Lowest Common Factor Of 4 And 9
Juapaving
Mar 04, 2025 · 5 min read
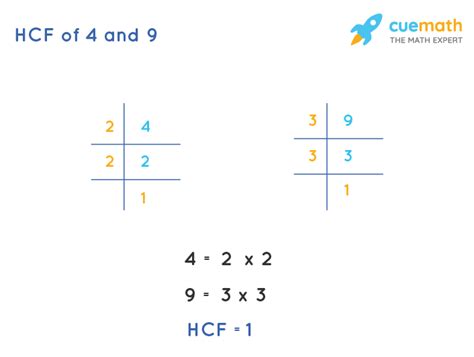
Table of Contents
Finding the Lowest Common Factor (LCF) of 4 and 9: A Deep Dive into Number Theory
The concept of the lowest common factor (LCF), also known as the greatest common divisor (GCD), is a fundamental element in number theory. Understanding how to find the LCF is crucial for various mathematical applications, from simplifying fractions to solving complex algebraic equations. This comprehensive guide delves into the methods of determining the LCF of 4 and 9, exploring the underlying principles and expanding on the broader context of number theory.
Understanding Factors and Divisors
Before we delve into finding the LCF of 4 and 9, let's establish a clear understanding of the terminology. A factor of a number is a whole number that divides the number evenly without leaving a remainder. A divisor is simply another term for a factor.
Let's consider the number 4. Its factors are 1, 2, and 4. These are the whole numbers that divide 4 completely.
Similarly, for the number 9, the factors are 1, 3, and 9.
Identifying the Common Factors of 4 and 9
To find the LCF (or GCD), we need to identify the factors that are common to both 4 and 9. Looking at the factors of each number:
- Factors of 4: 1, 2, 4
- Factors of 9: 1, 3, 9
The only number that appears in both lists is 1. Therefore, the lowest common factor (LCF) of 4 and 9 is 1.
Methods for Finding the LCF/GCD
While listing factors works well for smaller numbers like 4 and 9, it becomes less efficient for larger numbers. Let's explore more robust methods for determining the LCF/GCD:
1. Prime Factorization Method
This method involves expressing each number as a product of its prime factors. A prime number is a whole number greater than 1 that has only two divisors: 1 and itself.
- Prime factorization of 4: 2 x 2 = 2²
- Prime factorization of 9: 3 x 3 = 3²
To find the LCF using prime factorization:
- Identify the prime factors: We have 2 and 3.
- Find the common prime factors: There are no common prime factors between 4 and 9.
- The LCF is the product of the common prime factors raised to the lowest power. Since there are no common prime factors, the LCF is 1.
2. Euclidean Algorithm
The Euclidean algorithm is a highly efficient method for finding the GCD of two numbers. It's particularly useful for larger numbers where prime factorization might be cumbersome. The algorithm relies on repeated application of the division algorithm.
Let's illustrate with 4 and 9:
- Divide the larger number (9) by the smaller number (4): 9 = 2 x 4 + 1
- Replace the larger number with the smaller number (4) and the smaller number with the remainder (1): Now we consider the numbers 4 and 1.
- Repeat the process: 4 = 4 x 1 + 0
- The GCD (or LCF) is the last non-zero remainder. In this case, the last non-zero remainder is 1. Therefore, the LCF of 4 and 9 is 1.
Significance of the LCF/GCD
The LCF/GCD plays a crucial role in various mathematical concepts and applications:
- Simplifying Fractions: The LCF helps simplify fractions to their lowest terms. For example, the fraction 4/9 is already in its simplest form because the LCF of 4 and 9 is 1.
- Solving Diophantine Equations: These are equations where only integer solutions are sought. The GCD plays a critical role in determining the solvability of certain Diophantine equations.
- Modular Arithmetic: The GCD is fundamental in modular arithmetic, which deals with remainders after division.
- Cryptography: Concepts related to GCD are used extensively in various cryptographic algorithms.
- Computer Science: The Euclidean algorithm, a method for finding the GCD, is widely used in computer science for its efficiency.
Relatively Prime Numbers
Numbers whose greatest common divisor (GCD) is 1 are called relatively prime or coprime numbers. Since the GCD of 4 and 9 is 1, they are relatively prime. This means they share no common factors other than 1.
Expanding on Number Theory Concepts
The LCF/GCD is just one facet of the broader field of number theory. Other important concepts include:
- Least Common Multiple (LCM): This is the smallest number that is a multiple of two or more given numbers.
- Modular Arithmetic: This branch of number theory deals with arithmetic operations on integers modulo a given number.
- Diophantine Equations: These are algebraic equations where only integer solutions are considered.
- Prime Numbers and Distribution: The study of prime numbers, their distribution, and their properties is a significant area of number theory.
- Congruences: Congruences are relationships between numbers based on their remainders when divided by a certain number (the modulus).
Practical Applications and Real-World Examples
While the LCF/GCD might seem abstract, it has practical applications in various real-world scenarios:
- Scheduling: Determining when events will occur simultaneously (like bus schedules aligning).
- Resource Allocation: Distributing resources fairly among groups or individuals (like dividing work tasks).
- Measurement: Converting units of measurement and finding common denominators.
- Pattern Recognition: Identifying repeating patterns and cycles in data (like in engineering or scientific research).
Conclusion
Understanding the lowest common factor, and the broader concepts within number theory, is essential for many areas of mathematics and its applications. The simple example of finding the LCF of 4 and 9 not only demonstrates a fundamental concept but also serves as a gateway to understanding more complex mathematical ideas. The methods explored here, particularly the Euclidean algorithm, provide efficient ways to determine the LCF/GCD, even for larger numbers. By mastering these concepts, one can strengthen their mathematical foundation and open doors to solving more complex problems across diverse fields. The exploration of relatively prime numbers further highlights the significance of this fundamental concept in number theory. The seemingly simple task of finding the LCF of 4 and 9 unveils a rich tapestry of mathematical relationships and their applications in the real world.
Latest Posts
Latest Posts
-
Write 88 As A Product Of Prime Factors
Mar 04, 2025
-
Why Cant Aluminum Be Reduced With Carbon
Mar 04, 2025
-
Which Of The Following Is Insoluble In Water
Mar 04, 2025
-
How Do Hypotheses Differ From Theories
Mar 04, 2025
-
What Is The Least Common Multiple Of 7 And 10
Mar 04, 2025
Related Post
Thank you for visiting our website which covers about Lowest Common Factor Of 4 And 9 . We hope the information provided has been useful to you. Feel free to contact us if you have any questions or need further assistance. See you next time and don't miss to bookmark.
