Lowest Common Multiple Of 4 5 6
Juapaving
Mar 16, 2025 · 5 min read
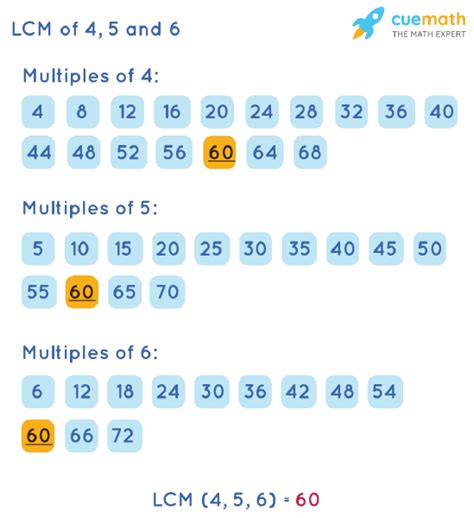
Table of Contents
Finding the Lowest Common Multiple (LCM) of 4, 5, and 6: A Comprehensive Guide
Finding the lowest common multiple (LCM) might seem like a simple arithmetic task, but understanding the underlying concepts and various methods for calculating it is crucial for a strong foundation in mathematics. This comprehensive guide will delve deep into finding the LCM of 4, 5, and 6, exploring multiple approaches and highlighting the importance of LCM in various mathematical applications. We'll move beyond a simple answer and build a robust understanding of this fundamental concept.
Understanding the Lowest Common Multiple (LCM)
The lowest common multiple (LCM) of two or more integers is the smallest positive integer that is divisible by all the integers. In simpler terms, it's the smallest number that all the given numbers can divide into without leaving a remainder. For instance, if we consider the numbers 2 and 3, their multiples are:
- Multiples of 2: 2, 4, 6, 8, 10, 12, 14, 16, 18...
- Multiples of 3: 3, 6, 9, 12, 15, 18...
The common multiples are 6, 12, 18, and so on. The smallest of these common multiples is 6, therefore, the LCM of 2 and 3 is 6.
Methods for Calculating the LCM
There are several methods to determine the LCM, each with its own advantages and disadvantages. Let's explore the most common methods and apply them to find the LCM of 4, 5, and 6.
1. Listing Multiples Method
This is the most straightforward method, especially for smaller numbers. We list the multiples of each number until we find the smallest common multiple.
- Multiples of 4: 4, 8, 12, 16, 20, 24, 28, 30, 32, 36, 40, 44, 48, 50, 52, 56, 60...
- Multiples of 5: 5, 10, 15, 20, 25, 30, 35, 40, 45, 50, 55, 60...
- Multiples of 6: 6, 12, 18, 24, 30, 36, 42, 48, 54, 60...
By examining the lists, we can see that the smallest common multiple of 4, 5, and 6 is 60. While simple, this method becomes cumbersome with larger numbers.
2. Prime Factorization Method
This method is more efficient for larger numbers. It involves finding the prime factorization of each number and then constructing the LCM using the highest powers of each prime factor present.
Let's find the prime factorization of 4, 5, and 6:
- 4 = 2²
- 5 = 5
- 6 = 2 × 3
Now, we identify the highest power of each prime factor present in the factorizations:
- 2²: The highest power of 2 is 2².
- 3: The highest power of 3 is 3.
- 5: The highest power of 5 is 5.
To find the LCM, we multiply these highest powers together:
LCM(4, 5, 6) = 2² × 3 × 5 = 4 × 3 × 5 = 60
3. Greatest Common Divisor (GCD) Method
The LCM and GCD (Greatest Common Divisor) are closely related. We can use the relationship:
LCM(a, b) × GCD(a, b) = a × b
This formula works for two numbers. To extend it to three or more numbers, we can apply it iteratively. First, find the LCM of two numbers, then find the LCM of that result and the third number, and so on. However, for finding the LCM of 4, 5, and 6 directly using this method might be less efficient than prime factorization. Let's demonstrate with two numbers first:
Let's find the LCM of 4 and 5 using the GCD method. The GCD of 4 and 5 is 1 (as they share no common factors other than 1).
LCM(4, 5) * GCD(4,5) = 4 * 5 LCM(4, 5) * 1 = 20 LCM(4, 5) = 20
Now let's find the LCM of 20 and 6:
The GCD of 20 and 6 is 2. LCM(20, 6) * GCD(20, 6) = 20 * 6 LCM(20, 6) * 2 = 120 LCM(20, 6) = 60
Therefore, the LCM(4, 5, 6) = 60. While possible, this method is generally less efficient for more than two numbers compared to prime factorization.
Applications of LCM
The LCM has numerous applications in various fields:
1. Fractions and Arithmetic
Finding the LCM is crucial when adding or subtracting fractions with different denominators. We find the LCM of the denominators to create equivalent fractions with a common denominator, simplifying the addition or subtraction process. For example: 1/4 + 1/5 + 1/6 requires finding the LCM of 4, 5, and 6 (which is 60) to solve.
2. Scheduling and Cycles
LCM is essential for solving problems involving cyclical events. For instance, if three buses arrive at a station every 4, 5, and 6 hours respectively, the LCM helps determine when all three buses will arrive simultaneously. In this case, the LCM of 4, 5, and 6 (60 hours) indicates they'll all arrive together after 60 hours.
3. Number Theory and Modular Arithmetic
LCM plays a critical role in number theory, particularly in modular arithmetic and solving congruence problems. It helps to find solutions where multiple congruences must be satisfied simultaneously.
4. Music Theory
The LCM can be applied to determine the least common period of musical intervals when working with rhythmic patterns.
Conclusion
The lowest common multiple is a fundamental concept with far-reaching applications. We've explored three methods for calculating the LCM of 4, 5, and 6—listing multiples, prime factorization, and the GCD method. While the listing multiples method works well for smaller numbers, prime factorization proves to be more efficient and systematic for larger numbers. Understanding the LCM is not only essential for solving mathematical problems but also for tackling real-world scenarios involving cycles, scheduling, and various other applications. The ability to efficiently calculate the LCM forms a crucial part of a strong mathematical foundation. This comprehensive guide provides a detailed explanation of the LCM and its significance across various domains, solidifying your understanding of this fundamental mathematical concept. Remember to choose the method that best suits the context and the complexity of the numbers involved.
Latest Posts
Latest Posts
-
Least Common Multiple Of 5 6 7
Mar 17, 2025
-
How Do You Find The Inverse Of A Relation
Mar 17, 2025
-
Does Cold Air Go Up Or Down
Mar 17, 2025
-
Least Common Multiple Of 20 And 3
Mar 17, 2025
-
Function Of The Motor End Plate
Mar 17, 2025
Related Post
Thank you for visiting our website which covers about Lowest Common Multiple Of 4 5 6 . We hope the information provided has been useful to you. Feel free to contact us if you have any questions or need further assistance. See you next time and don't miss to bookmark.
