Least Common Multiple Of 12 And 10
Juapaving
Mar 23, 2025 · 5 min read
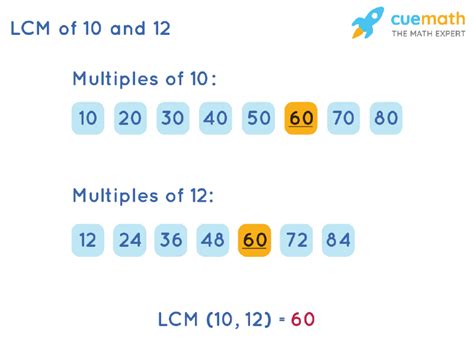
Table of Contents
Unveiling the Least Common Multiple (LCM) of 12 and 10: A Comprehensive Guide
Finding the least common multiple (LCM) might seem like a simple arithmetic task, but understanding its underlying principles and diverse applications reveals a surprisingly rich mathematical concept. This comprehensive guide delves into the intricacies of calculating the LCM of 12 and 10, exploring various methods, showcasing real-world applications, and expanding on the broader significance of LCM in mathematics and beyond.
Understanding Least Common Multiple (LCM)
The least common multiple (LCM) of two or more integers is the smallest positive integer that is divisible by all the integers. It's a fundamental concept in number theory with far-reaching implications in various fields. For instance, determining when events will coincide, optimizing scheduling, and even simplifying fractions all rely on the LCM.
Let's focus on our specific example: finding the LCM of 12 and 10. This means we're looking for the smallest positive number that is divisible by both 12 and 10 without leaving a remainder.
Methods for Calculating LCM(12, 10)
Several methods can effectively determine the LCM of 12 and 10. We will explore the three most common approaches:
1. Listing Multiples Method
This method, while straightforward, can be time-consuming for larger numbers. We simply list the multiples of each number until we find the smallest common multiple.
- Multiples of 12: 12, 24, 36, 48, 60, 72, 84, 96, 108, 120, ...
- Multiples of 10: 10, 20, 30, 40, 50, 60, 70, 80, 90, 100, 110, 120, ...
By comparing the lists, we observe that the smallest common multiple is 60. Therefore, LCM(12, 10) = 60.
2. Prime Factorization Method
This method is generally more efficient, especially for larger numbers. It involves finding the prime factorization of each number and then constructing the LCM using the highest powers of each prime factor present.
- Prime factorization of 12: 2² x 3
- Prime factorization of 10: 2 x 5
To find the LCM, we take the highest power of each prime factor present in either factorization:
- Highest power of 2: 2² = 4
- Highest power of 3: 3¹ = 3
- Highest power of 5: 5¹ = 5
Multiplying these together: 4 x 3 x 5 = 60. Therefore, LCM(12, 10) = 60.
3. Greatest Common Divisor (GCD) Method
This method utilizes the relationship between the LCM and the greatest common divisor (GCD) of two numbers. The formula connecting LCM and GCD is:
LCM(a, b) x GCD(a, b) = a x b
First, we need to find the GCD of 12 and 10. We can use the Euclidean algorithm for this:
- Divide 12 by 10: 12 = 10 x 1 + 2
- Divide 10 by the remainder 2: 10 = 2 x 5 + 0
The last non-zero remainder is the GCD, which is 2.
Now, using the formula:
LCM(12, 10) x GCD(12, 10) = 12 x 10 LCM(12, 10) x 2 = 120 LCM(12, 10) = 120 / 2 = 60
Therefore, LCM(12, 10) = 60.
Real-World Applications of LCM
The concept of LCM extends far beyond the realm of theoretical mathematics. It finds practical applications in various real-world scenarios:
1. Scheduling and Synchronization
Imagine you have two machines that perform a task at different intervals. Machine A completes a cycle every 12 minutes, while Machine B completes a cycle every 10 minutes. To find out when both machines will complete a cycle simultaneously, you need to find the LCM of 12 and 10. The LCM, 60, indicates that both machines will finish a cycle together after 60 minutes.
2. Fraction Addition and Subtraction
Adding or subtracting fractions with different denominators requires finding a common denominator, which is the LCM of the denominators. For example, to add 1/12 and 1/10, the LCM of 12 and 10 (60) becomes the common denominator.
3. Pattern Recognition and Cyclic Events
LCM is useful in identifying repeating patterns or events that occur at regular but different intervals. This is frequently used in tasks involving repeating sequences, such as in music, signal processing, and even some aspects of computer science.
LCM and its Significance in Advanced Mathematics
The concept of LCM extends to more advanced mathematical fields. It plays a crucial role in:
1. Abstract Algebra
In abstract algebra, the concept of LCM is generalized to other algebraic structures, like rings and modules, where it's related to concepts like ideals and least common multiples of ideals.
2. Number Theory
LCM is fundamental in various number-theoretic problems, particularly in the study of divisibility and prime factorization. It's intricately linked to the GCD and other arithmetic functions.
3. Modular Arithmetic
LCM is crucial in understanding modular arithmetic, a system of arithmetic for integers where numbers "wrap around" upon reaching a certain value (the modulus). Solving congruences often involves using LCM to find solutions.
Conclusion: The Power and Practicality of LCM
The seemingly simple calculation of the LCM of 12 and 10, as shown in this comprehensive guide, reveals a concept with significant mathematical depth and diverse applications. From optimizing schedules to facilitating complex calculations, LCM demonstrates its relevance in various fields, highlighting its importance as a fundamental mathematical tool. By understanding the different methods for calculating LCM and appreciating its applications, we can unlock a deeper understanding of its power and practicality in both theoretical and real-world contexts. Whether you're a student grappling with basic arithmetic or a researcher working on advanced mathematical problems, the principle of the least common multiple remains a cornerstone of mathematical understanding. Further exploration of this concept will undoubtedly reveal even more of its multifaceted nature and continued relevance across diverse disciplines.
Latest Posts
Latest Posts
-
Whats The Hottest Layer Of Earth
Mar 24, 2025
-
Definition Of Integers For Class 7
Mar 24, 2025
-
Where Does Most Reabsorption Occur In The Nephron
Mar 24, 2025
-
How Many Lines Of Symmetry Are In An Equilateral Triangle
Mar 24, 2025
-
Least Common Multiple Of 6 12 And 15
Mar 24, 2025
Related Post
Thank you for visiting our website which covers about Least Common Multiple Of 12 And 10 . We hope the information provided has been useful to you. Feel free to contact us if you have any questions or need further assistance. See you next time and don't miss to bookmark.
