Rf Value In Thin Layer Chromatography
Juapaving
Mar 14, 2025 · 6 min read
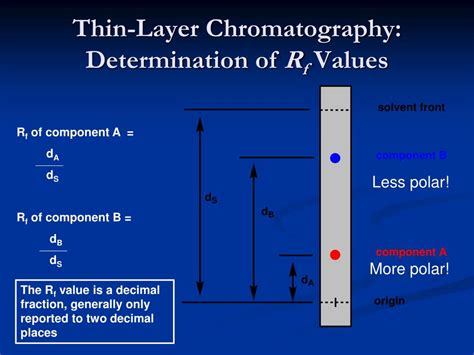
Table of Contents
Understanding Rf Value in Thin Layer Chromatography: A Comprehensive Guide
Thin layer chromatography (TLC) is a widely used, simple, and inexpensive analytical technique employed to separate components of a mixture. It's a crucial tool in various fields, including organic chemistry, biochemistry, and pharmaceutical analysis. A critical parameter in interpreting TLC results is the retention factor (Rf) value. This article provides a comprehensive exploration of Rf values in TLC, covering their calculation, significance, limitations, and applications.
What is Rf Value in TLC?
The Rf value, or retention factor, is a dimensionless number that represents the ratio of the distance traveled by a compound to the distance traveled by the solvent front in thin layer chromatography. It's a crucial indicator of a compound's affinity for the stationary and mobile phases. A higher Rf value indicates that the compound has a greater affinity for the mobile phase (solvent) and thus travels further up the TLC plate. Conversely, a lower Rf value signifies a stronger affinity for the stationary phase (the TLC plate material), resulting in less movement.
Formula for Calculating Rf Value
The Rf value is calculated using a straightforward formula:
Rf = (Distance traveled by the compound) / (Distance traveled by the solvent front)
It's crucial to measure both distances from the same origin, typically the point where the sample was applied. The distances should be measured to the center of the compound spot and the solvent front, respectively.
Factors Affecting Rf Values
Several factors can influence the Rf value of a compound in TLC. Understanding these factors is vital for obtaining reliable and reproducible results.
1. The Nature of the Stationary Phase
The stationary phase's material significantly impacts the Rf value. Silica gel is the most common stationary phase, but others, such as alumina, are also used. The polarity of the stationary phase influences its interaction with the compound, affecting how far the compound travels. Polar compounds generally have lower Rf values on a polar stationary phase like silica gel because they interact strongly with the stationary phase.
2. The Nature of the Mobile Phase
The mobile phase, or solvent system, plays a crucial role in determining the Rf value. The solvent's polarity, composition, and the presence of additives directly affect the compound's solubility and its movement up the TLC plate. A more polar mobile phase will generally increase the Rf values of polar compounds as it enhances their solubility and reduces their interaction with the stationary phase. Careful selection of the solvent system is critical for optimal separation.
3. Temperature
Temperature affects the solubility of the compound in the mobile phase. Changes in temperature can alter the Rf value; maintaining a consistent temperature is crucial for reproducible results.
4. The Amount of Sample Applied
Applying an excessive amount of sample can lead to streaking or distorted spots, hindering accurate Rf value determination. Optimizing the sample amount is crucial for obtaining sharp, well-defined spots.
5. Development Conditions
The atmosphere within the developing chamber influences the Rf value. Saturated chambers minimize solvent evaporation, ensuring consistent solvent strength throughout the development process. Proper chamber saturation enhances reproducibility.
6. Adsorbent Layer Thickness
A thicker adsorbent layer provides more interaction sites for the compound, resulting in lower Rf values. Using TLC plates with consistent layer thickness is recommended.
Significance of Rf Values
Rf values hold significant importance in TLC analysis for several reasons:
- Compound Identification: While not definitive on its own, the Rf value provides a crucial piece of information for identifying a compound. Comparing the Rf value of an unknown compound to the Rf values of known standards under identical conditions can aid in identification.
- Purity Assessment: A single spot on the TLC plate with a well-defined Rf value suggests a pure compound. Multiple spots indicate the presence of impurities.
- Reaction Monitoring: TLC is invaluable in monitoring chemical reactions. Tracking the Rf values of reactants and products over time allows for real-time assessment of reaction progress and completion.
- Optimization of Separation: Rf values assist in optimizing the separation of compounds by guiding the selection of appropriate solvent systems and stationary phases. Aiming for Rf values between 0.2 and 0.8 generally yields better separations.
- Quantitative Analysis: Although not as precise as other techniques, TLC can provide semi-quantitative information about the relative amounts of different components in a mixture based on spot intensity.
Limitations of Rf Values
While Rf values are valuable, they are not without limitations:
- Not an absolute identifier: Rf values depend heavily on experimental conditions. The same compound may exhibit different Rf values under different conditions (e.g., solvent system, stationary phase, temperature). Therefore, Rf values alone cannot conclusively identify a compound.
- Sensitivity limitations: TLC has limited sensitivity, meaning it may not be able to detect trace amounts of certain compounds.
- Subjective measurements: Rf value determination involves visual assessment of spot positions, introducing a degree of subjectivity.
Applications of Rf Value in Various Fields
Rf values find widespread applications in numerous fields:
1. Organic Chemistry
In organic chemistry, TLC is routinely used to monitor reactions, assess purity of synthesized compounds, and optimize separation procedures.
2. Biochemistry
TLC plays a crucial role in analyzing biological molecules like amino acids, sugars, and lipids. Rf values aid in separating and identifying these biomolecules.
3. Pharmaceutical Analysis
In the pharmaceutical industry, TLC is employed to analyze drug formulations, detect impurities, and ensure drug quality control.
4. Environmental Analysis
TLC can be used to analyze environmental samples for the presence of pollutants and contaminants. Rf values facilitate the identification of these substances.
5. Forensic Science
Forensic scientists utilize TLC for analyzing various samples, such as drugs, explosives, and inks, where Rf values contribute to evidence analysis.
Tips for Obtaining Accurate and Reproducible Rf Values
To obtain reliable and consistent Rf values, consider the following best practices:
- Use consistent TLC plates: Ensure uniform layer thickness and consistent stationary phase quality.
- Maintain a controlled environment: Maintain consistent temperature and humidity throughout the experiment.
- Use a saturated developing chamber: Saturated chambers reduce solvent evaporation and ensure uniform solvent strength.
- Apply consistent sample volume: Use a micropipette for precise sample application to avoid streaking.
- Visualize the spots carefully: Choose an appropriate visualization technique (e.g., UV light, iodine staining) and carefully mark the spot boundaries.
- Measure accurately: Use a ruler to accurately measure the distances traveled by the compound and solvent front.
- Record experimental conditions: Meticulously record all experimental details, including solvent system composition, temperature, and visualization method. This ensures reproducibility.
Conclusion
The Rf value is a crucial parameter in thin layer chromatography, providing valuable information about the behavior of compounds on the TLC plate. While it has limitations, understanding its calculation, the factors influencing it, and its applications enables researchers and analysts to effectively utilize TLC for various purposes, from monitoring reactions to identifying components in complex mixtures. By adhering to best practices and carefully considering the influencing factors, accurate and reliable Rf values can be obtained, supporting the interpretation of TLC results and enhancing the reliability of experimental findings. Remember that Rf values are best used in conjunction with other analytical techniques for definitive compound identification.
Latest Posts
Latest Posts
-
Shapes With 3 Lines Of Symmetry
May 09, 2025
-
Is 1 Cc The Same As 1 Ml
May 09, 2025
-
A Fully Loaded Slow Moving Freight Elevator
May 09, 2025
-
Is Potato A Root Or Stem Vegetable
May 09, 2025
-
Which Element Has The Least Metallic Character
May 09, 2025
Related Post
Thank you for visiting our website which covers about Rf Value In Thin Layer Chromatography . We hope the information provided has been useful to you. Feel free to contact us if you have any questions or need further assistance. See you next time and don't miss to bookmark.