Lcm Of 2 3 And 7
Juapaving
Mar 15, 2025 · 5 min read
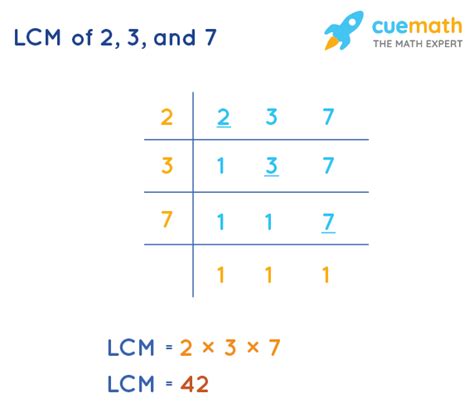
Table of Contents
Finding the Least Common Multiple (LCM) of 2, 3, and 7: A Comprehensive Guide
Finding the least common multiple (LCM) is a fundamental concept in mathematics with wide-ranging applications, from scheduling to simplifying fractions. This article will delve deep into calculating the LCM of 2, 3, and 7, exploring various methods and highlighting the importance of understanding this concept. We'll also touch upon related mathematical ideas and explore how to extend these methods to larger sets of numbers.
Understanding Least Common Multiple (LCM)
Before we dive into the specifics of finding the LCM of 2, 3, and 7, let's solidify our understanding of what the LCM actually represents. The least common multiple of two or more integers is the smallest positive integer that is divisible by all the integers without leaving a remainder. It's essentially the smallest number that contains all the given integers as factors.
Think of it like this: imagine you have three different gears, each with 2, 3, and 7 teeth respectively. You want to find the smallest number of rotations required for all three gears to simultaneously return to their starting positions. That number is the LCM of 2, 3, and 7.
Method 1: Listing Multiples
One of the simplest methods, especially for smaller numbers like 2, 3, and 7, is to list the multiples of each number until you find the smallest common multiple.
- Multiples of 2: 2, 4, 6, 8, 10, 12, 14, 16, 18, 20, 21, 22, 24, 26, 28, 30, ...
- Multiples of 3: 3, 6, 9, 12, 15, 18, 21, 24, 27, 30, ...
- Multiples of 7: 7, 14, 21, 28, 35, 42, ...
By examining the lists, we can see that the smallest number appearing in all three lists is 42. Therefore, the LCM of 2, 3, and 7 is 42.
Method 2: Prime Factorization
This method is more efficient for larger numbers and provides a deeper understanding of the underlying mathematical principles. It involves expressing each number as a product of its prime factors.
- Prime factorization of 2: 2¹
- Prime factorization of 3: 3¹
- Prime factorization of 7: 7¹
The LCM is found by taking the highest power of each prime factor present in the factorizations. In this case, we have:
2¹ * 3¹ * 7¹ = 42
Therefore, the LCM of 2, 3, and 7 is 42. This method is particularly useful when dealing with larger numbers or a greater number of integers. It systematically accounts for all prime factors ensuring you find the smallest common multiple.
Method 3: Greatest Common Divisor (GCD) and LCM Relationship
The LCM and the greatest common divisor (GCD) are intimately related. The product of the LCM and GCD of two or more integers is equal to the product of the integers themselves. This relationship provides an alternative method for finding the LCM.
First, let's find the GCD of 2, 3, and 7 using the Euclidean algorithm or prime factorization. Since 2, 3, and 7 are all prime numbers, their GCD is 1.
Now, we can use the relationship:
LCM(a, b, c) * GCD(a, b, c) = a * b * c
Substituting the values:
LCM(2, 3, 7) * 1 = 2 * 3 * 7
LCM(2, 3, 7) = 42
Applications of LCM
The LCM has numerous applications across various fields:
-
Scheduling: Imagine you have two events that occur at regular intervals. The LCM helps determine when both events will occur simultaneously. For example, if one event happens every 2 days and another every 3 days, they will both occur on the same day every 6 days (the LCM of 2 and 3).
-
Fraction Addition and Subtraction: Finding the LCM of the denominators is crucial when adding or subtracting fractions. This allows you to find a common denominator, simplifying the calculation process.
-
Modular Arithmetic: LCM plays a crucial role in modular arithmetic, a branch of mathematics dealing with remainders after division. It helps solve problems related to congruences and cycles.
-
Music Theory: The LCM is used to determine the least common period of two or more musical notes with different frequencies.
-
Project Management: In project scheduling, LCM helps to determine the time it will take for multiple tasks with varying durations to be completed concurrently.
Extending the Concept to Larger Sets of Numbers
The methods described above can be extended to find the LCM of more than three numbers. For the prime factorization method, you simply include all prime factors from all numbers, taking the highest power of each. For the listing method, you'll have more lists to compare, but the principle remains the same. The relationship between LCM and GCD remains valid regardless of the number of integers.
Practical Example: Scheduling Tasks
Let's say you have three tasks: Task A takes 2 days, Task B takes 3 days, and Task C takes 7 days. If you start all three tasks on the same day, when will all three tasks be completed simultaneously?
The answer is found by calculating the LCM of 2, 3, and 7, which we know is 42. Therefore, all three tasks will be completed simultaneously after 42 days.
Conclusion
Finding the least common multiple is a straightforward yet powerful mathematical technique with practical implications across various disciplines. Understanding the different methods – listing multiples, prime factorization, and the LCM-GCD relationship – equips you with the tools to solve problems involving LCM effectively. Whether you're dealing with simple scheduling problems or more complex mathematical calculations, mastering the concept of LCM is essential for success. Remember that practicing different problems will solidify your understanding and help you develop proficiency in applying these techniques. The seemingly simple problem of finding the LCM of 2, 3, and 7 serves as a gateway to a deeper understanding of fundamental mathematical principles with wide-ranging applications.
Latest Posts
Latest Posts
-
How Do You Find The Inverse Of A Relation
Mar 17, 2025
-
Does Cold Air Go Up Or Down
Mar 17, 2025
-
Least Common Multiple Of 20 And 3
Mar 17, 2025
-
Function Of The Motor End Plate
Mar 17, 2025
-
A Push Or A Pull Is Called
Mar 17, 2025
Related Post
Thank you for visiting our website which covers about Lcm Of 2 3 And 7 . We hope the information provided has been useful to you. Feel free to contact us if you have any questions or need further assistance. See you next time and don't miss to bookmark.
