Number Of Neutrons In Carbon 14
Juapaving
May 12, 2025 · 6 min read
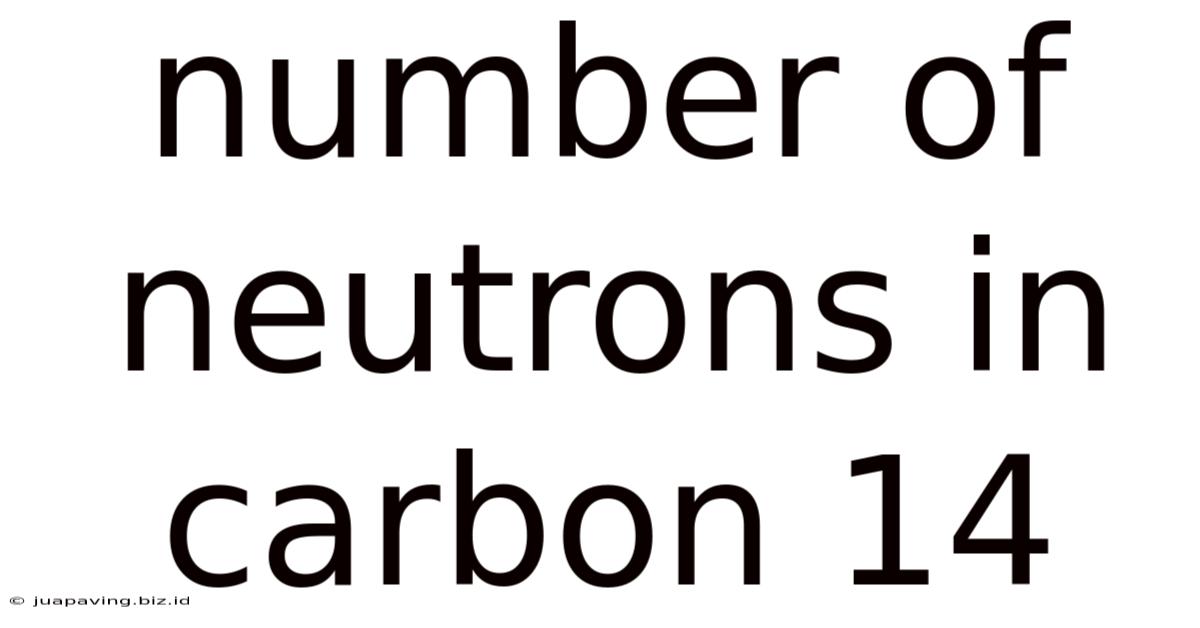
Table of Contents
Delving Deep into Carbon-14: Understanding its Neutrons and Significance
Carbon-14, a fascinating isotope of carbon, plays a pivotal role in various scientific fields, most notably in radiocarbon dating. Understanding its unique nuclear structure, particularly the number of neutrons it possesses, is crucial to grasping its properties and applications. This article will comprehensively explore Carbon-14, focusing on its neutron count, its formation, decay process, and its widespread applications in archaeology, geology, and environmental science.
The Atomic Structure of Carbon-14: Unveiling the Neutrons
All atoms are composed of protons, neutrons, and electrons. The number of protons defines the element; in the case of carbon, it always has six protons. However, the number of neutrons can vary, leading to different isotopes of the same element. These isotopes share the same chemical properties but differ in their atomic mass and nuclear stability.
Carbon-14, specifically, is a radioactive isotope of carbon. This means its nucleus is unstable and undergoes radioactive decay over time. The standard notation for Carbon-14 is ¹⁴C, where the superscript 14 represents its mass number (protons + neutrons).
Since carbon always has six protons, the number of neutrons in Carbon-14 can be easily calculated:
Mass number (A) = Number of protons (Z) + Number of neutrons (N)
Therefore, Number of neutrons (N) = Mass number (A) - Number of protons (Z) = 14 - 6 = 8
Consequently, Carbon-14 has eight neutrons. This extra two neutrons compared to the stable Carbon-12 (which has six protons and six neutrons) are responsible for its radioactivity.
The Formation of Carbon-14: A Cosmic Process
Unlike other isotopes of carbon, Carbon-14 is not naturally abundant on Earth. It is primarily produced in the upper atmosphere through a fascinating interaction between cosmic rays and nitrogen-14 (¹⁴N).
Cosmic rays, high-energy particles originating from outer space, constantly bombard Earth's atmosphere. When these particles collide with nitrogen-14 atoms, a nuclear reaction occurs. A neutron from the cosmic ray interacts with the nitrogen-14 nucleus, knocking out a proton. This process transforms the nitrogen-14 atom into a carbon-14 atom:
¹⁴N + n → ¹⁴C + p
This reaction continuously produces a small amount of Carbon-14 in the atmosphere. This newly formed Carbon-14 then reacts with oxygen to form carbon dioxide (¹⁴CO₂), which is then incorporated into the biosphere through photosynthesis.
The Decay of Carbon-14: Beta Decay and Half-Life
Carbon-14's instability is due to its extra neutrons. It undergoes a process called beta decay, where a neutron in the nucleus transforms into a proton, emitting a beta particle (an electron) and an antineutrino:
¹⁴C → ¹⁴N + β⁻ + ν̅ₑ
This decay process converts Carbon-14 into nitrogen-14, a stable isotope. The beta particle emitted carries energy, and this energy emission is the basis for detecting Carbon-14.
The rate of decay for Carbon-14 is characterized by its half-life, which is approximately 5,730 years. This means that after 5,730 years, half of a given sample of Carbon-14 will have decayed into nitrogen-14. After another 5,730 years, half of the remaining Carbon-14 will decay, and so on. This predictable decay rate is fundamental to radiocarbon dating.
Understanding Half-Life in Detail
The concept of half-life is crucial for understanding the applications of Carbon-14. It allows scientists to estimate the age of organic materials. As an organism dies, it stops incorporating Carbon-14 from the atmosphere. The Carbon-14 already present in its tissues then begins to decay at a known rate. By measuring the remaining amount of Carbon-14 in a sample and comparing it to the initial amount (assumed to be the same as the atmospheric concentration at the time of death), scientists can determine how long ago the organism died. However, this process has limitations, as explained further below.
Applications of Carbon-14: Unlocking the Past
The predictable decay of Carbon-14 makes it an invaluable tool in various scientific disciplines:
1. Radiocarbon Dating: Peering into History
This is perhaps the most well-known application of Carbon-14. By analyzing the ratio of Carbon-14 to Carbon-12 in organic materials like wood, bones, and textiles, researchers can estimate the age of these artifacts. This technique has revolutionized archaeology, paleontology, and geology, allowing scientists to accurately date historical events and artifacts spanning thousands of years. However, it's important to acknowledge limitations, such as the assumption of a constant atmospheric Carbon-14 concentration throughout history, which isn't entirely accurate.
2. Studying Atmospheric Processes: Tracking Carbon Cycles
Scientists use Carbon-14 measurements to study the movement and distribution of carbon in the atmosphere and oceans. By tracking the levels of Carbon-14 in different environmental reservoirs, researchers can gain insights into carbon cycling processes, which are crucial for understanding climate change. Analyzing the variations in Carbon-14 concentrations helps track pollution and other changes in the global carbon cycle.
3. Tracing Geological Processes: Dating Sediments and Rocks
Carbon-14 dating isn't limited to organic materials. It can also be applied to date certain geological formations, particularly younger sediments and rocks that contain organic carbon. This approach helps geologists reconstruct the timing of past geological events and understand the evolution of landscapes over time. However, its applicability here is more limited than in dating organic materials due to the often smaller amounts of Carbon-14 available in these geological samples.
4. Medical Applications: Tracer Studies
Carbon-14's radioactive properties also find applications in medical research. It's used as a tracer in various biochemical and physiological studies. By incorporating Carbon-14 into specific molecules, researchers can track their movement and metabolism within the body, providing valuable insights into biological processes. However, ethical considerations and safety protocols are paramount in such medical applications.
Limitations of Carbon-14 Dating: Considerations and Calibration
While immensely useful, Carbon-14 dating has some limitations:
-
Limited Dating Range: The half-life of Carbon-14 restricts its use to dating materials younger than approximately 50,000 years. Beyond this timeframe, the amount of remaining Carbon-14 is too low to be reliably measured.
-
Atmospheric Carbon-14 Variations: The concentration of Carbon-14 in the atmosphere hasn't been constant throughout history. Variations caused by solar activity, geomagnetic field changes, and human activities can affect the accuracy of dating. Calibration curves are used to account for these fluctuations and improve dating accuracy.
-
Contamination: Samples can be contaminated with younger or older carbon, affecting the results. Careful sample preparation and handling are essential to minimize contamination.
-
Reservoir Effects: Some organisms may have absorbed Carbon-14 from sources with different concentrations than the atmosphere. This “reservoir effect” can lead to inaccurate dating. This is especially true for marine organisms that may have absorbed Carbon-14 that had already undergone some decay.
Conclusion: The Enduring Importance of Carbon-14
Carbon-14, with its eight neutrons and unique radioactive properties, remains a powerful tool for scientific investigation. Understanding its formation, decay, and applications is crucial for comprehending its significant contributions to various fields, from archaeology and geology to environmental science and medicine. While limitations exist, advancements in calibration techniques and analytical methods continue to enhance the accuracy and expand the applications of Carbon-14 dating and related research. Its importance in unraveling the mysteries of the past and understanding the present remains undeniable.
Latest Posts
Latest Posts
-
What Is 3 20 As A Percentage
May 12, 2025
-
For The Following Distribution Find The Modal Class
May 12, 2025
-
List The First 5 Multiples Of 6
May 12, 2025
-
How Energy Is Lost In A Food Chain
May 12, 2025
-
What Fraction Of An Hour Is 45 Minutes
May 12, 2025
Related Post
Thank you for visiting our website which covers about Number Of Neutrons In Carbon 14 . We hope the information provided has been useful to you. Feel free to contact us if you have any questions or need further assistance. See you next time and don't miss to bookmark.