Lowest Common Multiple Of 15 And 9
Juapaving
Mar 13, 2025 · 5 min read
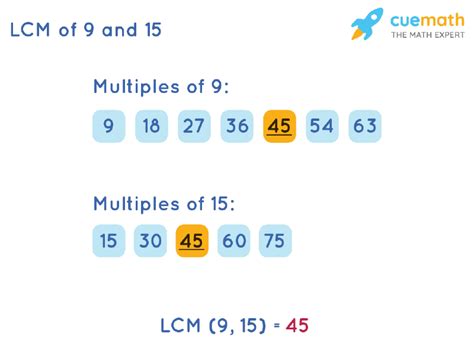
Table of Contents
Finding the Lowest Common Multiple (LCM) of 15 and 9: A Comprehensive Guide
Finding the Lowest Common Multiple (LCM) is a fundamental concept in mathematics, particularly in number theory and arithmetic. Understanding how to calculate the LCM is crucial for various applications, from simplifying fractions to solving problems in algebra and beyond. This comprehensive guide will delve into the process of determining the LCM of 15 and 9, exploring various methods and providing a deeper understanding of the underlying principles. We'll also touch upon the broader applications of LCMs in different mathematical contexts.
What is the Lowest Common Multiple (LCM)?
The Lowest Common Multiple (LCM) of two or more integers is the smallest positive integer that is a multiple of each of the integers. In simpler terms, it's the smallest number that both (or all) numbers divide into evenly. For instance, if we consider the numbers 2 and 3, their multiples are:
- Multiples of 2: 2, 4, 6, 8, 10, 12, 14, 16, 18, 20...
- Multiples of 3: 3, 6, 9, 12, 15, 18, 21, 24...
The common multiples are 6, 12, 18, and so on. The smallest common multiple, and therefore the LCM, is 6.
Methods for Finding the LCM of 15 and 9
There are several ways to calculate the LCM, each with its own advantages and disadvantages. Let's explore the most common methods, focusing on their application to finding the LCM of 15 and 9:
1. Listing Multiples Method
This is a straightforward method, especially for smaller numbers. We list the multiples of each number until we find the smallest common multiple.
- Multiples of 15: 15, 30, 45, 60, 75, 90, 105...
- Multiples of 9: 9, 18, 27, 36, 45, 54, 63, 72, 81, 90, 99...
By inspecting the lists, we see that the smallest common multiple is 45. Therefore, the LCM(15, 9) = 45. This method works well for smaller numbers but becomes cumbersome with larger numbers.
2. Prime Factorization Method
This method is more efficient for larger numbers. It involves finding the prime factorization of each number and then constructing the LCM using the highest powers of each prime factor.
- Prime factorization of 15: 3 x 5
- Prime factorization of 9: 3 x 3 = 3²
To find the LCM, we take the highest power of each prime factor present in the factorizations:
- Highest power of 3: 3² = 9
- Highest power of 5: 5¹ = 5
Therefore, LCM(15, 9) = 3² x 5 = 9 x 5 = 45.
This method is generally preferred for its efficiency and systematic approach, especially when dealing with larger numbers or multiple numbers.
3. Greatest Common Divisor (GCD) Method
This method utilizes the relationship between the LCM and the Greatest Common Divisor (GCD) of two numbers. The relationship is given by the formula:
LCM(a, b) x GCD(a, b) = a x b
First, we need to find the GCD of 15 and 9. We can use the Euclidean algorithm for this:
- Divide the larger number (15) by the smaller number (9): 15 ÷ 9 = 1 with a remainder of 6.
- Replace the larger number with the smaller number (9) and the smaller number with the remainder (6): 9 ÷ 6 = 1 with a remainder of 3.
- Repeat: 6 ÷ 3 = 2 with a remainder of 0.
- The GCD is the last non-zero remainder, which is 3.
Now, we can use the formula:
LCM(15, 9) x GCD(15, 9) = 15 x 9 LCM(15, 9) x 3 = 135 LCM(15, 9) = 135 ÷ 3 = 45
This method is efficient, especially when dealing with larger numbers where finding the prime factorization might be more challenging.
Applications of LCM in Real-World Scenarios
The concept of the LCM extends far beyond simple mathematical exercises. It finds practical applications in various real-world scenarios:
1. Scheduling and Time Management
Imagine two buses that depart from the same station at different intervals. One bus departs every 15 minutes, and the other every 9 minutes. To find out when both buses will depart at the same time again, we need to find the LCM(15, 9) = 45. Both buses will depart simultaneously again after 45 minutes.
2. Fraction Operations
The LCM plays a vital role in adding or subtracting fractions with different denominators. To add fractions like 1/15 and 1/9, we need to find the LCM of 15 and 9 (which is 45) and then rewrite the fractions with this common denominator before performing the addition.
3. Gear Ratios and Mechanical Engineering
In mechanical systems with gears, the LCM helps determine the synchronization of rotating components. Understanding gear ratios and their relationships relies on LCM calculations for optimal efficiency.
4. Music Theory
The LCM is used in music theory to determine the least common denominator for different rhythmic patterns or time signatures. It helps in harmonizing and creating musical sequences.
5. Construction and Design
In construction projects, LCM calculations might be used to synchronize the work of different teams or to determine the optimal arrangement of materials. For example, tiling a floor with tiles of two different dimensions will require LCM calculations to ensure a seamless pattern and minimize waste.
6. Computer Science
In computer programming and algorithms, LCM is used in various contexts, such as in scheduling tasks or synchronizing processes that operate at different frequencies.
Beyond the Basics: LCM for More Than Two Numbers
The methods described above can be extended to find the LCM of more than two numbers. For the prime factorization method, we simply consider all the prime factors of all the numbers and take the highest power of each. For the GCD method, it's more complex, often involving repeated applications of the GCD calculation.
Conclusion: Mastering LCM for Mathematical Proficiency
Understanding and calculating the LCM is a crucial skill in mathematics. Whether you are dealing with simple fraction problems or complex scheduling tasks, mastering the LCM will significantly enhance your problem-solving abilities and mathematical proficiency. The various methods described in this guide provide a flexible toolkit for tackling different scenarios and levels of complexity, making you confident in calculating the LCM of any set of numbers. Remember to choose the method most appropriate for the given numbers and context, and you will be well equipped to solve a wide array of mathematical problems effectively. The LCM, seemingly a simple concept, proves to be a powerful tool with wide-ranging applications in various fields, highlighting its importance in both theoretical and practical contexts.
Latest Posts
Latest Posts
-
The Structural And Functional Unit Of The Kidney Is The
May 09, 2025
-
What Chemical Is Inside A Battery
May 09, 2025
-
What Is 1 5 Cm In Mm
May 09, 2025
-
How Does A Subsidy Affect Supply
May 09, 2025
-
What Is The Purpose Of A Contractile Vacuole
May 09, 2025
Related Post
Thank you for visiting our website which covers about Lowest Common Multiple Of 15 And 9 . We hope the information provided has been useful to you. Feel free to contact us if you have any questions or need further assistance. See you next time and don't miss to bookmark.