Lines Of Symmetry On An Octagon
Juapaving
Mar 10, 2025 · 6 min read
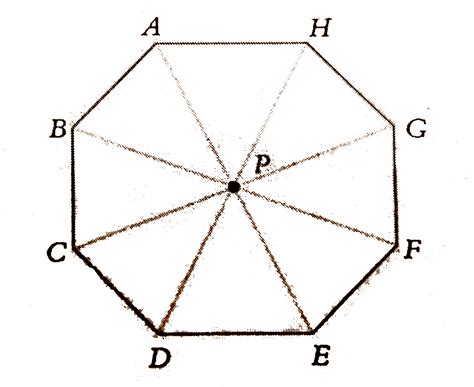
Table of Contents
Lines of Symmetry on an Octagon: A Comprehensive Exploration
The octagon, an eight-sided polygon, presents a fascinating study in geometry, particularly when exploring its lines of symmetry. Understanding these lines of symmetry unlocks deeper insights into the octagon's properties and its relationship to other geometric shapes. This article delves into the intricacies of octagonal symmetry, providing a comprehensive guide for students, educators, and anyone intrigued by the beauty of mathematics.
What is a Line of Symmetry?
Before diving into the specifics of octagonal symmetry, let's establish a clear understanding of what constitutes a line of symmetry. A line of symmetry, also known as a line of reflection or axis of symmetry, is a line that divides a shape into two identical halves. If you were to fold the shape along the line of symmetry, the two halves would perfectly overlap. This means that every point on one half of the shape has a corresponding point on the other half, equidistant from the line of symmetry.
Types of Octagons and Their Symmetry
Not all octagons are created equal. The number and type of lines of symmetry an octagon possesses depends crucially on its regularity.
Regular Octagon: The Perfect Symmetry
A regular octagon is defined as an octagon with all eight sides of equal length and all eight interior angles of equal measure (135 degrees). This perfect symmetry leads to a high number of lines of symmetry. A regular octagon possesses eight lines of symmetry. These lines can be categorized into two types:
1. Lines of Symmetry through Opposite Vertices: Four Lines
Four lines of symmetry pass through opposite vertices of the regular octagon. These lines bisect the octagon, dividing it into two congruent quadrilaterals. Imagine drawing a line from one corner to the corner directly opposite it – you've found a line of symmetry. Repeat this process for all four pairs of opposite vertices, and you'll have identified four lines of symmetry.
2. Lines of Symmetry through Midpoints of Opposite Sides: Four Lines
Another set of four lines of symmetry connects the midpoints of opposite sides of the regular octagon. These lines also bisect the octagon, but in a slightly different way than the lines through opposite vertices. They divide the octagon into two congruent shapes, each consisting of four sides.
Irregular Octagons: Varying Symmetry
An irregular octagon, in contrast to a regular octagon, has sides and angles of varying lengths and measures. The number of lines of symmetry in an irregular octagon can vary greatly, ranging from zero to a maximum of eight. The presence of lines of symmetry in an irregular octagon depends entirely on the specific arrangement of its sides and angles. Some irregular octagons might possess only one or two lines of symmetry, while others might have none at all. It's important to note that the irregular octagon may exhibit reflectional symmetry or rotational symmetry (or both), however these are not directly categorized as lines of symmetry.
Exploring Symmetry through Transformations
Understanding lines of symmetry can be enhanced by considering geometric transformations. Specifically, reflection is intrinsically linked to lines of symmetry.
Reflection and Lines of Symmetry
A reflection across a line of symmetry maps each point of the shape to its corresponding point on the other half. This transformation leaves the shape unchanged – it's superimposed on itself. This highlights the fundamental connection between lines of symmetry and the concept of reflectional symmetry.
Rotational Symmetry in Octagons
While this article focuses on lines of symmetry, it's important to acknowledge that regular octagons also exhibit rotational symmetry. A regular octagon has rotational symmetry of order 8, meaning it can be rotated about its center by 45-degree increments (360°/8 = 45°) and still appear unchanged. This rotational symmetry is distinct from, yet complementary to, its reflectional symmetry.
Practical Applications of Octagonal Symmetry
Understanding the symmetry of octagons extends beyond theoretical geometry; it finds applications in various fields:
-
Architecture and Design: Octagons are frequently used in architectural designs, offering both aesthetic appeal and structural efficiency. The lines of symmetry are often exploited to create balanced and visually pleasing structures. Consider the use of octagonal floor plans or the intricate patterns found in Islamic architecture.
-
Art and Crafts: The symmetrical nature of octagons makes them a popular choice in artistic creations. From tile mosaics to intricate designs in stained glass windows, the balanced geometry provides a pleasing visual effect.
-
Engineering and Manufacturing: The symmetries inherent in regular octagons can be utilized in the design of mechanical parts and structures, ensuring balanced weight distribution and efficient functionality.
-
Computer Graphics and Game Design: Understanding octagonal symmetry is valuable in creating symmetrical game levels, character models, and other visual elements. Exploiting this symmetry simplifies design processes and creates a sense of balance and visual harmony.
Beyond the Octagon: Generalizing Symmetry in Polygons
The concept of lines of symmetry extends to all polygons. The number of lines of symmetry in a regular polygon is equal to the number of sides. For example:
- A regular triangle (equilateral triangle) has 3 lines of symmetry.
- A square has 4 lines of symmetry.
- A regular pentagon has 5 lines of symmetry.
- And so on...
Irregular polygons, however, follow no such simple rule and their number of lines of symmetry may vary greatly based on their individual characteristics.
Advanced Concepts and Further Exploration
For those seeking a deeper understanding of symmetry, several advanced concepts can be explored:
-
Group Theory: Group theory provides a powerful mathematical framework for studying symmetries. The symmetry operations of a regular octagon form a mathematical group, allowing for a more rigorous and abstract analysis of its symmetry properties.
-
Tessellations: Octagons can be used to create fascinating tessellations, patterns that cover a plane without gaps or overlaps. Exploring these tessellations reveals further insights into the symmetries and geometric properties of octagons.
-
Fractal Geometry: The concept of symmetry can be extended to fractal geometries, revealing intriguing self-similar patterns at various scales.
Conclusion: The Enduring Fascination of Octagonal Symmetry
The lines of symmetry in an octagon, particularly the regular octagon, provide a rich area of study within geometry. Understanding these lines of symmetry unlocks a deeper appreciation for the mathematical elegance of this shape and its applications across various disciplines. From its simple definition to its complex applications in advanced mathematics, the octagon offers a constant source of fascination and learning. Whether you're a student grappling with geometrical concepts or an enthusiast seeking to understand the underlying beauty of shapes, the exploration of octagonal symmetry offers a rewarding journey into the fascinating world of mathematics.
Latest Posts
Latest Posts
-
What Is The Multiples Of 14
Mar 10, 2025
-
Dilation By A Scale Factor Of 1 2
Mar 10, 2025
-
A Quadrilateral With Both Pairs Of Opposite Sides Parallel
Mar 10, 2025
-
The Correct Sequence Of Events In Translation Is
Mar 10, 2025
-
What Degree Is A Straight Line
Mar 10, 2025
Related Post
Thank you for visiting our website which covers about Lines Of Symmetry On An Octagon . We hope the information provided has been useful to you. Feel free to contact us if you have any questions or need further assistance. See you next time and don't miss to bookmark.
