Least Common Multiple Of 4 8 And 12
Juapaving
Mar 14, 2025 · 5 min read
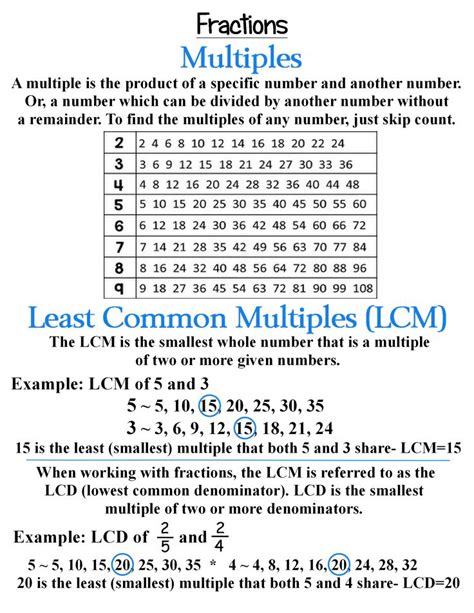
Table of Contents
Finding the Least Common Multiple (LCM) of 4, 8, and 12: A Comprehensive Guide
The least common multiple (LCM) is a fundamental concept in mathematics, particularly in number theory and arithmetic. Understanding how to calculate the LCM is crucial for various applications, from simplifying fractions to solving complex mathematical problems. This comprehensive guide will delve into the methods of finding the LCM of 4, 8, and 12, explaining the underlying principles and providing practical examples. We'll also explore the broader context of LCM and its significance in different mathematical fields.
Understanding Least Common Multiple (LCM)
Before diving into the calculation, let's solidify our understanding of the LCM. The least common multiple of two or more integers is the smallest positive integer that is divisible by all the integers without leaving a remainder. In simpler terms, it's the smallest number that all the given numbers can divide into evenly.
For instance, let's consider the numbers 2 and 3. The multiples of 2 are 2, 4, 6, 8, 10, 12... and the multiples of 3 are 3, 6, 9, 12, 15... The common multiples of 2 and 3 are 6, 12, 18... The smallest of these common multiples is 6, therefore, the LCM of 2 and 3 is 6.
Methods for Calculating LCM
Several methods exist for calculating the LCM of a set of numbers. We'll explore the most common and efficient approaches, focusing on their application to finding the LCM of 4, 8, and 12.
1. Listing Multiples Method
This method involves listing the multiples of each number until you find the smallest common multiple. While simple for smaller numbers, it becomes less efficient as the numbers get larger.
- Multiples of 4: 4, 8, 12, 16, 20, 24, 28, 32...
- Multiples of 8: 8, 16, 24, 32, 40...
- Multiples of 12: 12, 24, 36, 48...
From the lists above, we can see that the smallest common multiple of 4, 8, and 12 is 24.
2. Prime Factorization Method
This method is more efficient, especially for larger numbers. It involves finding the prime factorization of each number and then constructing the LCM using the highest powers of each prime factor present.
- Prime factorization of 4: 2²
- Prime factorization of 8: 2³
- Prime factorization of 12: 2² * 3
To find the LCM, we take the highest power of each prime factor present in the factorizations:
- Highest power of 2: 2³ = 8
- Highest power of 3: 3¹ = 3
Therefore, the LCM of 4, 8, and 12 is 2³ * 3 = 8 * 3 = 24.
3. Greatest Common Divisor (GCD) Method
This method utilizes the relationship between the LCM and the greatest common divisor (GCD) of two or more numbers. The relationship is expressed by the formula:
LCM(a, b) * GCD(a, b) = a * b
While this formula is generally used for two numbers, it can be extended to multiple numbers by applying it iteratively. First, find the GCD of two numbers, then find the LCM of those two numbers, and then use that LCM to find the LCM of that result and the third number and so on.
Let's apply this method to 4, 8, and 12.
- Find the GCD of 4 and 8: The GCD of 4 and 8 is 4.
- Find the LCM of 4 and 8: Using the formula: LCM(4, 8) * GCD(4, 8) = 4 * 8 => LCM(4, 8) * 4 = 32 => LCM(4, 8) = 8
- Find the GCD of 8 and 12: The GCD of 8 and 12 is 4.
- Find the LCM of 8 and 12: Using the formula: LCM(8, 12) * GCD(8, 12) = 8 * 12 => LCM(8, 12) * 4 = 96 => LCM(8, 12) = 24
Therefore, the LCM of 4, 8, and 12 is 24.
Applications of LCM
The LCM finds extensive applications across various mathematical and real-world scenarios. Here are a few examples:
-
Fraction Addition and Subtraction: When adding or subtracting fractions with different denominators, finding the LCM of the denominators is essential for obtaining a common denominator.
-
Scheduling and Cyclical Events: LCM is crucial in scheduling problems where events occur at regular intervals. For example, if event A occurs every 4 days, event B every 8 days, and event C every 12 days, the LCM (24) determines when all three events will occur simultaneously.
-
Modular Arithmetic: LCM plays a critical role in modular arithmetic, a branch of number theory dealing with remainders after division.
-
Music Theory: The LCM helps determine the least common multiple of note durations in music, useful in rhythmic calculations and compositions.
-
Engineering and Construction: In engineering and construction, LCM is used in projects involving repeating patterns or cyclical processes, for optimizing resource allocation and scheduling.
Why is understanding LCM important?
Understanding and calculating the LCM is a fundamental building block for more advanced mathematical concepts and problem-solving. Mastering this skill is crucial for students progressing through higher levels of mathematics. Its applications extend far beyond the classroom, permeating various fields where efficient scheduling, resource allocation, and precise calculations are paramount.
Beyond the Basics: Exploring LCM further
The LCM concept is not limited to finding the smallest common multiple for just three numbers. You can extend the same principles and methods to find the LCM of any number of integers. The prime factorization method remains particularly efficient for larger sets of numbers.
Furthermore, the concept of LCM is closely related to the greatest common divisor (GCD). Understanding the relationship between LCM and GCD provides a more comprehensive understanding of number theory and its practical applications.
The exploration of LCM can extend to more advanced topics like modular arithmetic, abstract algebra, and even cryptography. The foundational understanding you gain by working with LCM concepts will provide a strong basis for exploring these higher-level mathematical fields.
Conclusion
Finding the least common multiple of 4, 8, and 12, as demonstrated through multiple methods, highlights the importance of understanding and applying fundamental mathematical concepts. Whether using the listing multiples, prime factorization, or GCD methods, the result remains consistent: the LCM is 24. This understanding forms a foundation for tackling more complex mathematical problems and opens the door to applications across various disciplines. The ability to efficiently calculate LCM is a valuable skill applicable in numerous real-world contexts, emphasizing its significance in both theoretical and practical realms. Mastering the LCM calculation not only enhances mathematical skills but also fosters problem-solving abilities and analytical thinking, essential assets across a wide spectrum of fields.
Latest Posts
Latest Posts
-
How Many Stereoisomers Are Possible For
May 09, 2025
-
14 Rounded To The Nearest Tenth
May 09, 2025
-
What Is The Si Unit For Distance
May 09, 2025
-
How Many Lines Of Symmetry Does H Have
May 09, 2025
-
18 Inches Equals How Many Feet
May 09, 2025
Related Post
Thank you for visiting our website which covers about Least Common Multiple Of 4 8 And 12 . We hope the information provided has been useful to you. Feel free to contact us if you have any questions or need further assistance. See you next time and don't miss to bookmark.