Lcm Of 8 12 And 4
Juapaving
Mar 15, 2025 · 5 min read
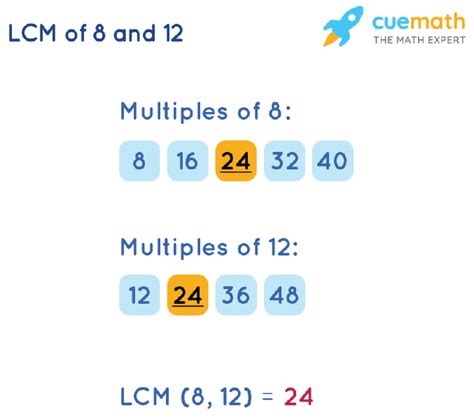
Table of Contents
Finding the Least Common Multiple (LCM) of 8, 12, and 4: A Comprehensive Guide
The least common multiple (LCM) is a fundamental concept in mathematics with wide-ranging applications, from simplifying fractions to solving complex scheduling problems. This article provides a comprehensive exploration of how to find the LCM of 8, 12, and 4, illustrating various methods and delving into the underlying mathematical principles. We'll also explore the significance of LCM in real-world scenarios and provide practical tips for solving similar problems.
Understanding Least Common Multiple (LCM)
Before diving into the calculation, let's solidify our understanding of what LCM actually means. The LCM of two or more numbers is the smallest positive integer that is a multiple of all the numbers. In simpler terms, it's the smallest number that all the given numbers can divide into evenly without leaving a remainder.
For example, let's consider the numbers 2 and 3. The multiples of 2 are 2, 4, 6, 8, 10, 12... and the multiples of 3 are 3, 6, 9, 12, 15... The smallest number that appears in both lists is 6. Therefore, the LCM of 2 and 3 is 6.
Methods for Calculating LCM
There are several efficient methods to calculate the LCM, particularly useful when dealing with larger numbers or multiple numbers. We'll explore the most common techniques:
1. Listing Multiples Method
This is a straightforward method, particularly useful for smaller numbers. We list the multiples of each number until we find the smallest common multiple.
- Multiples of 8: 8, 16, 24, 32, 40, 48, 56, 64, 72, 80...
- Multiples of 12: 12, 24, 36, 48, 60, 72, 84, 96, 108, 120...
- Multiples of 4: 4, 8, 12, 16, 20, 24, 28, 32, 36, 40, 44, 48, 52, 56, 60, 64, 68, 72, 76, 80...
By inspecting the lists, we can see that the smallest number common to all three lists is 24. Therefore, the LCM(8, 12, 4) = 24.
This method is simple but can become tedious and time-consuming with larger numbers.
2. Prime Factorization Method
This method is more efficient, especially for larger numbers. It involves finding the prime factorization of each number and then constructing the LCM using the highest powers of each prime factor present.
- Prime factorization of 8: 2³
- Prime factorization of 12: 2² x 3
- Prime factorization of 4: 2²
To find the LCM, we take the highest power of each prime factor present in the factorizations:
- The highest power of 2 is 2³ = 8
- The highest power of 3 is 3¹ = 3
Now, we multiply these highest powers together: 8 x 3 = 24. Therefore, LCM(8, 12, 4) = 24.
This method is generally preferred for its efficiency and systematic approach.
3. Greatest Common Divisor (GCD) Method
The LCM and GCD (greatest common divisor) are closely related. We can use the following formula to calculate the LCM:
LCM(a, b, c) = (a x b x c) / GCD(a, b, c)
This formula requires first finding the GCD of the three numbers. Let’s find the GCD of 8, 12, and 4 using the Euclidean algorithm:
- GCD(8, 12) = 4
- GCD(4, 4) = 4
Now, we can use the formula:
LCM(8, 12, 4) = (8 x 12 x 4) / 4 = 96 / 4 = 24
Therefore, LCM(8, 12, 4) = 24. This method is also efficient but requires understanding of GCD calculation.
Choosing the Right Method
The best method for finding the LCM depends on the numbers involved:
- Listing multiples: Suitable for small numbers where the LCM is easily identifiable.
- Prime factorization: Most efficient for larger numbers and provides a systematic approach.
- GCD method: Efficient if you already know the GCD or need to use it for other calculations.
For the numbers 8, 12, and 4, the listing multiples and prime factorization methods are relatively straightforward. However, the prime factorization method is generally preferred for its efficiency and applicability to larger or more complex sets of numbers.
Applications of LCM
The concept of LCM has practical applications in various fields:
1. Fraction Addition and Subtraction
Finding the LCM of denominators is crucial when adding or subtracting fractions with different denominators. The LCM becomes the common denominator, allowing for easy addition or subtraction of the numerators.
2. Scheduling Problems
LCM is essential in solving scheduling problems, such as determining when events will occur simultaneously. For instance, if three buses arrive at a stop every 8, 12, and 4 minutes respectively, the LCM will tell you when all three buses will arrive at the same time again. In this case, the LCM(8, 12, 4) = 24 minutes, indicating that all three buses will coincide every 24 minutes.
3. Cyclic Patterns
LCM helps determine when repeating patterns or cycles will align. For instance, in music, understanding the LCM of different rhythmic patterns can help compose complex musical pieces.
4. Gear Ratios
In mechanical engineering, LCM plays a role in calculating gear ratios and determining when different gears will synchronize.
Conclusion: Mastering LCM Calculations
Finding the least common multiple is a fundamental skill with far-reaching applications. This article explored different methods for calculating the LCM, emphasizing the efficiency and applicability of the prime factorization method. Understanding LCM is crucial not only for solving mathematical problems but also for tackling real-world scenarios involving scheduling, cycles, and other repeating patterns. By mastering these techniques, you can confidently approach LCM problems of varying complexity, improving your problem-solving skills and expanding your mathematical understanding. Remember to choose the method best suited to the specific numbers you're working with for optimal efficiency. Practice is key to mastering LCM calculations and appreciating its diverse applications.
Latest Posts
Latest Posts
-
At What Temp Does Blood Boil
Mar 15, 2025
-
The Supply Curve Is Upward Sloping Because
Mar 15, 2025
-
What Are The Prime Factors Of 22
Mar 15, 2025
-
Find The Number Of Subsets For The Following Set
Mar 15, 2025
-
Where Is The Breathing Center Located
Mar 15, 2025
Related Post
Thank you for visiting our website which covers about Lcm Of 8 12 And 4 . We hope the information provided has been useful to you. Feel free to contact us if you have any questions or need further assistance. See you next time and don't miss to bookmark.
