Life Cycle Of The Silk Moth
Juapaving
Apr 01, 2025 · 6 min read
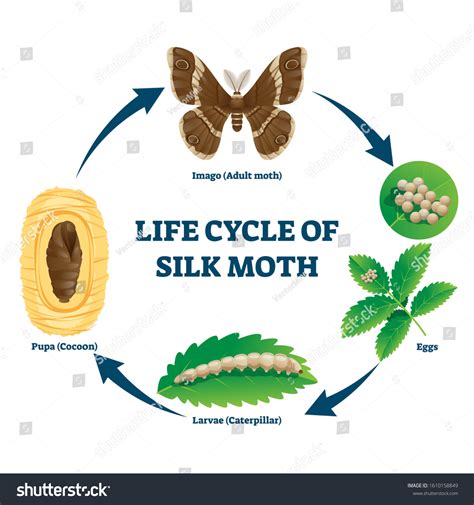
Table of Contents
The Fascinating Life Cycle of the Silk Moth: From Egg to Exquisite Silk
The silk moth, a creature of remarkable beauty and economic significance, undergoes a captivating metamorphosis throughout its life cycle. This journey, from a tiny egg to a magnificent moth capable of producing the luxurious silk we cherish, is a testament to nature's intricate design. Understanding this life cycle provides a deeper appreciation for the silk industry and the delicate balance of nature. This comprehensive guide delves into each stage, exploring the fascinating details of the silk moth's transformation.
Stage 1: The Egg Stage – A Tiny Beginning
The life cycle of the silk moth begins with the egg, a minuscule marvel packed with the potential for future splendor. These oval-shaped eggs, typically measuring around 1mm in diameter, are initially a pale creamy white or yellowish color. As they mature, they gradually darken to a grayish or bluish hue. A female silk moth can lay anywhere from 300 to 500 eggs, carefully depositing them on mulberry leaves – the sole food source for the silkworms that will hatch from them. The incubation period for these eggs is temperature-dependent, typically ranging from 8 to 10 days under optimal conditions. However, in colder temperatures, the eggs may enter a state of diapause (dormancy), delaying hatching until conditions become favorable. The quantity and quality of eggs laid directly impact the success of subsequent stages in the silk moth's life cycle.
Factors Affecting Egg Hatching:
- Temperature: Consistent warm temperatures are crucial for successful hatching. Fluctuations can lead to developmental delays or mortality.
- Humidity: Appropriate humidity levels maintain egg viability and prevent desiccation.
- Parental Genetics: The health and genetic makeup of the parent moths play a significant role in egg fertility and the overall quality of the offspring.
Stage 2: The Larva Stage – The Silkworm's Feast
Upon hatching, the egg reveals a tiny, dark-colored larva – commonly known as a silkworm. These voracious eaters immediately begin their insatiable quest for mulberry leaves. Silkworms are essentially eating machines, growing rapidly during this stage. Their bodies are segmented, with distinct head, thorax, and abdomen regions. They possess powerful mandibles perfectly adapted for consuming mulberry leaves, their exclusive diet. This diet is essential as the leaves provide the necessary nutrients for the silkworms to spin their cocoons later on.
Growth and Molting:
The larval stage is marked by several molts, during which the silkworm sheds its exoskeleton to accommodate its rapid growth. Typically, a silkworm undergoes four to five molts, gradually increasing in size with each shedding. Each molt marks a significant milestone in its development, transitioning from a small, dark larva to a larger, creamier-colored one. The duration of this stage is highly variable, but it generally lasts for around 25-30 days under optimal conditions.
Importance of Mulberry Leaves:
Mulberry leaves are crucial for the silkworms' health and development. Their nutritional content directly affects the quality of the silk produced. A proper diet ensures adequate growth and the formation of a strong, high-quality cocoon. The specific type of mulberry leaf can even influence the final color and texture of the silk thread.
Stage 3: The Pupa Stage – Cocoon Construction
Once the silkworm reaches its full size, it enters the pupa stage. This is a remarkable phase characterized by the creation of the cocoon. The silkworm spins a protective silken casing around itself using silk filaments produced by special glands located in its body. The silk is a protein-based fiber that is incredibly strong and lightweight. The process of cocoon construction involves meticulous work, taking around 3-4 days. During this period, the silkworm constantly rotates its head, producing continuous strands of silk that form the cocoon’s intricate structure.
The Chemistry of Silk Production:
The silk is created from a liquid protein called fibroin, which is produced in the silk glands. This liquid fibroin is then combined with another protein called sericin, which acts as a glue, holding the silk fibers together. The silkworm meticulously lays down these silk threads in a figure-eight pattern, building a tough and protective cocoon that shields the developing pupa within.
Cocoon Characteristics:
The cocoon is typically oval-shaped, ranging in color from creamy white to yellowish or even slightly greenish, depending on the breed of silk moth. The texture is smooth and soft, and the entire structure is surprisingly strong considering the delicate nature of the silk threads. The cocoon is not just a protective shell; it's a carefully engineered structure designed to support the transformation within.
Stage 4: The Metamorphosis – From Pupa to Moth
Inside the protective cocoon, a remarkable transformation occurs. The silkworm undergoes metamorphosis, a complete change in its body structure and physiology. The larval tissues are broken down and reorganized into the adult form of the moth. This process takes approximately 10 to 14 days. During this period, the pupa remains relatively inactive within the cocoon, its body undergoing significant changes.
The Emergence of the Moth:
Once metamorphosis is complete, the adult moth is ready to emerge from its cocoon. It secretes an enzyme that softens the silk threads, creating an opening through which it can escape. This marks the transition from the pupa stage to the adult moth.
Stage 5: The Adult Stage – Reproduction and Legacy
The adult silk moth is a relatively short-lived creature, its primary purpose being reproduction. The moth has a soft, furry body with large, delicate wings. The wings are usually a pale brownish color, with subtle markings depending on the breed. Males are typically smaller than females and have more prominently feathery antennae, used to detect pheromones released by the females.
Mating and Egg Laying:
Mating takes place shortly after emergence, with the female releasing pheromones to attract the male. After mating, the female moth begins laying her eggs, starting the cycle anew. This completes the life cycle of the silk moth, perpetuating the generation and ensuring the continuation of the valuable silk production.
Economic Importance:
The silk moth's life cycle is intimately linked to the silk industry. Human intervention is crucial in this process, with silk farmers carefully managing the silkworms from egg stage to cocoon collection. The cocoons are harvested before the moth emerges, as the emergence process damages the continuous silk filament. The harvesting of cocoons and subsequent processing of the silk represents a significant economic activity in many parts of the world.
Conservation and Sustainability:
The silk industry faces challenges related to sustainability and conservation. Overharvesting and habitat loss threaten wild silk moth populations. Sustainable practices, including ethical harvesting techniques and the conservation of mulberry forests, are essential to ensure the long-term viability of the industry and the preservation of this fascinating creature's natural environment.
Conclusion: A Masterpiece of Nature
The life cycle of the silk moth is a mesmerizing journey of transformation, illustrating the wonder of nature's design. From the tiny egg to the exquisite silk and the delicate adult moth, each stage is filled with remarkable biological processes and intricate details. Understanding this life cycle allows us to appreciate both the beauty of the creature and the valuable resource it provides, emphasizing the importance of sustainable practices to protect this vital part of our ecosystem and its economic contribution. The meticulous process of silk production is not just a marvel of nature; it's also a testament to the interwoven relationship between humans and the natural world. Appreciating this connection fosters responsible stewardship and a deeper understanding of the delicate balance that supports this remarkable creature's existence.
Latest Posts
Latest Posts
-
Largest Cell Of The Human Body
Apr 02, 2025
-
What Is The Difference Between Solute And Solvent
Apr 02, 2025
-
How Big Is 7cm In Inches
Apr 02, 2025
-
What Is The Electron Configuration For Calcium
Apr 02, 2025
-
What Are The Chanses Of Getting Two
Apr 02, 2025
Related Post
Thank you for visiting our website which covers about Life Cycle Of The Silk Moth . We hope the information provided has been useful to you. Feel free to contact us if you have any questions or need further assistance. See you next time and don't miss to bookmark.
