How Many Lines Of Symmetry Circle
Juapaving
Mar 16, 2025 · 5 min read
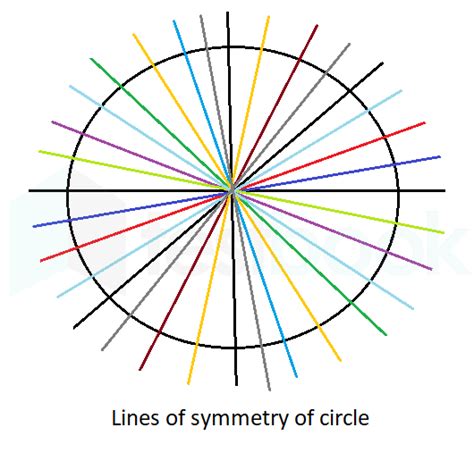
Table of Contents
How Many Lines of Symmetry Does a Circle Have? An Exploration of Rotational and Reflectional Symmetry
The seemingly simple question, "How many lines of symmetry does a circle have?" opens a fascinating door into the world of geometry, specifically exploring concepts of symmetry, reflection, and rotation. While the answer might seem immediately obvious to some, a deeper dive reveals a richer understanding of the mathematical properties that define a circle and its unique relationship with symmetry.
Understanding Lines of Symmetry
Before tackling the circle specifically, let's define what we mean by a line of symmetry. A line of symmetry, also known as a line of reflection, is a line that divides a shape into two identical halves that are mirror images of each other. If you were to fold the shape along the line of symmetry, the two halves would perfectly overlap. This principle applies to various two-dimensional shapes, from simple shapes like squares and rectangles to more complex figures.
Consider a square. It has four lines of symmetry: two that run vertically and horizontally through the center, and two that run diagonally from corner to corner. A rectangle, on the other hand, possesses only two lines of symmetry – one vertical and one horizontal. The number of lines of symmetry a shape possesses directly relates to its inherent geometric properties and its degree of regularity.
Exploring the Unique Properties of a Circle
A circle, unlike polygons with straight sides, is defined by a single continuous curved line. This continuous curvature is key to understanding its unique symmetry characteristics. Unlike a square or rectangle, the circle lacks distinct vertices or edges. Every point on the circumference is equidistant from the center. This inherent property is fundamental to its infinite lines of symmetry.
The Infinite Lines of Symmetry
The answer to the question, "How many lines of symmetry does a circle have?" is infinite. This is because any line drawn through the center of the circle will act as a line of symmetry. Imagine drawing a line from any point on the circumference, passing directly through the center, and continuing to the opposite point on the circumference. Folding the circle along this line would perfectly overlap the two halves, proving its symmetrical nature.
This infinite number of lines of symmetry stems from the circle's rotational symmetry. Every line passing through the center acts as both a line of reflectional symmetry and an axis of rotational symmetry. This concept intertwines the ideas of reflectional and rotational symmetry, highlighting the circle's exceptional geometrical properties.
Rotational Symmetry: A Complementary Perspective
While reflectional symmetry (lines of symmetry) is crucial, examining a circle's rotational symmetry provides another layer of understanding. Rotational symmetry refers to the ability of a shape to be rotated around a central point (in this case, the center of the circle) and still appear unchanged.
A circle exhibits perfect rotational symmetry about its center for any angle of rotation. This means you can rotate the circle by any degree, and it will look exactly the same. This infinite rotational symmetry is intimately connected to its infinite lines of reflectional symmetry. Every line of symmetry also defines an axis of rotation.
Connecting Lines of Symmetry and Rotational Symmetry
The relationship between lines of symmetry and rotational symmetry is particularly strong in circles. The infinite lines of symmetry can be viewed as resulting directly from the infinite rotational symmetry. Every line passing through the center represents both an axis of rotation and a line of reflection. This interconnectedness is a key feature distinguishing a circle's symmetry from that of other shapes.
Practical Applications and Real-World Examples
The concept of a circle's infinite lines of symmetry is not merely a theoretical concept; it has numerous real-world applications. Many natural phenomena and man-made objects exhibit circular symmetry.
- Wheels: The circular shape of wheels ensures smooth rotation and allows for efficient transfer of force. Their symmetry contributes to consistent motion and minimizes vibration.
- Planets and Stars: Many celestial bodies, from planets to stars, are approximately spherical, displaying remarkable symmetry. This symmetry is fundamental to their gravitational properties.
- Optical Lenses: Circular lenses utilize their inherent symmetry to focus light effectively. The symmetrical distribution of refractive power ensures uniform image formation.
- Design and Art: Artists and designers frequently leverage circular symmetry in their work. The elegance and balance created by the circle’s infinite lines of symmetry are aesthetically pleasing and impactful.
Distinguishing the Circle's Symmetry from Other Shapes
It's important to emphasize the unique nature of a circle's symmetry compared to other shapes. While other shapes might possess multiple lines of symmetry, none can match the circle's infinity. This uniqueness underscores the circle's fundamental place within geometry. The concept of infinite lines of symmetry sets it apart and reinforces its fundamental properties.
Beyond the Basics: Advanced Concepts and Considerations
While the basic understanding of a circle's infinite lines of symmetry is relatively straightforward, exploring advanced geometric concepts can provide a deeper appreciation. Concepts such as:
- Group Theory: This branch of mathematics provides a formal framework for studying symmetry, and the circle's symmetry group is an interesting and unique structure.
- Higher-Dimensional Analogues: The concept of symmetry can be extended to higher dimensions, and the higher-dimensional equivalents of a circle (spheres, hyperspheres) also possess remarkable symmetry properties.
- Fractal Geometry: Fractals often display self-similarity and intricate symmetry patterns, sometimes exhibiting features akin to the infinite symmetry of a circle, although in a more complex and self-repeating manner.
These advanced topics offer opportunities for further exploration and a deeper understanding of the mathematical richness surrounding the seemingly simple question of a circle's symmetry.
Conclusion: The Enduring Significance of Circular Symmetry
The simple question of how many lines of symmetry a circle possesses leads to a rich and rewarding exploration of geometric concepts. The answer – infinity – is not merely a numerical value, but rather a reflection of the circle's unique properties. Its infinite lines of symmetry, intimately linked to its perfect rotational symmetry, highlight the circle's fundamental role in mathematics, science, and art. This concept extends beyond basic geometry, enriching our understanding of the world around us, and serving as a testament to the elegance and power of mathematical principles. The circle, with its infinite symmetry, remains a timeless symbol of perfection and balance.
Latest Posts
Latest Posts
-
The Energy Of A Photon Is Inversely Proportional To Its
Mar 16, 2025
-
Which Set Of Numbers Is Closed Under Subtraction
Mar 16, 2025
-
How To Convert Hex To Octal
Mar 16, 2025
-
What Is One Half As A Percentage
Mar 16, 2025
-
Difference Between Independent Assortment And Law Of Segregation
Mar 16, 2025
Related Post
Thank you for visiting our website which covers about How Many Lines Of Symmetry Circle . We hope the information provided has been useful to you. Feel free to contact us if you have any questions or need further assistance. See you next time and don't miss to bookmark.
