Least Common Multiple Of 8 12 And 15
Juapaving
Mar 16, 2025 · 5 min read
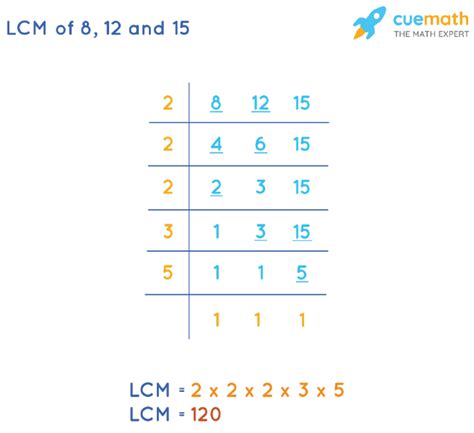
Table of Contents
Finding the Least Common Multiple (LCM) of 8, 12, and 15: A Comprehensive Guide
Determining the least common multiple (LCM) is a fundamental concept in mathematics with wide-ranging applications. This article dives deep into calculating the LCM of 8, 12, and 15, exploring various methods, and highlighting the importance of understanding LCM in different contexts. We’ll go beyond a simple answer and delve into the underlying principles, providing you with a comprehensive understanding of this mathematical operation.
Understanding Least Common Multiple (LCM)
Before we tackle the specific numbers 8, 12, and 15, let's establish a solid foundation. The least common multiple (LCM) of two or more integers is the smallest positive integer that is divisible by all the integers without leaving a remainder. Think of it as the smallest number that contains all the given numbers as factors.
This concept is crucial in various mathematical fields, including:
- Fraction arithmetic: Finding the LCM is essential when adding or subtracting fractions with different denominators.
- Scheduling problems: Determining the LCM helps in solving problems related to repeating events, such as determining when two or more cyclical processes will coincide.
- Number theory: LCM plays a vital role in exploring properties and relationships between integers.
Method 1: Prime Factorization Method
This method is considered one of the most efficient ways to find the LCM of multiple numbers. It involves breaking down each number into its prime factors – numbers that are only divisible by 1 and themselves.
Step 1: Prime Factorization
Let's find the prime factorization of 8, 12, and 15:
- 8: 2 x 2 x 2 = 2³
- 12: 2 x 2 x 3 = 2² x 3
- 15: 3 x 5
Step 2: Identifying the Highest Powers
Now, identify the highest power of each prime factor present in the factorizations:
- The highest power of 2 is 2³ (from the factorization of 8).
- The highest power of 3 is 3¹ (from the factorization of 12 and 15).
- The highest power of 5 is 5¹ (from the factorization of 15).
Step 3: Calculating the LCM
Multiply the highest powers of each prime factor together:
LCM(8, 12, 15) = 2³ x 3 x 5 = 8 x 3 x 5 = 120
Therefore, the least common multiple of 8, 12, and 15 is 120.
Method 2: Listing Multiples Method
This method is more straightforward but can be less efficient for larger numbers. It involves listing the multiples of each number until a common multiple is found.
Step 1: List Multiples
List the multiples of 8, 12, and 15:
- Multiples of 8: 8, 16, 24, 32, 40, 48, 56, 64, 72, 80, 88, 96, 104, 112, 120, 128...
- Multiples of 12: 12, 24, 36, 48, 60, 72, 84, 96, 108, 120, 132...
- Multiples of 15: 15, 30, 45, 60, 75, 90, 105, 120, 135...
Step 2: Identify the Least Common Multiple
The smallest multiple that appears in all three lists is 120.
Therefore, the least common multiple of 8, 12, and 15 is 120.
Method 3: Using the Greatest Common Divisor (GCD)
The LCM and GCD (greatest common divisor) are closely related. We can use the GCD to calculate the LCM using the following formula:
LCM(a, b) = (|a x b|) / GCD(a, b)
This formula can be extended to more than two numbers by applying it iteratively.
Step 1: Finding the GCD
Let's find the GCD of 8, 12, and 15 using the Euclidean algorithm:
- GCD(8, 12) = 4
- GCD(4, 15) = 1
The GCD of 8, 12, and 15 is 1.
Step 2: Applying the Formula
It's crucial to understand that the formula LCM(a, b) = (|a x b|) / GCD(a, b) is primarily for two numbers. For multiple numbers, we need to apply the GCD iteratively. A simpler approach for multiple numbers is generally the prime factorization method. However, we can illustrate the concept:
LCM(8, 12, 15) can't be directly calculated using this formula for three numbers. We'd need to calculate LCM(8,12) first, then LCM(result, 15).
LCM(8,12) = (812)/GCD(8,12) = (96)/4 = 24 LCM(24, 15) = (2415)/GCD(24,15) = 360/3 = 120
Therefore, the least common multiple is 120. While this method works, the prime factorization method is generally more efficient and less prone to errors for multiple numbers.
Applications of LCM
The LCM isn't just an abstract mathematical concept; it has practical applications across various fields:
-
Scheduling: Imagine two buses departing from the same station, one every 8 minutes and the other every 12 minutes. The LCM (24 minutes) tells us when both buses will depart simultaneously again.
-
Fraction Addition/Subtraction: To add fractions like 1/8 + 1/12 + 1/15, we need a common denominator. The LCM of 8, 12, and 15 (120) provides the least common denominator, simplifying the calculation.
-
Project Management: In project management, tasks might repeat on different cycles. Understanding LCM helps to synchronize tasks and optimize project timelines.
Conclusion: The Power of the LCM
Calculating the least common multiple, especially for numbers like 8, 12, and 15, might seem like a simple arithmetic exercise. However, understanding the underlying principles and the various methods for calculation, as well as the broad applications of the LCM in different contexts, provides a much deeper appreciation of its mathematical significance and practical utility. Mastering the LCM lays a crucial foundation for tackling more complex mathematical problems and real-world scenarios. The prime factorization method stands out as the most robust and efficient approach, especially when dealing with larger numbers or multiple integers. Remember to choose the method most suitable for the specific problem you're tackling.
Latest Posts
Latest Posts
-
What Is 2 Out Of 10 As A Percentage
Mar 16, 2025
-
Standard Deviation And Relative Standard Deviation
Mar 16, 2025
-
One Of Chargaffs Rules States That
Mar 16, 2025
-
Why Is Fire Not A Living Thing
Mar 16, 2025
-
What Is The Multiples Of 28
Mar 16, 2025
Related Post
Thank you for visiting our website which covers about Least Common Multiple Of 8 12 And 15 . We hope the information provided has been useful to you. Feel free to contact us if you have any questions or need further assistance. See you next time and don't miss to bookmark.
