Organelles That Are The Sites Of Protein Synthesis
Juapaving
Mar 31, 2025 · 6 min read
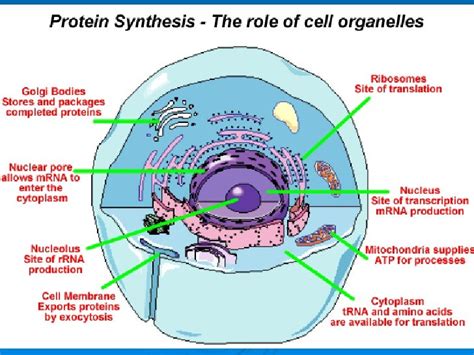
Table of Contents
Organelles That Are the Sites of Protein Synthesis: A Deep Dive
Protein synthesis, the intricate process of creating proteins from genetic instructions, is fundamental to all life. This complex biological process relies heavily on specialized cellular compartments known as organelles. While the nucleus holds the genetic blueprint, several organelles play crucial roles in the various stages of protein synthesis, from transcription to translation and post-translational modification. This article will delve into the key organelles involved, exploring their structure, function, and the intricate interplay that allows for the precise creation and deployment of proteins within the cell.
The Nucleus: The Control Center of Protein Synthesis
The nucleus, the cell's command center, houses the cell's genetic material – DNA. DNA contains the genes, which are sequences of nucleotides that encode the instructions for building proteins. Protein synthesis begins in the nucleus with transcription, the process of creating a messenger RNA (mRNA) molecule that is a complementary copy of a gene. This mRNA molecule carries the genetic code from the nucleus to the ribosomes, the sites of protein synthesis.
Transcriptional Regulation: Fine-Tuning Protein Production
The process of transcription is not simply a passive copying of genetic information. It is highly regulated, ensuring that proteins are synthesized at the appropriate time and in the appropriate amounts. This regulation is achieved through a complex interplay of transcription factors, which are proteins that bind to specific DNA sequences and either enhance or repress transcription.
RNA Processing: Preparing the mRNA for Translation
The newly synthesized mRNA molecule undergoes several processing steps before it can be translated into a protein. These include:
- Capping: Addition of a protective cap to the 5' end of the mRNA molecule.
- Splicing: Removal of non-coding sequences called introns and joining of the coding sequences, or exons.
- Polyadenylation: Addition of a poly(A) tail to the 3' end, which enhances stability and helps with translation.
These processing steps are crucial for ensuring the accuracy and efficiency of protein synthesis.
Ribosomes: The Protein Synthesis Factories
Ribosomes, the cellular machinery responsible for protein synthesis, are complex ribonucleoprotein complexes. They consist of two subunits: a large subunit and a small subunit. These subunits are composed of ribosomal RNA (rRNA) and proteins. Ribosomes are found in two main locations within the cell:
Free Ribosomes: Synthesizing Cytosolic Proteins
Free ribosomes are found floating freely in the cytoplasm. They synthesize proteins that will function within the cytosol, the fluid-filled space of the cell. These proteins include enzymes involved in metabolic processes, structural proteins, and many more.
Bound Ribosomes: Synthesizing Membrane-Bound and Secreted Proteins
Bound ribosomes are attached to the endoplasmic reticulum (ER), a network of membranes extending throughout the cytoplasm. These ribosomes synthesize proteins destined for:
- Secretion: Proteins that are secreted from the cell, such as hormones and enzymes.
- Membrane incorporation: Proteins that become part of the cell membrane, including membrane receptors and transporters.
- Organelle targeting: Proteins that are targeted to other organelles, such as lysosomes and mitochondria.
The signal recognition particle (SRP) plays a critical role in targeting proteins synthesized by bound ribosomes. The SRP recognizes a signal sequence on the growing polypeptide chain and directs the ribosome to the ER membrane.
Endoplasmic Reticulum (ER): The Protein Folding and Modification Center
The endoplasmic reticulum (ER) is a vast network of interconnected membranes that extends throughout the cytoplasm. It plays a critical role in protein synthesis, folding, and modification. The ER has two distinct regions:
Rough Endoplasmic Reticulum (RER): Protein Synthesis and Initial Modification
The rough endoplasmic reticulum (RER), studded with ribosomes, is the primary site of protein synthesis for proteins destined for secretion, membrane incorporation, or targeting to other organelles. As the polypeptide chain emerges from the ribosome, it enters the lumen of the RER, where it begins to fold into its three-dimensional structure. This process is aided by chaperone proteins, which prevent aggregation and ensure correct folding. The RER also carries out initial glycosylation, the addition of sugar molecules to proteins.
Smooth Endoplasmic Reticulum (SER): Lipid and Steroid Synthesis
The smooth endoplasmic reticulum (SER) lacks ribosomes and is primarily involved in lipid and steroid synthesis. While not directly involved in protein synthesis, the SER plays a crucial indirect role by providing lipids for the construction of cellular membranes, which are essential for the function of organelles involved in protein synthesis.
Golgi Apparatus: The Protein Processing and Sorting Station
The Golgi apparatus, or Golgi complex, is a stack of flattened membrane-bound sacs called cisternae. It receives proteins from the ER and further processes, modifies, and sorts them for delivery to their final destinations.
Glycosylation and Other Modifications: Fine-Tuning Protein Function
The Golgi apparatus continues and modifies glycosylation initiated in the ER. It also adds other types of modifications, such as phosphorylation and sulfation, that are crucial for protein function.
Protein Sorting and Packaging: Directing Proteins to Their Destinations
The Golgi apparatus sorts proteins based on their destination, packaging them into vesicles for transport to various locations within the cell, including the plasma membrane, lysosomes, and other organelles. These vesicles bud off from the Golgi and are transported along the cytoskeleton to their final destinations.
Lysosomes: The Protein Degradation and Recycling Center
Lysosomes are membrane-bound organelles containing hydrolytic enzymes. They are involved in the degradation of proteins and other cellular components. Proteins that are misfolded, damaged, or no longer needed are targeted to lysosomes for degradation. The resulting amino acids can then be recycled for the synthesis of new proteins.
Mitochondria: Powering Protein Synthesis
While not directly involved in the synthesis of proteins, the mitochondria play a crucial role by providing the energy (ATP) needed for the process. Protein synthesis is an energy-intensive process, requiring a significant amount of ATP. Mitochondria generate ATP through cellular respiration, providing the necessary fuel for all aspects of protein synthesis.
Peroxisomes: Supporting Protein Synthesis through Lipid Metabolism
Peroxisomes are organelles involved in various metabolic processes, including lipid metabolism. They play an indirect role in protein synthesis by contributing to the production of lipids needed for cellular membranes and the function of other organelles involved in the process. They also help detoxify harmful substances that could interfere with protein synthesis.
Conclusion: A Coordinated Effort
Protein synthesis is a remarkably intricate process requiring the coordinated action of numerous organelles. From the nucleus, where the genetic code resides, to the ribosomes, where proteins are assembled, and the ER, Golgi, and lysosomes, where proteins are modified, sorted, and degraded, each organelle plays a vital role in ensuring the accurate and efficient production of proteins, the workhorses of the cell. Understanding the intricate interplay between these organelles is crucial for comprehending the fundamental processes of life and for developing effective therapies for various diseases caused by defects in protein synthesis. Further research into the mechanisms and regulation of protein synthesis holds significant promise for advancements in medicine and biotechnology.
Latest Posts
Latest Posts
-
What Is The Refractive Index Of A Vacuum
Apr 01, 2025
-
Predict The Product For The Following Reaction
Apr 01, 2025
-
What Is The Common Name Of Sodium Bicarbonate
Apr 01, 2025
-
Be Verb Forms V1 V2 V3 V4 V5
Apr 01, 2025
-
What Is The Multiple Of 23
Apr 01, 2025
Related Post
Thank you for visiting our website which covers about Organelles That Are The Sites Of Protein Synthesis . We hope the information provided has been useful to you. Feel free to contact us if you have any questions or need further assistance. See you next time and don't miss to bookmark.
