Definition Of Integers For Class 7
Juapaving
Mar 24, 2025 · 6 min read
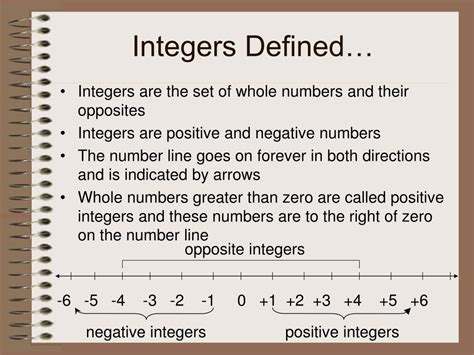
Table of Contents
Diving Deep into Integers: A Class 7 Guide
Welcome, Class 7 students! This comprehensive guide will unravel the fascinating world of integers. We’ll explore their definition, properties, and applications, ensuring you grasp this crucial mathematical concept thoroughly. By the end, you'll not only understand integers but also feel confident tackling any integer-related problem.
What are Integers? A Clear Definition
Integers are a fundamental part of the number system. Simply put, integers are whole numbers, including zero, and their negative counterparts. This means they don't have any fractional or decimal parts.
Think of a number line stretching infinitely in both directions. Zero sits comfortably in the middle. To the right, you have positive integers (1, 2, 3, and so on), extending towards infinity. To the left, you find negative integers (-1, -2, -3, and so on), also stretching infinitely.
Therefore, the set of integers can be represented as: {..., -3, -2, -1, 0, 1, 2, 3, ...}
The three dots (...) indicate that the sequence continues indefinitely in both positive and negative directions.
Key Differences from Other Number Types:
To fully understand integers, let's compare them to other types of numbers:
-
Natural Numbers (Counting Numbers): These are the numbers we use for counting: 1, 2, 3, and so on. Integers include natural numbers, but they also include zero and negative numbers.
-
Whole Numbers: These are natural numbers plus zero (0, 1, 2, 3...). Integers encompass whole numbers, extending to include negative numbers.
-
Rational Numbers: These can be expressed as a fraction p/q, where p and q are integers and q is not zero. Integers are a subset of rational numbers because any integer can be written as a fraction (e.g., 3 can be written as 3/1).
-
Irrational Numbers: These cannot be expressed as a fraction of two integers. Examples include π (pi) and √2 (the square root of 2). Integers are distinct from irrational numbers.
-
Real Numbers: This is the broadest category, encompassing all rational and irrational numbers. Integers are a subset of real numbers.
Properties of Integers: Understanding their Behavior
Integers possess several important properties that govern how they behave in mathematical operations:
1. Closure Property:
- Addition: The sum of any two integers is always another integer. For example, 5 + (-3) = 2, which is an integer.
- Subtraction: The difference between any two integers is always another integer. For example, 7 - 10 = -3, which is an integer.
- Multiplication: The product of any two integers is always another integer. For example, 4 x (-6) = -24, which is an integer.
However, the closure property does not hold true for division. Dividing two integers doesn't always result in an integer (e.g., 5 ÷ 2 = 2.5, which is not an integer).
2. Commutative Property:
This property applies to addition and multiplication but not subtraction or division.
- Addition: The order of integers in addition doesn't affect the result. a + b = b + a. For example, 2 + 5 = 5 + 2 = 7.
- Multiplication: Similarly, the order of integers in multiplication doesn't affect the result. a x b = b x a. For example, 3 x 4 = 4 x 3 = 12.
3. Associative Property:
This property also applies to addition and multiplication.
- Addition: When adding three or more integers, the grouping of the numbers doesn't affect the result. (a + b) + c = a + (b + c). For example, (2 + 3) + 4 = 2 + (3 + 4) = 9.
- Multiplication: Similarly, the grouping of integers in multiplication doesn't affect the result. (a x b) x c = a x (b x c). For example, (2 x 3) x 4 = 2 x (3 x 4) = 24.
4. Distributive Property:
This property connects addition and multiplication.
a x (b + c) = (a x b) + (a x c)
For example: 2 x (3 + 4) = (2 x 3) + (2 x 4) = 14
5. Identity Property:
- Additive Identity: Adding zero to any integer doesn't change its value. a + 0 = a.
- Multiplicative Identity: Multiplying any integer by 1 doesn't change its value. a x 1 = a.
6. Inverse Property:
- Additive Inverse: Every integer has an additive inverse (opposite). The sum of an integer and its additive inverse is zero. a + (-a) = 0. For example, 5 + (-5) = 0.
- Multiplicative Inverse: Only the integers 1 and -1 have multiplicative inverses. The product of an integer and its multiplicative inverse is 1.
Operations with Integers: Mastering the Calculations
Let's delve into performing calculations with integers. Understanding the rules for addition, subtraction, multiplication, and division is crucial.
1. Addition of Integers:
- Adding Integers with the Same Sign: Add the absolute values of the integers and keep the common sign. For example: 5 + 3 = 8; (-5) + (-3) = -8.
- Adding Integers with Different Signs: Subtract the smaller absolute value from the larger absolute value. The result takes the sign of the integer with the larger absolute value. For example: 7 + (-3) = 4; (-7) + 3 = -4.
2. Subtraction of Integers:
Subtraction is essentially the addition of the additive inverse. To subtract an integer, add its opposite (additive inverse).
For example:
- 8 - 3 = 8 + (-3) = 5
- 5 - (-2) = 5 + 2 = 7
- (-6) - 2 = (-6) + (-2) = -8
- (-4) - (-7) = (-4) + 7 = 3
3. Multiplication of Integers:
- Multiplying Integers with the Same Sign: Multiply the absolute values. The result is positive.
- Multiplying Integers with Different Signs: Multiply the absolute values. The result is negative.
4. Division of Integers:
Similar rules apply to division as multiplication regarding signs:
- Dividing Integers with the Same Sign: Divide the absolute values. The result is positive.
- Dividing Integers with Different Signs: Divide the absolute values. The result is negative.
Remember, division by zero is undefined.
Real-World Applications of Integers: Where You'll Find Them
Integers aren't just abstract concepts; they have practical applications in numerous areas:
-
Temperature: Temperature scales (Celsius and Fahrenheit) use integers to represent temperatures below and above zero.
-
Finance: Integers represent financial transactions – profits are positive, losses are negative. Bank balances can be positive or negative (overdrafts).
-
Elevation: Measuring elevation above and below sea level uses integers. Heights above sea level are positive; depths below sea level are negative.
-
Gaming: Many video games utilize integers to represent scores, health points, and other game variables. A negative score might indicate a penalty.
-
Coding: Integers are fundamental in computer programming for representing numerical data and controlling program flow.
-
Science: Integers are used to represent various measurements, such as charge in physics or changes in population in biology.
Practice Problems: Test Your Understanding
Let’s solidify your understanding with some practice problems:
- What is the additive inverse of -12?
- Calculate: (-5) + 8 - (-3)
- What is the result of (-6) x 7?
- Solve: 15 ÷ (-3)
- True or False: The product of two negative integers is always positive.
- Explain the difference between whole numbers and integers.
- Give three real-world examples where negative integers are used.
Conclusion: Mastering the Integer Realm
Congratulations! You’ve journeyed through the world of integers, learning their definition, properties, and applications. Remember, consistent practice is key to mastering this mathematical concept. Use the practice problems, explore further examples, and don't hesitate to ask questions if you need clarification. The more you engage with integers, the more comfortable and confident you’ll become! Now go forth and conquer the world of numbers!
Latest Posts
Latest Posts
-
Which Of The Following Statements Describes The Process Of Globalization
Mar 26, 2025
-
What Are The Greatest Common Factors Of 48
Mar 26, 2025
-
The Unit Of Energy In S I Units Is
Mar 26, 2025
-
How Does Temperature Relate To Kinetic Energy
Mar 26, 2025
-
The Flow Of Electrons Is Called
Mar 26, 2025
Related Post
Thank you for visiting our website which covers about Definition Of Integers For Class 7 . We hope the information provided has been useful to you. Feel free to contact us if you have any questions or need further assistance. See you next time and don't miss to bookmark.
