Smallest Organ Of The Human Body
Juapaving
Mar 20, 2025 · 6 min read
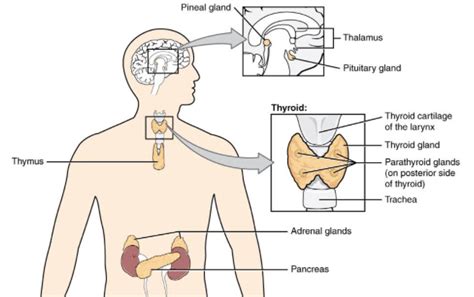
Table of Contents
The Smallest Human Organ: Unveiling the Enigma of the Pineal Gland
The human body, a marvel of biological engineering, comprises a complex network of organs, each playing a crucial role in maintaining overall health and well-being. While we often focus on the larger, more visible organs like the heart and brain, the intricate tapestry of life also includes remarkably tiny structures that exert profound influence. Among these miniature powerhouses lies the smallest organ in the human body: the pineal gland. This unassuming structure, about the size of a grain of rice, holds a fascinating position in both anatomy and esoteric lore, captivating scientists and enthusiasts alike.
Understanding the Pineal Gland: Location and Structure
Situated deep within the brain, nestled between the two hemispheres near the thalamus, the pineal gland is a small, endocrine gland. Its diminutive size, typically measuring around 5-8 millimeters in length and weighing less than 0.2 grams, belies its significant physiological roles. Despite its minute proportions, the pineal gland is a remarkably complex structure, exhibiting a unique architecture. It's composed primarily of specialized cells called pinealocytes, responsible for synthesizing and secreting the crucial hormone melatonin. Other cell types, including glial cells, also contribute to its function. The gland’s highly vascularized nature reflects its endocrine function, facilitating the efficient release of melatonin into the bloodstream.
The Pineal Gland's Unique Composition and Function
The pineal gland stands apart from other endocrine glands due to its unique composition and functions. Its structure is not uniform throughout, with distinct regions exhibiting varying cellular densities and activity levels. This structural complexity underscores the gland's intricate regulatory mechanisms. Furthermore, the pineal gland's primary function—the regulation of circadian rhythms—sets it apart. Its influence extends beyond the simple production of melatonin, impacting numerous physiological processes that govern our daily cycles.
Melatonin: The Hormone of Darkness
The pineal gland's most renowned product, melatonin, is a potent hormone with far-reaching effects on the human body. This indoleamine hormone is primarily synthesized from the amino acid tryptophan, undergoing a series of enzymatic transformations within the pinealocytes. The production and release of melatonin are meticulously regulated by light exposure. Light inhibits melatonin synthesis, while darkness stimulates its production, establishing a critical link between the pineal gland and the sleep-wake cycle.
The Crucial Role of Melatonin in Circadian Rhythms
Melatonin's primary function is the regulation of the circadian rhythm, the internal biological clock that dictates our daily cycles of sleep, wakefulness, hormone release, and other physiological processes. The pineal gland acts as a biological pacemaker, synchronizing our internal clock with the external environment. As darkness falls, melatonin levels rise, promoting sleepiness and preparing the body for rest. Conversely, as light increases, melatonin production decreases, initiating the wake-up process.
Beyond Sleep: Melatonin's Expanding Roles
The influence of melatonin extends far beyond simply regulating sleep. A growing body of research highlights its diverse roles in various physiological processes, including:
- Immune System Modulation: Melatonin exhibits potent antioxidant and immunomodulatory properties, protecting cells from damage and influencing immune responses.
- Antioxidant Protection: Melatonin acts as a powerful antioxidant, scavenging free radicals and reducing oxidative stress, protecting against cellular damage.
- Cardiovascular Health: Emerging evidence suggests that melatonin may play a beneficial role in cardiovascular health, potentially influencing blood pressure and cholesterol levels.
- Neuroprotection: Studies indicate melatonin may offer neuroprotective effects, shielding brain cells from damage and potentially slowing age-related cognitive decline.
- Regulation of Other Hormones: Melatonin may influence the production and secretion of other hormones, contributing to the intricate endocrine balance within the body.
The Pineal Gland: Beyond Science and into the Realm of Mysticism
While scientific understanding of the pineal gland continues to evolve, its unique anatomical location and functions have fueled significant interest beyond the purely scientific realm. Throughout history, various cultures have attributed mystical significance to the pineal gland, viewing it as a spiritual center or the "seat of the soul."
The Pineal Gland in History and Philosophy: A Spiritual Connotation
Ancient civilizations, from the Egyptians to the Greeks, recognized the pineal gland's importance, though their understanding was often embedded within spiritual or philosophical contexts. Some considered it the connection between the physical and spiritual realms, a conduit for higher consciousness or divine inspiration.
Modern Interpretations of the Pineal Gland's Mystical Significance
Modern interpretations of the pineal gland's mystical significance often draw upon its role in regulating circadian rhythms and its association with dream states and altered states of consciousness. Some believe the pineal gland facilitates access to hidden levels of awareness or psychic abilities. However, it is vital to acknowledge that these interpretations often lack rigorous scientific support and should be viewed within the appropriate context.
Potential Health Implications of Pineal Gland Dysfunction
While the pineal gland is relatively small, its dysfunction can have significant consequences. Several factors can disrupt the gland's function, leading to a variety of health problems.
Conditions Affecting Pineal Gland Function: Exploring the Possibilities
The pineal gland is susceptible to various conditions, including calcification, tumors, and inflammation. Calcification, a common phenomenon with age, can impair the gland’s function, potentially affecting melatonin production and circadian rhythms. Pineal tumors, while rare, can cause a range of neurological symptoms. Inflammation of the pineal gland is less common but can also interfere with its normal function.
Symptoms of Pineal Dysfunction: Recognizing the Warning Signs
The symptoms associated with pineal dysfunction can be varied and depend on the underlying cause. Disruptions to circadian rhythms may manifest as sleep disorders, fatigue, mood changes, and difficulties concentrating. Pineal tumors can produce more severe neurological symptoms, such as headaches, vision problems, and hormonal imbalances.
Protecting and Supporting Pineal Gland Health: Practical Strategies
Maintaining the health and optimal function of the pineal gland is vital for overall well-being. Several lifestyle strategies can contribute to pineal health:
Lifestyle Factors Impacting Pineal Health: Diet, Light Exposure, and Stress Management
A balanced diet rich in antioxidants, regular exposure to natural light, and stress management techniques can all contribute to supporting pineal health. Adequate sleep, regular exercise, and minimizing exposure to environmental toxins are also essential factors to consider.
Further Research and Understanding: The Ongoing Quest to Understand the Pineal Gland
Research into the pineal gland and its functions is ongoing, constantly revealing new facets of its influence on the human body. Further investigation into its role in various physiological processes, potential therapeutic applications, and the interaction between its physiological and spiritual connotations will deepen our understanding of this remarkable miniature organ.
Conclusion: The Smallest Organ, the Largest Impact
The pineal gland, despite its diminutive size, plays a pivotal role in the human body. Its significance extends far beyond the production of melatonin, encompassing numerous physiological processes and influencing our daily lives in profound ways. Understanding the complexities of this tiny gland, both from a scientific and a broader perspective, provides valuable insights into the intricate workings of the human body and the interconnectedness of mind, body, and spirit. As research continues to unravel the secrets of the pineal gland, we gain a deeper appreciation for the remarkable power residing within even the smallest of our organs. Further exploration into its functions, potential therapeutic uses, and the careful consideration of lifestyle factors that influence its health will undoubtedly contribute to a more comprehensive understanding of this fascinating and important endocrine structure.
Latest Posts
Latest Posts
-
Difference Between Photosystem 1 And 2
Mar 20, 2025
-
Strong Acid And Strong Base Titration
Mar 20, 2025
-
Lowest Common Multiple Of 25 And 30
Mar 20, 2025
-
What Is The Least Common Multiple Of 8 And 4
Mar 20, 2025
-
Difference Between Dihybrid And Monohybrid Cross
Mar 20, 2025
Related Post
Thank you for visiting our website which covers about Smallest Organ Of The Human Body . We hope the information provided has been useful to you. Feel free to contact us if you have any questions or need further assistance. See you next time and don't miss to bookmark.
