Least Common Multiple Of 6 8 And 12
Juapaving
Mar 15, 2025 · 5 min read
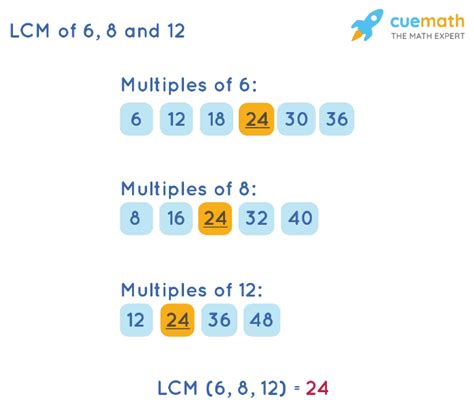
Table of Contents
Finding the Least Common Multiple (LCM) of 6, 8, and 12: A Comprehensive Guide
The least common multiple (LCM) is a fundamental concept in mathematics, particularly in number theory and algebra. Understanding how to calculate the LCM is crucial for various applications, ranging from simplifying fractions to solving problems involving periodic events. This article delves deep into finding the LCM of 6, 8, and 12, exploring different methods and providing a comprehensive understanding of the underlying principles. We'll move beyond simply finding the answer and explore the broader context of LCMs and their relevance.
Understanding Least Common Multiples
Before we tackle the specific problem of finding the LCM of 6, 8, and 12, let's solidify our understanding of what an LCM actually represents. The least common multiple of two or more integers is the smallest positive integer that is a multiple of all the integers. In simpler terms, it's the smallest number that all the given numbers can divide into evenly.
For instance, consider the numbers 2 and 3. The multiples of 2 are 2, 4, 6, 8, 10, 12, and so on. The multiples of 3 are 3, 6, 9, 12, 15, and so on. Notice that 6 and 12 are common multiples of both 2 and 3. However, 6 is the smallest common multiple, hence it's the LCM of 2 and 3.
Methods for Calculating the LCM
Several methods exist for determining the LCM of a set of numbers. We'll explore the most common and efficient approaches, focusing on their application to finding the LCM of 6, 8, and 12.
1. Listing Multiples Method
This is the most straightforward method, especially for smaller numbers. We simply list the multiples of each number until we find the smallest common multiple.
- Multiples of 6: 6, 12, 18, 24, 30, 36, 42, 48, 54, 60...
- Multiples of 8: 8, 16, 24, 32, 40, 48, 56, 64, 72, 80...
- Multiples of 12: 12, 24, 36, 48, 60, 72, 84, 96, 108, 120...
By comparing the lists, we can see that the smallest number appearing in all three lists is 24. Therefore, the LCM of 6, 8, and 12 is 24. This method is effective for smaller numbers but becomes cumbersome and inefficient for larger numbers.
2. Prime Factorization Method
This method is more efficient for larger numbers and provides a deeper understanding of the underlying mathematical principles. It involves finding the prime factorization of each number and then constructing the LCM using the highest powers of each prime factor.
- Prime factorization of 6: 2 × 3
- Prime factorization of 8: 2³
- Prime factorization of 12: 2² × 3
To find the LCM, we take the highest power of each prime factor present in the factorizations:
- The highest power of 2 is 2³ = 8
- The highest power of 3 is 3¹ = 3
Multiplying these highest powers together gives us the LCM: 8 × 3 = 24. This method is significantly more efficient than listing multiples for larger numbers.
3. Greatest Common Divisor (GCD) Method
The LCM and GCD (greatest common divisor) of a set of numbers are closely related. The product of the LCM and GCD of two numbers is equal to the product of the two numbers. This relationship can be extended to more than two numbers, although the calculation becomes slightly more complex. We can use the Euclidean algorithm to find the GCD efficiently.
First, let's find the GCD of 6, 8, and 12 using the Euclidean algorithm. We start by finding the GCD of 6 and 8:
- 8 = 1 × 6 + 2
- 6 = 3 × 2 + 0
The GCD of 6 and 8 is 2. Now, let's find the GCD of this result (2) and 12:
- 12 = 6 × 2 + 0
The GCD of 6, 8, and 12 is 2.
While directly calculating the LCM from the GCD for three or more numbers is complex, we can utilize the prime factorization method which is generally more efficient for multiple numbers.
Applications of LCM
The concept of the least common multiple has wide-ranging applications across various fields:
1. Fraction Simplification
Finding the LCM is crucial when adding or subtracting fractions with different denominators. We find the LCM of the denominators and then convert the fractions to equivalent fractions with the LCM as the common denominator. This allows for straightforward addition or subtraction.
2. Scheduling Problems
LCMs are essential in solving problems related to scheduling recurring events. For example, if event A occurs every 6 days, event B every 8 days, and event C every 12 days, finding the LCM (24) tells us when all three events will occur on the same day again.
3. Gear Ratios and Mechanical Systems
In mechanical engineering, the LCM is used to determine the optimal gear ratios and synchronize the movements of different components in machines.
4. Music Theory
In music theory, the LCM is used to calculate the least common multiple of the lengths of notes and rhythms to determine the length of a complete musical phrase.
Beyond the Basics: Extending the Concept
While we've focused on finding the LCM of 6, 8, and 12, the principles and methods discussed are applicable to any set of integers. For larger sets of numbers, the prime factorization method remains the most efficient approach. The availability of computational tools can further simplify the process for extremely large numbers.
Furthermore, the concept of LCM extends beyond integers to other mathematical structures, such as polynomials. Finding the LCM of polynomials involves similar techniques, but the prime factorization is replaced by factorization into irreducible polynomials.
Conclusion: Mastering the LCM
Understanding and mastering the calculation of the least common multiple is a cornerstone of mathematical proficiency. Whether using the listing method, prime factorization, or the GCD approach, the chosen method should be tailored to the complexity of the numbers involved. The prime factorization method provides a robust and efficient approach for a broader range of applications. Remember that the LCM is not just a theoretical concept; it holds significant practical value in various fields, underscoring its importance in mathematics and beyond. By understanding its calculation and applications, you equip yourself with a valuable tool for solving a wide variety of problems.
Latest Posts
Latest Posts
-
How Tall Is 62 Inches In Feet
Mar 15, 2025
-
Which Of The Following Are Correctly Matched
Mar 15, 2025
-
Whats The Square Root Of X
Mar 15, 2025
-
Whats The Square Root Of 128
Mar 15, 2025
-
72 In Is How Many Feet
Mar 15, 2025
Related Post
Thank you for visiting our website which covers about Least Common Multiple Of 6 8 And 12 . We hope the information provided has been useful to you. Feel free to contact us if you have any questions or need further assistance. See you next time and don't miss to bookmark.
