving.
Practical Applications and Examples
The concept of the sum of exterior angles of a hexagon, and polygons in general, has several practical applications in various fields:
1. Architecture and Design: Architects and designers use geometric principles, including the properties of polygons, to create aesthetically pleasing and structurally sound buildings. Understanding exterior angles helps in designing roof structures, tiling patterns, and other architectural elements.
2. Engineering: Engineers apply geometric concepts when designing bridges, roads, and other infrastructure projects. The properties of polygons, including the sum of their exterior angles, are vital in ensuring structural stability and efficient design.
3. Computer Graphics and Game Development: In computer graphics and game development, understanding polygons and their angles is crucial for creating realistic and detailed 3D models. The properties of polygons are used extensively in computer-aided design (CAD) software.
Example Problem 1:
A hexagon has exterior angles measuring 40°, 50°, 70°, 80°, x, and y. Find the values of x and y if x = y + 10°.
Solution:
The sum of exterior angles must be 360°. Therefore:
40° + 50° + 70° + 80° + x + y = 360° 240° + x + y = 360° x + y = 120°
Since x = y + 10°, we can substitute:
(y + 10°) + y = 120° 2y + 10° = 120° 2y = 110° y = 55°
And since x = y + 10°, x = 55° + 10° = 65°
Therefore, x = 65° and y = 55°.
Example Problem 2:
An irregular hexagon has interior angles measuring 110°, 120°, 130°, 140°, 150°, and z. Find the value of z.
Solution:
The sum of interior angles of a hexagon is 720°. Therefore:
110° + 120° + 130° + 140° + 150° + z = 720° 650° + z = 720° z = 70°
Therefore, the missing interior angle z is 70°. Note that finding the exterior angles and then using the supplementary property to find the missing interior angle would yield the same result.
Beyond Hexagons: Extending the Concept
The fundamental principle of the sum of exterior angles being 360° applies to all polygons, regardless of the number of sides. This general rule simplifies many geometric problems concerning polygons. This consistency makes it a powerful tool across various geometric contexts.
For example, for a pentagon (5 sides), the sum of exterior angles remains 360°. Similarly, for an octagon (8 sides), the sum of exterior angles remains 360°, and so on. This consistency is a core concept in understanding the geometry of polygons.
Conclusion
Understanding the sum of the exterior angles of a hexagon, and the broader concept for all polygons, is essential for anyone studying geometry. This simple yet powerful principle simplifies problem-solving across many fields. From architecture to computer graphics, the consistent 360° sum simplifies complex geometric calculations. Mastering this concept provides a solid foundation for tackling more advanced geometric problems and further exploring mathematical concepts. The ability to apply this knowledge practically showcases a strong understanding of core geometric principles. Remember that the exterior angles of a polygon always sum to 360 degrees, regardless of the number of sides the polygon has. This universal truth is the cornerstone of many geometric calculations and applications.
Latest Posts
Latest Posts
-
What Color Has The Longest Wavelength
Mar 21, 2025
-
5 Out Of 8 As A Percentage
Mar 21, 2025
-
Boiling Point Of Water Kelvin Scale
Mar 21, 2025
-
150 Cm Is How Many Inches
Mar 21, 2025
-
120 Sq Mt To Sq Ft
Mar 21, 2025
Related Post
Thank you for visiting our website which covers about Sum Of Exterior Angles Of A Hexagon . We hope the information provided has been useful to you. Feel free to contact us if you have any questions or need further assistance. See you next time and don't miss to bookmark.
