Perimeter And Area Of A Triangle
Juapaving
Mar 17, 2025 · 5 min read
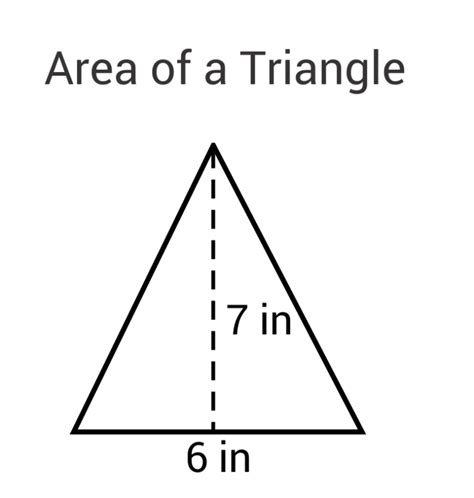
Table of Contents
- Perimeter And Area Of A Triangle
- Table of Contents
- Perimeter and Area of a Triangle: A Comprehensive Guide
- Understanding the Basics: Perimeter of a Triangle
- Delving Deeper: Area of a Triangle
- 1. Using Base and Height: The Standard Formula
- 2. Heron's Formula: Using Only Side Lengths
- 3. Using Trigonometry: Area with Two Sides and Included Angle
- Advanced Concepts and Problem Solving
- 1. Triangles in Coordinate Geometry
- 2. Equilateral Triangles: A Special Case
- 3. Right-Angled Triangles: Pythagorean Theorem and Area
- 4. Solving Complex Problems: Combining Methods
- Real-World Applications: Beyond the Textbook
- Conclusion
- Latest Posts
- Latest Posts
- Related Post
Perimeter and Area of a Triangle: A Comprehensive Guide
The triangle, a fundamental geometric shape, holds a significant place in mathematics and its applications. Understanding its properties, particularly its perimeter and area, is crucial for various fields, from architecture and engineering to cartography and computer graphics. This comprehensive guide will delve deep into the calculation of a triangle's perimeter and area, exploring different methods, formulas, and real-world applications. We'll also touch upon advanced concepts and problem-solving techniques.
Understanding the Basics: Perimeter of a Triangle
The perimeter of any polygon, including a triangle, is simply the total distance around its exterior. For a triangle, this means summing the lengths of all three sides.
Formula:
Perimeter (P) = a + b + c
Where 'a', 'b', and 'c' represent the lengths of the three sides of the triangle.
Example:
Consider a triangle with sides measuring 5 cm, 7 cm, and 9 cm. Its perimeter would be:
P = 5 cm + 7 cm + 9 cm = 21 cm
Units: Remember to always maintain consistency in units. If the sides are measured in centimeters, the perimeter will also be in centimeters. Similarly, for meters, feet, inches, etc.
Applications:
The concept of perimeter is vital in various real-world applications:
- Construction: Calculating the perimeter is essential for determining the amount of fencing, wall materials, or other border materials needed for a triangular plot of land or structure.
- Framing: In carpentry and picture framing, knowing the perimeter allows for accurate cutting of materials to fit a triangular frame.
- Surveying: Land surveyors frequently use perimeter calculations to measure and delineate property boundaries that have triangular sections.
Delving Deeper: Area of a Triangle
The area of a triangle represents the two-dimensional space enclosed within its three sides. Unlike the perimeter, calculating the area requires more than just the lengths of the sides. Several methods exist, depending on the available information.
1. Using Base and Height: The Standard Formula
The most common and straightforward method to find the area of a triangle involves its base and height.
Formula:
Area (A) = (1/2) * base * height
Where:
- Base: Any one of the triangle's sides can be chosen as the base.
- Height: The perpendicular distance from the base to the opposite vertex (corner).
Example:
If a triangle has a base of 10 cm and a height of 6 cm, its area is:
A = (1/2) * 10 cm * 6 cm = 30 cm²
Important Note: The height must be perpendicular to the chosen base. If the height isn't explicitly given, you might need to use trigonometry (discussed later) to calculate it.
2. Heron's Formula: Using Only Side Lengths
Heron's formula provides an elegant way to calculate the area of a triangle when only the lengths of its three sides are known.
Formula:
Area (A) = √[s(s-a)(s-b)(s-c)]
Where:
- a, b, and c are the lengths of the three sides.
- s is the semi-perimeter: s = (a + b + c) / 2
Example:
Let's consider a triangle with sides a = 5 cm, b = 6 cm, and c = 7 cm.
- Calculate the semi-perimeter: s = (5 + 6 + 7) / 2 = 9 cm
- Apply Heron's formula: A = √[9(9-5)(9-6)(9-7)] = √(9 * 4 * 3 * 2) = √216 ≈ 14.7 cm²
3. Using Trigonometry: Area with Two Sides and Included Angle
When you know two sides and the angle between them (the included angle), trigonometry provides a convenient method.
Formula:
Area (A) = (1/2) * a * b * sin(C)
Where:
- a and b are the lengths of two sides.
- C is the angle between sides a and b.
Example:
Suppose a triangle has sides a = 8 cm and b = 10 cm, with an included angle C = 30°.
A = (1/2) * 8 cm * 10 cm * sin(30°) = 40 cm² * 0.5 = 20 cm²
Advanced Concepts and Problem Solving
While the above methods cover the basics, several advanced concepts and problem-solving techniques can further enhance your understanding:
1. Triangles in Coordinate Geometry
When triangles are defined by their vertices' coordinates in a Cartesian plane, the area can be calculated using the determinant method.
Formula:
A = (1/2) |(x₁ (y₂ - y₃) + x₂ (y₃ - y₁) + x₃ (y₁ - y₂))|
where (x₁, y₁), (x₂, y₂), and (x₃, y₃) are the coordinates of the vertices. The absolute value ensures a positive area.
2. Equilateral Triangles: A Special Case
Equilateral triangles, with all three sides equal, have simplified formulas for both perimeter and area.
- Perimeter: P = 3a (where 'a' is the length of a side)
- Area: A = (√3/4) * a²
3. Right-Angled Triangles: Pythagorean Theorem and Area
Right-angled triangles, with one angle measuring 90°, allow for the use of the Pythagorean theorem (a² + b² = c²) to find the lengths of sides if two are known. The area is simply (1/2) * base * height, where the base and height are the two shorter sides.
4. Solving Complex Problems: Combining Methods
Many problems require combining multiple methods to solve for unknown quantities before calculating the perimeter or area. This might involve using trigonometry to find a missing side length, then applying Heron's formula to find the area.
Real-World Applications: Beyond the Textbook
The concepts of perimeter and area extend far beyond theoretical exercises:
- Architecture and Engineering: Calculating the area of triangular roof sections, designing triangular support structures, and determining the amount of material needed for triangular windows are all essential applications.
- Land Surveying and Geographic Information Systems (GIS): Accurate area calculations are critical for land ownership disputes, property valuations, and environmental impact assessments. Triangular subdivisions are often used for precise mapping.
- Computer Graphics and Game Development: Triangles are the fundamental building blocks of many 3D models and simulations. The ability to calculate their area and perimeter is crucial for texture mapping, collision detection, and realistic rendering.
- Navigation: Triangulation, a technique utilizing triangles, is used in GPS systems and other navigational technologies to determine locations.
Conclusion
Understanding the perimeter and area of a triangle is a cornerstone of geometry with far-reaching implications in various fields. Mastering the different formulas and problem-solving techniques discussed here provides a solid foundation for tackling more complex geometric challenges and applying these concepts to real-world situations. From the simple calculations of fencing needs to the intricate designs of complex structures and simulations, the triangle’s properties remain indispensable tools for problem-solving and innovation. Continue exploring and practicing these concepts to strengthen your understanding and expand your mathematical capabilities.
Latest Posts
Latest Posts
-
Does Liquid Have A Definite Volume
Mar 19, 2025
-
How Many Feet Is 40 M
Mar 19, 2025
-
How Many Pounds Is 63 Kilos
Mar 19, 2025
-
Lowest Common Multiple Of 3 And 9
Mar 19, 2025
-
1 X 1 X 1 X 1 X
Mar 19, 2025
Related Post
Thank you for visiting our website which covers about Perimeter And Area Of A Triangle . We hope the information provided has been useful to you. Feel free to contact us if you have any questions or need further assistance. See you next time and don't miss to bookmark.
