Sum Of Angles In A Quadrangle
Juapaving
Mar 16, 2025 · 6 min read
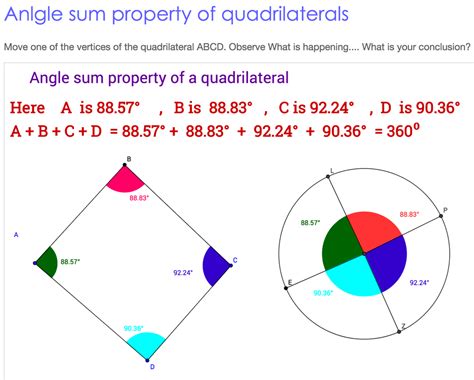
Table of Contents
The Sum of Angles in a Quadrilateral: A Deep Dive into Geometry
The sum of angles in a quadrilateral, a four-sided polygon, is a fundamental concept in geometry. While seemingly simple at first glance, understanding this concept opens doors to exploring a wealth of related geometric properties and theorems. This article will delve into the intricacies of quadrilateral angle sums, exploring different approaches to proving this essential theorem, examining special types of quadrilaterals, and highlighting its applications in various mathematical fields.
Understanding Quadrilaterals
Before diving into the sum of angles, let's establish a clear understanding of quadrilaterals. A quadrilateral is a polygon with four sides, four vertices (corners), and four angles. These sides can be of varying lengths, and the angles can be acute, obtuse, or right angles. The versatility of quadrilaterals makes them ubiquitous in geometry and real-world applications.
Types of Quadrilaterals
The world of quadrilaterals is diverse. Some notable types include:
- Trapezoid: A quadrilateral with at least one pair of parallel sides.
- Parallelogram: A quadrilateral with two pairs of parallel sides. Special cases of parallelograms include:
- Rectangle: A parallelogram with four right angles.
- Rhombus: A parallelogram with four sides of equal length.
- Square: A parallelogram with four right angles and four sides of equal length.
- Kite: A quadrilateral with two pairs of adjacent sides of equal length.
Proving the Sum of Angles in a Quadrilateral
The fundamental theorem states that the sum of the interior angles of any quadrilateral is always 360 degrees. This can be proven using several methods:
Method 1: Triangulation
This is perhaps the most common and intuitive method. Any quadrilateral can be divided into two triangles by drawing a diagonal connecting two opposite vertices. Since the sum of angles in a triangle is 180 degrees, the sum of angles in the quadrilateral is simply the sum of the angles in the two triangles: 180° + 180° = 360°.
Visual Representation:
Imagine a quadrilateral ABCD. Draw a diagonal AC. This divides the quadrilateral into two triangles, ΔABC and ΔACD. The angles of ΔABC are ∠BAC, ∠ABC, and ∠BCA. The angles of ΔACD are ∠CAD, ∠ADC, and ∠ACD. The sum of angles in quadrilateral ABCD is ∠BAC + ∠ABC + ∠BCA + ∠CAD + ∠ADC + ∠ACD = (∠BAC + ∠CAD) + ∠ABC + (∠BCA + ∠ACD) + ∠ADC = 180° + 180° = 360°.
Method 2: Exterior Angles
Another approach involves using exterior angles. An exterior angle of a polygon is formed by extending one of its sides. The sum of exterior angles of any polygon, regardless of the number of sides, is always 360 degrees. For a quadrilateral, each interior angle and its corresponding exterior angle are supplementary (they add up to 180°). If we let the interior angles be A, B, C, and D, and the exterior angles be A', B', C', and D', then:
A + A' = 180° B + B' = 180° C + C' = 180° D + D' = 180°
Adding these equations, we get:
A + B + C + D + A' + B' + C' + D' = 720°
Since A' + B' + C' + D' = 360° (sum of exterior angles), we can substitute this into the equation:
A + B + C + D + 360° = 720°
Therefore, A + B + C + D = 360°.
Method 3: Vector Approach (Advanced)
For those with a stronger mathematical background, a vector approach can elegantly prove the theorem. This method involves representing the sides of the quadrilateral as vectors and utilizing vector addition and dot products. While beyond the scope of a basic introduction, it's a powerful technique demonstrating the interconnectedness of different mathematical branches.
Applications and Implications
The 360° sum of angles in a quadrilateral has far-reaching applications:
1. Solving Geometric Problems
Knowing this property allows us to solve numerous geometric problems involving unknown angles within quadrilaterals. If we know three angles, we can easily find the fourth. This is crucial in surveying, architecture, and engineering.
2. Tessellations
The sum of angles is fundamental to understanding tessellations – patterns created by repeating geometric shapes that cover a surface without gaps or overlaps. Quadrilaterals, particularly squares and rectangles, are commonly used in tessellations.
3. Computer Graphics and Game Design
In computer graphics and game design, understanding the properties of quadrilaterals is vital for creating realistic and accurate representations of objects and environments. Quadrilaterals are frequently used as building blocks for 3D models and textures.
4. Cartography
In mapmaking (cartography), the properties of quadrilaterals, including their angle sums, play a role in representing geographical regions accurately.
5. Further Geometric Theorems
The sum of angles in a quadrilateral is a stepping stone to understanding more complex geometric theorems and properties, particularly those involving special types of quadrilaterals like cyclic quadrilaterals (quadrilaterals whose vertices lie on a circle). In a cyclic quadrilateral, opposite angles are supplementary (they add up to 180°). This is a direct consequence of the 360° angle sum and the properties of angles subtended by the same arc in a circle.
Beyond the Basics: Exploring Special Quadrilaterals
Let's delve deeper into the angle properties of specific quadrilaterals:
Parallelograms
In a parallelogram, opposite angles are equal. This means if we have angles A, B, C, and D, then A = C and B = D. Since A + B + C + D = 360°, we can deduce that A + B = 180° and C + D = 180°. This property is often used in solving problems involving parallelograms.
Rectangles
Rectangles are a special case of parallelograms, where all angles are right angles (90°). Therefore, the sum of angles is 4 * 90° = 360°.
Rhombuses
Rhombuses, like squares, have equal sides. However, their angles are not necessarily 90 degrees. Their opposite angles remain equal as with parallelograms, leading to the same 360-degree sum of interior angles.
Squares
Squares possess both the properties of a rectangle (four 90° angles) and a rhombus (four equal sides), leading inevitably to a 360° sum of interior angles.
Trapezoids
Trapezoids have at least one pair of parallel sides. While their angle relationships aren't as straightforward as parallelograms, the sum of their interior angles always equals 360°.
Kites
Kites, characterized by two pairs of adjacent equal sides, do not have any special angle relationships guaranteed except for the fundamental 360° sum. However, one pair of opposite angles are equal.
Conclusion: The Enduring Importance of Quadrilateral Angle Sums
The sum of angles in a quadrilateral, while seemingly a basic geometric concept, forms the foundation for numerous advanced theorems and applications. Understanding this fundamental principle unlocks a deeper appreciation for the elegance and interconnectedness of geometry. From solving practical problems to developing advanced mathematical models, the 360° angle sum in a quadrilateral remains a cornerstone of geometric understanding. This exploration has touched upon several methods of proof, highlighting the versatility of geometric reasoning and its ability to approach problems from various perspectives. The rich diversity within the quadrilateral family itself further emphasizes the significant role this seemingly simple theorem plays within the broader landscape of mathematics and its real-world applications.
Latest Posts
Latest Posts
-
How Do You Multiply By The Reciprocal
Mar 16, 2025
-
What Are The Advantages Of Having Four Chambered Heart
Mar 16, 2025
-
Who Is The Father Of The Renaissance
Mar 16, 2025
-
How Many Lines Of Symmetry Circle
Mar 16, 2025
-
What Are The Raw Materials Needed For Photosynthesis
Mar 16, 2025
Related Post
Thank you for visiting our website which covers about Sum Of Angles In A Quadrangle . We hope the information provided has been useful to you. Feel free to contact us if you have any questions or need further assistance. See you next time and don't miss to bookmark.
