Is The Square Root Of 14 A Rational Number
Juapaving
Mar 23, 2025 · 5 min read
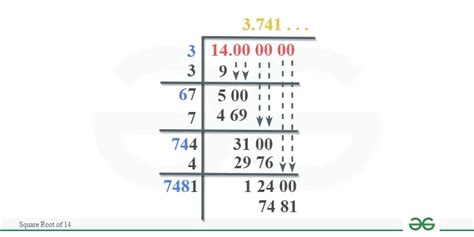
Table of Contents
Is the Square Root of 14 a Rational Number? A Deep Dive into Irrationality
The question of whether the square root of 14 is a rational number is a fundamental concept in mathematics, touching upon the core distinctions between rational and irrational numbers. This article will delve deep into this question, exploring the definition of rational and irrational numbers, demonstrating why √14 is irrational, and exploring related concepts to solidify your understanding.
Understanding Rational and Irrational Numbers
Before we tackle the specific case of √14, let's establish a clear understanding of rational and irrational numbers.
Rational Numbers: A rational number is any number that can be expressed as a fraction p/q, where 'p' and 'q' are integers, and 'q' is not equal to zero. This means the number can be represented as a terminating or repeating decimal. Examples include 1/2 (0.5), 3/4 (0.75), -2/3 (-0.666...), and even whole numbers like 5 (5/1).
Irrational Numbers: An irrational number is a number that cannot be expressed as a fraction p/q, where 'p' and 'q' are integers, and 'q' is not zero. Their decimal representation is non-terminating and non-repeating. Famous examples include π (pi), e (Euler's number), and the square root of most non-perfect squares.
Proving the Irrationality of √14
To prove that √14 is irrational, we'll employ a common proof technique called proof by contradiction. This method assumes the opposite of what we want to prove and then demonstrates that this assumption leads to a contradiction, thereby proving the original statement.
1. The Assumption:
Let's assume that √14 is a rational number. This means we can express it as a fraction p/q, where 'p' and 'q' are integers, 'q' is not zero, and the fraction is in its simplest form (meaning 'p' and 'q' share no common factors other than 1).
2. Squaring Both Sides:
If √14 = p/q, then squaring both sides gives us:
14 = p²/q²
3. Rearranging the Equation:
Multiplying both sides by q² gives:
14q² = p²
This equation tells us that p² is an even number (because it's a multiple of 14, which is even). If p² is even, then 'p' itself must also be even (because the square of an odd number is always odd).
4. Substituting and Simplifying:
Since 'p' is even, we can express it as 2k, where 'k' is another integer. Substituting this into our equation:
14q² = (2k)²
14q² = 4k²
Dividing both sides by 2:
7q² = 2k²
This equation shows that 2k² is divisible by 7. Since 2 and 7 are prime numbers and don't share common factors, it follows that q² must be divisible by 7, and therefore 'q' must also be divisible by 7.
5. The Contradiction:
We've now established that both 'p' and 'q' are divisible by 7. This contradicts our initial assumption that p/q is in its simplest form (meaning they share no common factors). Since our initial assumption leads to a contradiction, the assumption must be false.
6. Conclusion:
Therefore, our initial assumption that √14 is a rational number is incorrect. Consequently, √14 is an irrational number.
Further Exploration of Irrational Numbers
The irrationality of √14 is just one example within a vast landscape of irrational numbers. Let's explore some related concepts:
Square Roots of Non-Perfect Squares
The square root of any positive integer that is not a perfect square (1, 4, 9, 16, etc.) will always be an irrational number. This is because a perfect square's square root can be expressed as an integer (and thus as a rational number). Non-perfect squares, on the other hand, lack this property.
Other Types of Irrational Numbers
Beyond square roots, many other types of numbers are irrational. These include:
-
Transcendental Numbers: These are numbers that are not the root of any non-zero polynomial equation with rational coefficients. Famous examples include π and e. Their irrationality is significantly harder to prove than that of √14.
-
Algebraic Irrational Numbers: These are irrational numbers that are roots of polynomial equations with rational coefficients. √14 falls under this category.
Approximating Irrational Numbers
Although irrational numbers have non-terminating, non-repeating decimal expansions, we can approximate them using rational numbers. This is often done through truncating the decimal representation or using continued fractions. For instance, √14 is approximately 3.741657... We can approximate it with 3.74, 3.741, or more precise fractions.
Practical Implications and Applications
While the concept of irrational numbers might seem purely theoretical, they have practical applications in various fields:
-
Geometry: Irrational numbers are essential in geometric calculations involving circles, triangles, and other shapes. For example, calculating the circumference or area of a circle involves the irrational number π.
-
Physics: Many physical phenomena are described using irrational numbers. For example, the ratio of the circumference to the diameter of a circle (π) appears frequently in physics equations.
-
Engineering: Engineering designs often involve irrational numbers in calculations related to curves, angles, and proportions.
-
Computer Science: Representing and calculating with irrational numbers presents computational challenges, leading to the development of sophisticated algorithms and approximations.
Conclusion
The proof that √14 is irrational highlights a fundamental concept in number theory. Understanding the difference between rational and irrational numbers is crucial for grasping various mathematical and scientific principles. While we cannot represent √14 as a simple fraction, its irrationality does not diminish its significance or practical usefulness within numerous fields. Its existence and the methodology used to prove its irrationality showcase the beauty and complexity of the mathematical world. Remember, the journey of mathematical understanding is a continuous process of exploration and discovery.
Latest Posts
Latest Posts
-
Common Factors Of 20 And 40
Mar 25, 2025
-
How Many Lines Of Symmetry Does A Rectangle Has
Mar 25, 2025
-
Lowest Common Denominator Of 9 And 12
Mar 25, 2025
-
Is 15 A Prime Or Composite Number
Mar 25, 2025
-
Facilitated Diffusion And Active Transport Differ In That
Mar 25, 2025
Related Post
Thank you for visiting our website which covers about Is The Square Root Of 14 A Rational Number . We hope the information provided has been useful to you. Feel free to contact us if you have any questions or need further assistance. See you next time and don't miss to bookmark.
