Lcm Of 7 3 And 4
Juapaving
Mar 22, 2025 · 5 min read
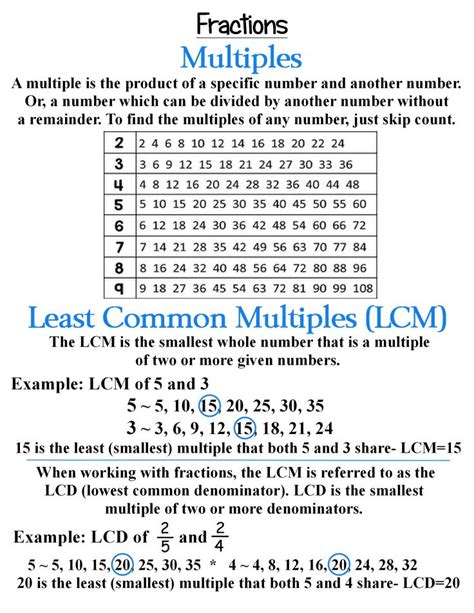
Table of Contents
Finding the LCM of 7, 3, and 4: A Comprehensive Guide
Finding the least common multiple (LCM) of a set of numbers is a fundamental concept in mathematics with applications ranging from simple fraction arithmetic to complex scheduling problems. This article will delve deep into calculating the LCM of 7, 3, and 4, exploring various methods and providing a thorough understanding of the underlying principles. We'll also touch upon the significance of LCM in real-world scenarios.
Understanding Least Common Multiple (LCM)
Before diving into the specific calculation, let's clarify the definition of the least common multiple. The LCM of two or more integers is the smallest positive integer that is divisible by all the integers without leaving a remainder. In simpler terms, it's the smallest number that contains all the given numbers as factors.
Key Characteristics of LCM:
- Positive Integer: The LCM is always a positive whole number.
- Divisibility: It's divisible by each of the given numbers.
- Smallest: It's the smallest number possessing this divisibility property.
Methods for Calculating LCM
There are several approaches to finding the LCM, each with its own advantages and disadvantages. We'll explore the most common methods, applying them to find the LCM of 7, 3, and 4.
1. Listing Multiples Method
This method involves listing the multiples of each number until a common multiple is found. While simple for smaller numbers, it becomes inefficient for larger numbers.
Multiples of 7: 7, 14, 21, 28, 35, 42, 49, 56, 63, 70, 77, 84... Multiples of 3: 3, 6, 9, 12, 15, 18, 21, 24, 27, 30, 33, 36, 39, 42, 45, 48, 51, 54, 57, 60, 63, 66, 69, 72, 75, 78, 81, 84... Multiples of 4: 4, 8, 12, 16, 20, 24, 28, 32, 36, 40, 44, 48, 52, 56, 60, 64, 68, 72, 76, 80, 84...
By comparing the lists, we can see that the smallest common multiple of 7, 3, and 4 is 84.
2. Prime Factorization Method
This method is more efficient, especially for larger numbers. It involves finding the prime factorization of each number and then constructing the LCM from the highest powers of all the prime factors involved.
- Prime Factorization of 7: 7 (7 is a prime number)
- Prime Factorization of 3: 3 (3 is a prime number)
- Prime Factorization of 4: 2²
To find the LCM, we take the highest power of each prime factor present in the factorizations:
LCM(7, 3, 4) = 2² × 3 × 7 = 4 × 3 × 7 = 84
This method is generally preferred for its efficiency and systematic approach.
3. Greatest Common Divisor (GCD) Method
The LCM and GCD (greatest common divisor) of a set of numbers are related. The product of the LCM and GCD of two numbers is equal to the product of the two numbers. While this relationship is most directly useful for two numbers, we can extend the concept. First, we find the GCD of any pair of the numbers and then use the relationship between the LCM and GCD. However, for three or more numbers, this method becomes more complex. Let's illustrate this with the numbers 7, 3, and 4:
- GCD(7,3) = 1 (7 and 3 share no common factors other than 1)
- GCD(1,4) = 1
The GCD of 7, 3, and 4 is 1. The product of the numbers is 7 x 3 x 4 = 84. Since the GCD is 1, this method doesn't directly help in finding the LCM in this specific case because the relationship simplifies to LCM = Product of numbers.
LCM in Real-World Applications
The concept of LCM finds practical applications in various real-world scenarios:
1. Scheduling and Time Management
Imagine you have three tasks: one that takes 7 days, another that takes 3 days, and a third that takes 4 days. If you want to perform all three tasks in cycles starting simultaneously, the LCM (84) indicates that all tasks will align again after 84 days. This is crucial in scheduling projects or repetitive events.
2. Fraction Operations
When adding or subtracting fractions, finding the LCM of the denominators is essential to create a common denominator, simplifying the calculation.
3. Gear Ratios and Rotations
In mechanical engineering, LCM is used to determine the least common multiple of gear rotations. This helps to synchronize the movements of multiple gears in a system.
4. Music Theory
The LCM is useful in musical theory, particularly when working with different rhythmic patterns or time signatures. Determining the LCM helps in coordinating the repetition of musical phrases and creating harmonious arrangements.
Beyond the Basics: Extending LCM Calculations
The methods outlined above can be extended to find the LCM of more than three numbers. For instance, to find the LCM of 7, 3, 4, and 5, we would follow the prime factorization method by finding the prime factorization of each number and taking the highest power of each prime factor:
- 7 = 7
- 3 = 3
- 4 = 2²
- 5 = 5
LCM(7, 3, 4, 5) = 2² × 3 × 5 × 7 = 420
Conclusion: Mastering LCM Calculations
Understanding the least common multiple is crucial for various mathematical and real-world applications. While the listing multiples method provides a basic approach, the prime factorization method offers a more efficient and systematic way, particularly for larger numbers. By mastering these methods and understanding the underlying principles, you can confidently tackle LCM calculations and leverage this fundamental concept to solve problems across diverse fields. Remember, practice is key to building proficiency. Experiment with different numbers and methods to solidify your understanding of the LCM and its practical significance.
Latest Posts
Latest Posts
-
Which Of The Following Compounds Has The Formula Kno
Mar 22, 2025
-
Write Number In Two Other Forms
Mar 22, 2025
-
What Are The Monomers Of A Dna Molecule
Mar 22, 2025
-
Two Ivory Balls Are Placed Together At Rest
Mar 22, 2025
-
Is Evaporation Of Water Endothermic Or Exothermic
Mar 22, 2025
Related Post
Thank you for visiting our website which covers about Lcm Of 7 3 And 4 . We hope the information provided has been useful to you. Feel free to contact us if you have any questions or need further assistance. See you next time and don't miss to bookmark.
