Six And Six Tenths In Decimal Form
Juapaving
Mar 24, 2025 · 5 min read
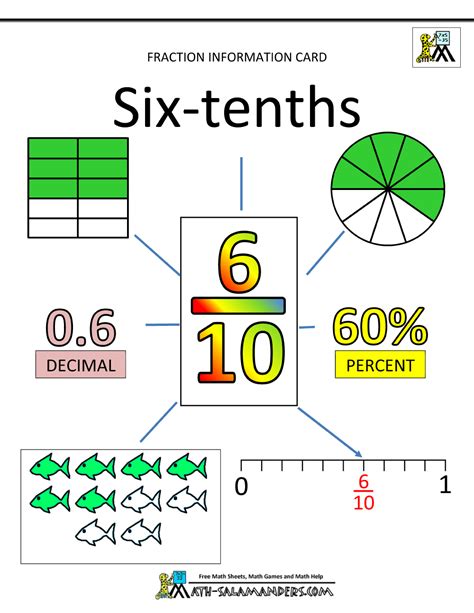
Table of Contents
Six and Six Tenths in Decimal Form: A Comprehensive Guide
Understanding decimal numbers is fundamental to mathematics and numerous applications in everyday life, from finance and engineering to scientific research and data analysis. This comprehensive guide delves deep into the representation of "six and six tenths" in decimal form, exploring the underlying concepts, practical examples, and related mathematical operations. We will also touch upon the importance of understanding decimals in various contexts.
What are Decimal Numbers?
Decimal numbers are a way of representing numbers that are not whole numbers. They use a base-10 system, meaning they are based on powers of 10. The decimal point separates the whole number part from the fractional part. To the left of the decimal point are the ones, tens, hundreds, and so on. To the right of the decimal point, we have tenths, hundredths, thousandths, and so on.
Think of it like this: the decimal point acts as a divider between whole units and parts of a unit. Each position to the right of the decimal point represents a progressively smaller fraction of one whole.
Representing Six and Six Tenths
The phrase "six and six tenths" clearly indicates a number consisting of a whole number part (six) and a fractional part (six tenths). To represent this in decimal form, we follow these steps:
-
Whole Number: The whole number part is simply "6".
-
Fractional Part: "Six tenths" can be written as the fraction 6/10.
-
Decimal Conversion: To convert the fraction 6/10 to a decimal, we divide the numerator (6) by the denominator (10). This gives us 0.6.
-
Combining Parts: Combining the whole number part and the decimal part, we get the final decimal representation: 6.6.
Therefore, six and six tenths in decimal form is 6.6.
Deeper Dive into Decimal Place Value
Understanding decimal place value is crucial for accurate interpretation and manipulation of decimal numbers. Let's examine the place value of each digit in 6.6:
- 6 (ones place): This represents six whole units.
- . (decimal point): This separates the whole number from the fractional part.
- 6 (tenths place): This represents six-tenths of a unit (6/10).
Equivalent Fractions and Decimals
It's important to note that 6.6 can be represented by equivalent fractions. For example:
- 66/10 (by multiplying the numerator and denominator of 6/10 by 11)
- 33/5 (by simplifying 66/10 by dividing by 2)
All these fractions represent the same value as the decimal 6.6. Understanding equivalent fractions is essential for simplifying calculations and comparing decimal numbers.
Practical Applications of 6.6
The decimal number 6.6 finds applications in various real-world scenarios:
- Measurements: Imagine measuring the length of a piece of wood. It might measure 6.6 meters.
- Finance: The price of an item could be $6.60.
- Science: Scientific experiments frequently involve measurements that result in decimal numbers like 6.6 liters or 6.6 grams.
- Data Analysis: Data sets often include decimal numbers representing averages, proportions, or other statistical measures. For example, a test score average might be 6.6 out of 10.
Operations with Decimals: Adding, Subtracting, Multiplying, and Dividing
Working with decimal numbers often involves performing basic arithmetic operations. Let's look at how these operations apply to 6.6:
Addition
Adding decimals involves aligning the decimal points and adding digits column by column. For instance, adding 6.6 and 3.4:
6.6
+ 3.4
-----
10.0
Subtraction
Subtraction of decimals follows a similar process to addition. Let's subtract 2.3 from 6.6:
6.6
- 2.3
-----
4.3
Multiplication
Multiplying decimals involves multiplying the numbers as if they were whole numbers and then placing the decimal point in the correct position. For example, multiplying 6.6 by 2:
6.6
x 2
-----
13.2
Division
Dividing decimals can be slightly more complex. A common method is to convert the divisor to a whole number by multiplying both the divisor and dividend by a power of 10. Let's divide 6.6 by 2:
6.6 / 2 = 3.3
Rounding Decimals
Sometimes, you need to round a decimal number to a certain number of decimal places. Rounding 6.6 to the nearest whole number would result in 7. The rule for rounding is to look at the digit to the right of the place you're rounding to. If it's 5 or greater, round up; otherwise, round down.
Converting Fractions to Decimals and Vice Versa
The ability to convert between fractions and decimals is crucial for solving various mathematical problems.
Fraction to Decimal: Divide the numerator by the denominator. For example, 3/4 = 0.75
Decimal to Fraction: Write the decimal as a fraction with a power of 10 as the denominator (e.g., 0.75 = 75/100). Then, simplify the fraction to its lowest terms (75/100 simplifies to 3/4).
The Significance of Understanding Decimals
A strong grasp of decimals is essential for success in numerous fields:
- Accounting and Finance: Managing money, calculating interest, and understanding financial statements all require proficiency in decimals.
- Engineering and Technology: Precision measurements and calculations in engineering rely heavily on decimal numbers.
- Science: Scientific data often involves decimal values, requiring accurate analysis and interpretation.
- Everyday Life: From shopping to cooking to understanding weather reports, decimals are used constantly.
Conclusion
Understanding "six and six tenths" in decimal form (6.6) is a stepping stone to mastering decimal arithmetic and its wide-ranging applications. This comprehensive guide has covered the fundamental concepts, practical examples, and relevant mathematical operations. By solidifying your understanding of decimals, you'll be well-equipped to tackle more complex mathematical challenges and excel in various fields that require numerical proficiency. Remember, practice is key to mastering this fundamental concept. Work through examples, practice conversions, and apply your knowledge in real-world situations to build a strong and intuitive understanding of decimals.
Latest Posts
Latest Posts
-
What Is The Chemical Formula For Protein
Mar 29, 2025
-
Louis Wants To Carpet The Rectangular Floor
Mar 29, 2025
-
Place Value To Find The Product
Mar 29, 2025
-
How To Write 800 In Words
Mar 29, 2025
-
Five Letter Words Ending In Ing
Mar 29, 2025
Related Post
Thank you for visiting our website which covers about Six And Six Tenths In Decimal Form . We hope the information provided has been useful to you. Feel free to contact us if you have any questions or need further assistance. See you next time and don't miss to bookmark.
