Modern Uses Of The Pinacol Rearrangement
Juapaving
Mar 06, 2025 · 5 min read
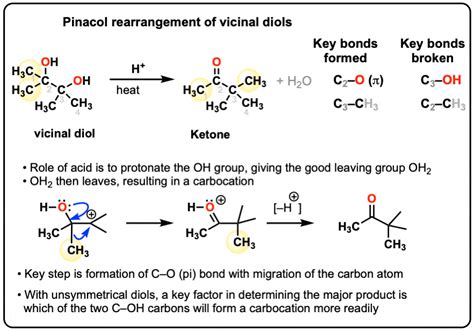
Table of Contents
Modern Uses of the Pinacol Rearrangement: A Versatile Tool in Organic Synthesis
The pinacol rearrangement, a classic name reaction in organic chemistry, continues to find widespread application in modern synthetic strategies. This 1,2-rearrangement, involving the acid-catalyzed conversion of 1,2-diols (pinacols) to carbonyl compounds, offers a powerful and versatile method for constructing carbon-carbon bonds and generating complex molecular architectures. Its enduring relevance stems from its ability to create chiral centers, its compatibility with various functional groups, and its adaptability to diverse synthetic challenges. This article delves into the modern uses of the pinacol rearrangement, highlighting its significant contributions to various fields of organic chemistry and beyond.
The Mechanism and Scope of the Pinacol Rearrangement
At the heart of the pinacol rearrangement lies a concerted mechanism involving a 1,2-alkyl or aryl shift. The reaction typically commences with protonation of one hydroxyl group in the 1,2-diol, forming a good leaving group (water). This facilitates the migration of an alkyl or aryl group from the adjacent carbon to the carbocation center, generating a more stable carbonyl compound. The driving force behind this rearrangement is the formation of a more stable carbonyl group, relative to the less stable carbocation intermediate.
Factors Influencing the Rearrangement:
Several factors significantly influence the outcome of the pinacol rearrangement, including:
-
Migratory Aptitude: The migrating group's ability to stabilize the developing carbocation is crucial. Generally, aryl groups and tertiary alkyl groups migrate preferentially over primary or secondary alkyl groups. This preferential migration can be exploited to control regioselectivity in the rearrangement.
-
Stereochemistry: The stereochemistry of the starting 1,2-diol significantly impacts the stereochemistry of the resulting carbonyl compound. This allows for the creation of chiral centers and the synthesis of enantiomerically pure products.
-
Acid Catalyst: The choice of acid catalyst is critical; strong acids like sulfuric acid, or Lewis acids such as boron trifluoride, can promote the rearrangement effectively. The choice of catalyst can influence the reaction rate and selectivity.
-
Solvent Effects: The solvent can also play a crucial role, influencing the reaction rate and selectivity.
Modern Applications of the Pinacol Rearrangement
The pinacol rearrangement's versatility is showcased in its diverse applications across various areas of organic synthesis:
1. Total Synthesis of Natural Products:
The pinacol rearrangement has been instrumental in the total synthesis of numerous natural products, often employed as a key step in the construction of complex carbon skeletons. The ability to create multiple stereocenters with high control has made it an indispensable tool in the synthesis of chiral molecules. Examples include its use in the synthesis of:
-
Terpenes: The construction of the intricate carbon frameworks of terpenes, including many bioactive molecules, frequently involves the pinacol rearrangement.
-
Steroids: The stereoselective formation of crucial rings in steroid molecules benefits from the regio- and stereoselectivity of this transformation.
-
Alkaloids: The synthesis of various alkaloid natural products has utilized the pinacol rearrangement to access specific ring systems and functionalities.
2. Development of New Synthetic Methods:
Researchers continuously explore modifications and variations of the pinacol rearrangement to expand its synthetic utility:
-
Asymmetric Pinacol Rearrangement: Significant advances have been made in developing asymmetric versions of the rearrangement, allowing for the synthesis of enantiomerically enriched products. Chiral catalysts and auxiliaries are employed to control the stereochemistry of the migrating group.
-
Oxidative Pinacol Rearrangement: This variation integrates oxidation steps to form carbonyl compounds directly from vicinal diols, streamlining the synthetic process.
-
Photochemical Pinacol Rearrangement: Employing light as an energy source has broadened the scope of the pinacol rearrangement, offering alternative reaction pathways and potentially enhanced selectivity.
3. Synthesis of Pharmaceuticals and Bioactive Molecules:
The pinacol rearrangement is vital in pharmaceutical chemistry, contributing to the synthesis of numerous drug candidates and bioactive molecules:
-
Synthesis of Drug Intermediates: The reaction is frequently used to produce key intermediates in the synthesis of complex drugs, streamlining the synthetic routes.
-
Synthesis of Heterocyclic Compounds: Modifications of the pinacol rearrangement have been used to access a wide variety of heterocyclic compounds, important building blocks in many pharmaceuticals.
-
Development of Targeted Drug Delivery Systems: Controlled release of drugs can be facilitated by creating drug conjugates using chemistry incorporating the pinacol rearrangement.
4. Materials Science and Polymer Chemistry:
The pinacol rearrangement has found applications beyond the realm of organic synthesis, extending into the fields of materials science and polymer chemistry:
-
Polymer Synthesis: The reaction can be employed to create specific polymeric structures with controlled architectures, leading to the development of advanced materials.
-
Preparation of Functional Polymers: Pinacol rearrangement can be integrated into the synthesis of polymers with specific functionalities, influencing the material properties.
-
Development of Biomaterials: Biocompatible polymers synthesized using the pinacol rearrangement can contribute to the development of implantable devices and other biomedical applications.
Challenges and Future Directions
Despite its remarkable versatility, several challenges remain to be addressed regarding the pinacol rearrangement:
-
Expanding Substrate Scope: Further research is needed to expand the range of substrates amenable to the rearrangement, particularly in handling sterically hindered or electronically challenging diols.
-
Developing More Efficient Catalysts: The development of more efficient, selective, and environmentally benign catalysts continues to be an active research area, focusing on both acid and metal catalysts.
-
Understanding Mechanistic Details: A deeper understanding of the reaction mechanism, particularly regarding the interplay between the catalyst, solvent, and substrate, is essential for optimization and predictability.
-
Integrating Flow Chemistry: Adapting the pinacol rearrangement to flow chemistry platforms can improve efficiency, scalability, and safety, offering opportunities for industrial applications.
Conclusion
The pinacol rearrangement, a classic name reaction, continues to serve as a valuable tool in modern organic synthesis. Its remarkable versatility, stemming from its ability to form carbon-carbon bonds, create chiral centers, and be compatible with diverse functional groups, has propelled its widespread use in total synthesis, pharmaceutical chemistry, materials science, and polymer chemistry. Ongoing research focuses on improving the reaction’s scope, selectivity, and efficiency, promising exciting new applications and advances in the future. As chemists continuously refine and adapt this classic transformation, the pinacol rearrangement will undoubtedly play an increasingly significant role in shaping the future of organic synthesis.
Latest Posts
Latest Posts
-
What Is The Percent Of 2 6
Mar 06, 2025
-
What Is The Lcm Of 3 8
Mar 06, 2025
-
Is A Sound Wave A Transverse Wave
Mar 06, 2025
-
What Is The Electron Configuration For Magnesium
Mar 06, 2025
-
What Is The Common Factor Of 12 And 36
Mar 06, 2025
Related Post
Thank you for visiting our website which covers about Modern Uses Of The Pinacol Rearrangement . We hope the information provided has been useful to you. Feel free to contact us if you have any questions or need further assistance. See you next time and don't miss to bookmark.
