Lcm Of 12 8 And 10
Juapaving
Mar 22, 2025 · 5 min read
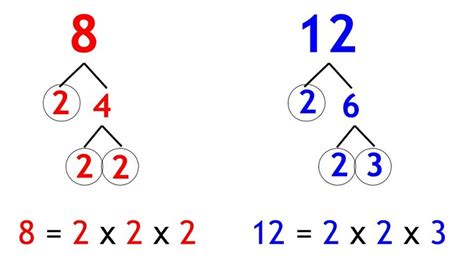
Table of Contents
Finding the Least Common Multiple (LCM) of 12, 8, and 10: A Comprehensive Guide
The least common multiple (LCM) is a fundamental concept in mathematics, particularly in number theory and arithmetic. Understanding how to calculate the LCM is crucial for various applications, from simplifying fractions to solving problems in algebra and beyond. This comprehensive guide will delve into the intricacies of finding the LCM of 12, 8, and 10, exploring multiple methods and providing a solid understanding of the underlying principles.
Understanding Least Common Multiple (LCM)
Before we tackle the specific problem of finding the LCM of 12, 8, and 10, let's establish a clear understanding of what the LCM represents. The least common multiple of two or more integers is the smallest positive integer that is divisible by all the given integers. In simpler terms, it's the smallest number that all the given numbers can divide into evenly without leaving a remainder.
For example, consider the numbers 4 and 6. The multiples of 4 are 4, 8, 12, 16, 20, 24... and the multiples of 6 are 6, 12, 18, 24, 30... The smallest number that appears in both lists is 12. Therefore, the LCM of 4 and 6 is 12.
Methods for Calculating the LCM
Several methods exist for calculating the LCM, each with its own advantages and disadvantages. We'll explore the most common approaches, focusing on their application to find the LCM of 12, 8, and 10.
Method 1: Listing Multiples
This is the most straightforward method, especially for smaller numbers. We list the multiples of each number until we find the smallest multiple common to all.
- Multiples of 12: 12, 24, 36, 48, 60, 72, 84, 96, 108, 120...
- Multiples of 8: 8, 16, 24, 32, 40, 48, 56, 64, 72, 80, 88, 96, 104, 112, 120...
- Multiples of 10: 10, 20, 30, 40, 50, 60, 70, 80, 90, 100, 110, 120...
By examining the lists, we observe that the smallest common multiple is 120. Therefore, the LCM(12, 8, 10) = 120. While simple for small numbers, this method becomes cumbersome and inefficient for larger numbers.
Method 2: Prime Factorization
This method is more efficient, especially for larger numbers. It involves finding the prime factorization of each number and then constructing the LCM from the prime factors.
- Prime factorization of 12: 2² x 3
- Prime factorization of 8: 2³
- Prime factorization of 10: 2 x 5
To find the LCM, we take the highest power of each prime factor present in the factorizations:
- Highest power of 2: 2³ = 8
- Highest power of 3: 3¹ = 3
- Highest power of 5: 5¹ = 5
Now, multiply these highest powers together: 8 x 3 x 5 = 120. Therefore, the LCM(12, 8, 10) = 120. This method is generally preferred for its efficiency and applicability to larger numbers.
Method 3: Using the Greatest Common Divisor (GCD)
The LCM and GCD (greatest common divisor) are closely related. The product of the LCM and GCD of two numbers is equal to the product of the two numbers. We can extend this relationship to multiple numbers, although the calculation becomes more complex. First, we need to find the GCD of the numbers.
We can use the Euclidean algorithm to find the GCD of 12, 8, and 10.
-
GCD(12, 8):
- 12 = 8 x 1 + 4
- 8 = 4 x 2 + 0 The GCD(12, 8) = 4
-
GCD(4, 10):
- 10 = 4 x 2 + 2
- 4 = 2 x 2 + 0 The GCD(4, 10) = 2
Therefore, the GCD(12, 8, 10) = 2. However, extending this method directly to find the LCM of three or more numbers is less intuitive and often involves iterative calculations.
While this method demonstrates the relationship between GCD and LCM, the prime factorization method remains the most straightforward and efficient approach for finding the LCM of multiple numbers.
Applications of LCM
The LCM finds practical applications in various fields:
- Fractions: Finding the least common denominator (LCD) when adding or subtracting fractions. The LCD is simply the LCM of the denominators.
- Scheduling: Determining when events will occur simultaneously. For example, if three events occur every 12, 8, and 10 days respectively, the LCM helps determine when they will all occur on the same day.
- Cyclic Patterns: Identifying the point where repeating cycles coincide.
- Modular Arithmetic: Solving congruences and other problems in number theory.
Solving Similar Problems
Let's practice finding the LCM of other sets of numbers using the prime factorization method:
Example 1: Find the LCM of 15, 20, and 25.
- Prime factorization of 15: 3 x 5
- Prime factorization of 20: 2² x 5
- Prime factorization of 25: 5²
LCM = 2² x 3 x 5² = 4 x 3 x 25 = 300
Example 2: Find the LCM of 18, 24, and 30.
- Prime factorization of 18: 2 x 3²
- Prime factorization of 24: 2³ x 3
- Prime factorization of 30: 2 x 3 x 5
LCM = 2³ x 3² x 5 = 8 x 9 x 5 = 360
Example 3: Find the LCM of 14, 21, and 35.
- Prime factorization of 14: 2 x 7
- Prime factorization of 21: 3 x 7
- Prime factorization of 35: 5 x 7
LCM = 2 x 3 x 5 x 7 = 210
Conclusion: Mastering LCM Calculations
The least common multiple is a fundamental concept with wide-ranging applications. While several methods exist for calculating the LCM, the prime factorization method provides the most efficient and systematic approach, especially when dealing with larger numbers or multiple numbers. By understanding the underlying principles and practicing different examples, you can confidently tackle LCM calculations and apply this crucial concept to solve problems in various mathematical contexts. Remember to break down each number into its prime factors and then carefully multiply the highest powers of each prime factor to find the LCM. This methodical approach will ensure accuracy and efficiency in your calculations. Mastering LCM calculations will significantly enhance your mathematical skills and problem-solving abilities.
Latest Posts
Latest Posts
-
What Happens When Air Masses Collide
Mar 23, 2025
-
The Outermost Layer Of The Suns Atmosphere
Mar 23, 2025
-
Area And Perimeter Of Similar Figures
Mar 23, 2025
-
Words That Have K In Them
Mar 23, 2025
-
Does A Rhombus Have All Equal Sides
Mar 23, 2025
Related Post
Thank you for visiting our website which covers about Lcm Of 12 8 And 10 . We hope the information provided has been useful to you. Feel free to contact us if you have any questions or need further assistance. See you next time and don't miss to bookmark.
