Least Common Multiple Of 7 9
Juapaving
Mar 25, 2025 · 5 min read
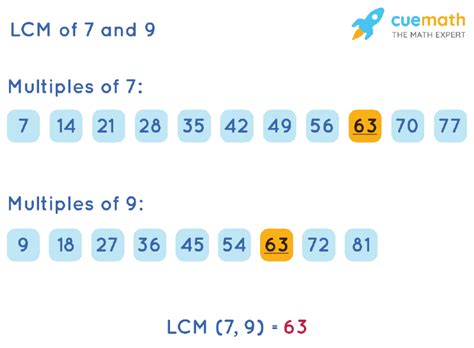
Table of Contents
Finding the Least Common Multiple (LCM) of 7 and 9: A Deep Dive
The least common multiple (LCM) is a fundamental concept in mathematics, particularly in number theory and arithmetic. Understanding LCM is crucial for solving various problems involving fractions, ratios, and cyclical events. This article will delve into the process of finding the LCM of 7 and 9, exploring different methods and providing a comprehensive understanding of the underlying principles. We'll also examine the broader implications of LCM in various mathematical contexts.
Understanding Least Common Multiple (LCM)
Before we tackle the specific LCM of 7 and 9, let's establish a solid understanding of what LCM actually means. The least common multiple of two or more integers is the smallest positive integer that is divisible by all the integers. In simpler terms, it's the smallest number that all the given numbers can divide into evenly.
For example, consider the numbers 2 and 3. Multiples of 2 are 2, 4, 6, 8, 10, 12... and multiples of 3 are 3, 6, 9, 12, 15... The smallest number that appears in both lists is 6. Therefore, the LCM of 2 and 3 is 6.
Method 1: Listing Multiples
The most straightforward method for finding the LCM of small numbers like 7 and 9 is to list their multiples until a common multiple is found.
Multiples of 7:
7, 14, 21, 28, 35, 42, 49, 56, 63, 70...
Multiples of 9:
9, 18, 27, 36, 45, 54, 63, 72...
By comparing the lists, we can see that the smallest number that appears in both sequences is 63. Therefore, the LCM of 7 and 9 is 63.
This method is effective for smaller numbers but becomes increasingly cumbersome as the numbers get larger.
Method 2: Prime Factorization
A more efficient method, especially for larger numbers, involves prime factorization. This method breaks down each number into its prime factors—numbers that are only divisible by 1 and themselves.
Prime Factorization of 7:
7 is a prime number, so its prime factorization is simply 7.
Prime Factorization of 9:
9 = 3 x 3 = 3²
To find the LCM using prime factorization, we take the highest power of each prime factor present in the factorizations of both numbers. In this case:
- The highest power of 3 is 3² = 9.
- The highest power of 7 is 7¹ = 7.
Multiplying these highest powers together gives us the LCM: 9 x 7 = 63.
This method is significantly more efficient than listing multiples, especially when dealing with larger numbers that have many factors. It's a systematic approach that minimizes guesswork.
Method 3: Using the Formula (LCM and GCD Relationship)
The least common multiple (LCM) and the greatest common divisor (GCD) are closely related. There's a formula that connects them:
LCM(a, b) = (|a x b|) / GCD(a, b)
where 'a' and 'b' are the two numbers, and GCD(a, b) represents the greatest common divisor of 'a' and 'b'.
First, we need to find the GCD of 7 and 9. Since 7 is a prime number and 9 is not divisible by 7, the GCD of 7 and 9 is 1. They share no common factors other than 1.
Now, we can apply the formula:
LCM(7, 9) = (|7 x 9|) / GCD(7, 9) = 63 / 1 = 63
This method elegantly utilizes the relationship between LCM and GCD, providing a concise calculation.
Applications of LCM in Real-World Scenarios
The concept of LCM isn't just confined to abstract mathematical problems; it has practical applications in various real-world situations:
1. Scheduling and Timing:
Imagine you have two machines that operate on different cycles. One machine completes a task every 7 minutes, and another completes a task every 9 minutes. To determine when both machines will complete a task simultaneously, you need to find the LCM of 7 and 9. The LCM (63) indicates that both machines will complete a task together after 63 minutes.
2. Fraction Operations:
Finding a common denominator when adding or subtracting fractions requires determining the LCM of the denominators. For instance, to add 1/7 and 1/9, you need to find the LCM of 7 and 9 (which is 63) and then rewrite the fractions with this common denominator before performing the addition.
3. Gear Ratios and Rotational Mechanics:
In engineering and mechanics, LCM is used to calculate gear ratios and synchronize rotating components. Understanding the LCM helps ensure that different parts of a system operate harmoniously and efficiently.
4. Cyclical Events:
LCM finds application in scenarios involving recurring events with different cycles. For example, if two planets have orbital periods of 7 and 9 years, respectively, the LCM would determine when they will be in the same relative position again.
5. Music Theory:
In music theory, LCM is used to determine the least common multiple of the denominators of musical rhythms or time signatures, leading to harmonious musical arrangements.
Expanding the Concept: LCM of More Than Two Numbers
The methods described above can be extended to find the LCM of more than two numbers. The prime factorization method is particularly useful in such cases. You would factorize each number into its prime factors, and then take the highest power of each prime factor present in any of the factorizations to determine the LCM.
For example, to find the LCM of 7, 9, and 14:
- Prime factorization of 7: 7
- Prime factorization of 9: 3²
- Prime factorization of 14: 2 x 7
The highest power of 2 is 2¹ = 2. The highest power of 3 is 3² = 9. The highest power of 7 is 7¹ = 7.
Therefore, the LCM(7, 9, 14) = 2 x 3² x 7 = 2 x 9 x 7 = 126
Conclusion: Mastering LCM for Mathematical Proficiency
Understanding and applying the least common multiple is a vital skill in various mathematical fields and practical situations. Whether you're simplifying fractions, solving scheduling problems, or tackling more complex mathematical concepts, mastering LCM enhances your problem-solving abilities. The different methods presented in this article – listing multiples, prime factorization, and using the LCM-GCD relationship – offer flexibility in approaching LCM calculations, allowing you to choose the most efficient method depending on the context and the numbers involved. By understanding the underlying principles and practicing these methods, you can confidently tackle LCM problems and appreciate their significance in a wide range of applications.
Latest Posts
Latest Posts
-
How Many Mm Is 8 Cm
Mar 26, 2025
-
1 Square Mile Is How Many Acres
Mar 26, 2025
-
What Is The Boiling Point And Freezing Point Of Water
Mar 26, 2025
-
What Is A Multiple Of 25
Mar 26, 2025
-
Are Multiples Of 4 Always Even
Mar 26, 2025
Related Post
Thank you for visiting our website which covers about Least Common Multiple Of 7 9 . We hope the information provided has been useful to you. Feel free to contact us if you have any questions or need further assistance. See you next time and don't miss to bookmark.
