Least Common Multiple Of 5 4 And 3
Juapaving
Mar 04, 2025 · 5 min read
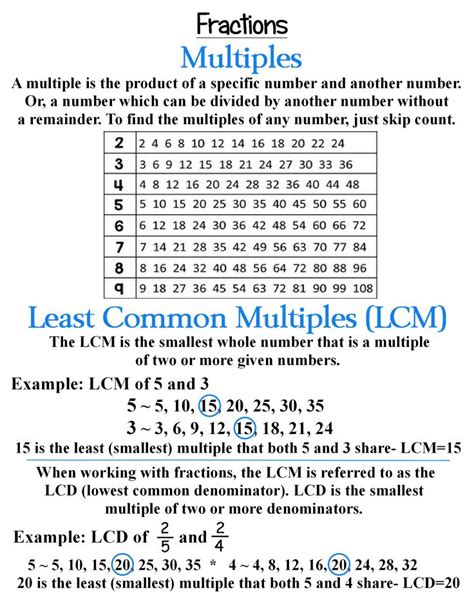
Table of Contents
Finding the Least Common Multiple (LCM) of 5, 4, and 3: A Comprehensive Guide
The least common multiple (LCM) is a fundamental concept in mathematics, particularly in number theory and arithmetic. Understanding how to calculate the LCM is crucial for various applications, from simplifying fractions to solving complex mathematical problems. This comprehensive guide will delve into the methods for finding the LCM of 5, 4, and 3, explain the underlying principles, and explore the broader significance of LCM in various fields.
What is the Least Common Multiple (LCM)?
The least common multiple (LCM) of two or more integers is the smallest positive integer that is divisible by all the given integers. In simpler terms, it's the smallest number that contains all the given numbers as factors. For example, the LCM of 2 and 3 is 6 because 6 is the smallest positive integer divisible by both 2 and 3.
Methods for Finding the LCM of 5, 4, and 3
There are several effective methods to determine the LCM of 5, 4, and 3. Let's explore the most common approaches:
1. Listing Multiples Method
This method involves listing the multiples of each number until you find the smallest common multiple.
- Multiples of 5: 5, 10, 15, 20, 25, 30, 35, 40, 45, 50, 60...
- Multiples of 4: 4, 8, 12, 16, 20, 24, 28, 32, 36, 40, 44, 48, 52, 56, 60...
- Multiples of 3: 3, 6, 9, 12, 15, 18, 21, 24, 27, 30, 33, 36, 39, 42, 45, 48, 51, 54, 57, 60...
By comparing the lists, we observe that the smallest common multiple is 60. Therefore, the LCM(5, 4, 3) = 60.
This method is straightforward for smaller numbers but can become cumbersome and time-consuming for larger numbers.
2. Prime Factorization Method
This method is more efficient, especially when dealing with larger numbers. It involves finding the prime factorization of each number and then constructing the LCM using the highest powers of each prime factor.
- Prime factorization of 5: 5 (5 is a prime number)
- Prime factorization of 4: 2² (4 = 2 x 2)
- Prime factorization of 3: 3 (3 is a prime number)
To find the LCM, we take the highest power of each prime factor present in the factorizations:
- Highest power of 2: 2² = 4
- Highest power of 3: 3¹ = 3
- Highest power of 5: 5¹ = 5
Now, multiply these highest powers together: 4 x 3 x 5 = 60. Therefore, the LCM(5, 4, 3) = 60.
This method is generally preferred for its efficiency and applicability to larger numbers.
3. Greatest Common Divisor (GCD) Method
The LCM and GCD (Greatest Common Divisor) are closely related. There's a formula that connects them:
LCM(a, b) x GCD(a, b) = a x b
This relationship holds true for two numbers. To extend it to three or more numbers, we can apply it iteratively. First, find the LCM of two numbers, and then find the LCM of the result and the third number, and so on.
Let's apply this to 5, 4, and 3:
- Find GCD(5, 4): The GCD of 5 and 4 is 1 (they share no common factors other than 1).
- Find LCM(5, 4): Using the formula: LCM(5, 4) x GCD(5, 4) = 5 x 4 => LCM(5, 4) = (5 x 4) / 1 = 20
- Find GCD(20, 3): The GCD of 20 and 3 is 1.
- Find LCM(20, 3): Using the formula: LCM(20, 3) x GCD(20, 3) = 20 x 3 => LCM(20, 3) = (20 x 3) / 1 = 60
Therefore, the LCM(5, 4, 3) = 60. This method demonstrates the interconnectedness between LCM and GCD.
Applications of LCM
The concept of LCM extends beyond simple arithmetic calculations. It finds practical applications in diverse fields:
1. Fraction Arithmetic
Finding a common denominator when adding or subtracting fractions requires determining the LCM of the denominators. For example, to add 1/3 + 1/4 + 1/5, we need to find the LCM of 3, 4, and 5, which is 60. This allows us to rewrite the fractions with a common denominator and perform the addition.
2. Scheduling Problems
LCM is valuable in scheduling problems. For example, if three buses depart from a station at intervals of 5 minutes, 4 minutes, and 3 minutes respectively, the LCM (60 minutes) determines when all three buses will depart simultaneously again.
3. Cyclic Phenomena
LCM plays a crucial role in analyzing cyclic phenomena like planetary orbits or repeating events. Identifying the LCM helps predict when events will align or coincide.
4. Music Theory
In music, LCM is used to determine the least common multiple of note durations. This is important in rhythmic calculations and in creating harmonious musical compositions.
5. Gear Ratios
In mechanical engineering, LCM is used to calculate gear ratios. It helps determine the optimal gear combinations for smooth and efficient operation of machinery.
6. Computer Science
LCM finds applications in computer algorithms and scheduling tasks. Optimizing processes frequently relies on understanding the LCM of different timing factors.
Understanding the Significance of LCM
The least common multiple is not just a mathematical curiosity; it is a powerful tool that simplifies complex calculations and facilitates problem-solving in diverse real-world scenarios. Its importance stems from its ability to unify disparate cycles and rhythms, making it invaluable in fields requiring synchronization and periodicity.
Conclusion
Calculating the LCM of 5, 4, and 3, whether through listing multiples, prime factorization, or the GCD method, consistently yields the result of 60. The understanding of LCM and its various computational methods is essential for mathematical proficiency and problem-solving across various disciplines. Mastering this concept strengthens your foundational mathematical skills and opens up a deeper understanding of numerical relationships. Its applications extend far beyond the classroom, demonstrating its practical relevance in various aspects of science, engineering, and everyday life. The ability to efficiently calculate LCM is a valuable asset for anyone working with numbers and looking to solve problems involving periodicity and synchronization.
Latest Posts
Latest Posts
-
Six Words To Describe Your Child
Mar 04, 2025
-
What Is One Singular Comon Noun
Mar 04, 2025
-
Whoch Of The Following Has The Units Og G Mol
Mar 04, 2025
-
How Many Lines Of Symmetry Does An Equilateral Triangle Have
Mar 04, 2025
-
How To Write 170 In Roman Numerals
Mar 04, 2025
Related Post
Thank you for visiting our website which covers about Least Common Multiple Of 5 4 And 3 . We hope the information provided has been useful to you. Feel free to contact us if you have any questions or need further assistance. See you next time and don't miss to bookmark.
