Square Root Of 50 Rational Or Irrational
Juapaving
Mar 18, 2025 · 5 min read
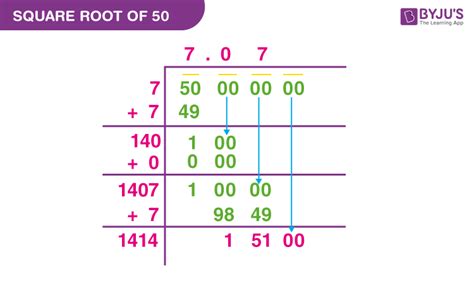
Table of Contents
Is the Square Root of 50 Rational or Irrational? A Deep Dive
The question of whether the square root of 50 is rational or irrational is a fundamental concept in mathematics. Understanding this requires a grasp of what rational and irrational numbers are and how to determine the nature of square roots. This article will explore this topic in detail, providing a comprehensive explanation accessible to a broad audience, from students grappling with the concept to those seeking a refresher on mathematical fundamentals. We'll delve into the definitions, provide clear examples, and explore the broader implications of this seemingly simple question.
Understanding Rational and Irrational Numbers
Before tackling the square root of 50, let's solidify our understanding of rational and irrational numbers.
Rational Numbers: These are numbers that can be expressed as a fraction p/q, where 'p' and 'q' are integers, and 'q' is not equal to zero. Essentially, any number that can be written as a simple fraction is rational. This includes whole numbers (like 5, which can be written as 5/1), integers (like -3, which is -3/1), and terminating or repeating decimals (like 0.75 which is 3/4, or 0.333... which is 1/3).
Irrational Numbers: These numbers cannot be expressed as a fraction of two integers. Their decimal representations are non-terminating and non-repeating; they go on forever without ever establishing a pattern. Famous examples include pi (π) and the square root of 2 (√2).
Determining the Nature of √50
Now, let's investigate whether √50 is rational or irrational. The key is to simplify the square root. We can do this by finding the prime factorization of 50:
50 = 2 x 5 x 5 = 2 x 5²
Therefore, √50 can be rewritten as:
√50 = √(2 x 5²) = √2 x √5² = 5√2
Notice that we've simplified √50 to 5 times the square root of 2. The crucial point here is that √2 is a well-known irrational number. Its decimal representation is approximately 1.41421356..., continuing infinitely without any repeating pattern.
Since √2 is irrational, and multiplying an irrational number (√2) by a rational number (5) still results in an irrational number, we can conclude that:
√50 is an irrational number.
Proof by Contradiction
We can further solidify this understanding by using a proof by contradiction. Let's assume, for the sake of argument, that √50 is rational. This means it can be expressed as a fraction p/q, where p and q are integers, q ≠ 0, and the fraction is in its simplest form (meaning p and q have no common factors other than 1).
If √50 = p/q, then squaring both sides gives:
50 = p²/q²
Rearranging, we get:
50q² = p²
This equation shows that p² is an even number (since it's a multiple of 50). If p² is even, then p must also be even (because the square of an odd number is always odd). This means we can express p as 2k, where k is another integer.
Substituting p = 2k into the equation above:
50q² = (2k)² = 4k²
Dividing both sides by 2:
25q² = 2k²
This shows that 25q² is an even number, which implies that q² is also even, and therefore q must be even.
We've now reached a contradiction. We initially assumed that p/q was in its simplest form, meaning p and q have no common factors. However, we've shown that both p and q are even, meaning they have a common factor of 2. This contradiction proves our initial assumption—that √50 is rational—must be false.
Therefore, √50 is irrational.
Further Exploration of Irrational Numbers and Square Roots
The irrationality of √50 highlights a broader characteristic of square roots. The square root of any integer that is not a perfect square (a number that can be obtained by squaring an integer) will be irrational. Perfect squares include 1, 4, 9, 16, 25, and so on. Since 50 is not a perfect square, its square root is irrational.
This concept extends to other roots as well. For example, the cube root of a number that is not a perfect cube will be irrational.
Practical Applications and Significance
While irrational numbers might seem abstract, they have significant real-world applications. They are fundamental in geometry (like calculating the diagonal of a square or the circumference of a circle), physics (various formulas involve pi and other irrational numbers), and many other fields. Understanding irrational numbers is crucial for comprehending advanced mathematical concepts and their applications.
Distinguishing Rational and Irrational Numbers: Practical Tips
Identifying whether a number is rational or irrational can sometimes be challenging. Here are some practical tips to help you differentiate between them:
- Check for a simple fraction: If the number can be expressed as a fraction of two integers (p/q, where q ≠ 0), it's rational.
- Examine the decimal representation: If the decimal representation terminates (ends) or repeats indefinitely in a pattern, it's rational. If the decimal representation is non-terminating and non-repeating, it's irrational.
- Consider the square root: The square root of any non-perfect square integer is irrational.
- Utilize prime factorization: Breaking down a number into its prime factors can help determine if it simplifies to a rational expression.
Conclusion: The Irrationality of √50 and Beyond
We've conclusively demonstrated that the square root of 50 is an irrational number. This understanding is built upon the definitions of rational and irrational numbers and the simplification of square roots through prime factorization. The proof by contradiction further reinforces the irrational nature of √50. This exploration goes beyond a simple answer; it provides a deeper understanding of number theory and the properties of rational and irrational numbers, highlighting their importance in various mathematical and scientific disciplines. Remember, grasping these fundamental concepts is essential for tackling more complex mathematical problems and applications in various fields. The exploration of irrational numbers opens up a world of fascinating mathematical concepts and their real-world significance.
Latest Posts
Latest Posts
-
Unit Of Pressure In Cgs System
Mar 19, 2025
-
Least Common Multiple 5 6 7
Mar 19, 2025
-
What Is A Half As A Percentage
Mar 19, 2025
-
What Are All The Factors For 33
Mar 19, 2025
-
Is Milk Of Magnesia A Base Or An Acid
Mar 19, 2025
Related Post
Thank you for visiting our website which covers about Square Root Of 50 Rational Or Irrational . We hope the information provided has been useful to you. Feel free to contact us if you have any questions or need further assistance. See you next time and don't miss to bookmark.
