How Many Lines Of Symmetry Does A Rectangle Has
Juapaving
Mar 25, 2025 · 5 min read
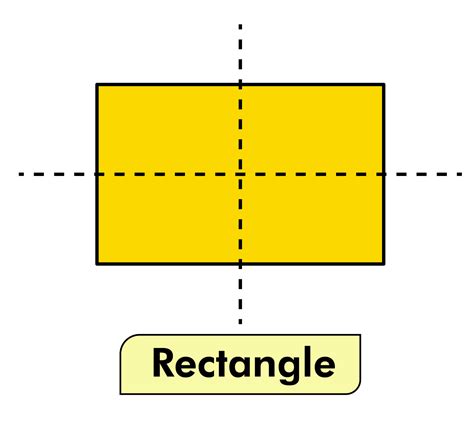
Table of Contents
How Many Lines of Symmetry Does a Rectangle Have? A Deep Dive into Geometric Symmetry
Symmetry, a fundamental concept in mathematics and art, captivates us with its inherent beauty and order. Understanding symmetry, particularly in geometric shapes, unlocks a deeper appreciation for the underlying principles of shape and form. This article delves into the fascinating world of symmetry, focusing specifically on the question: how many lines of symmetry does a rectangle possess? We'll explore the definition of symmetry, different types of symmetry, and then meticulously examine the case of the rectangle, clarifying any potential confusion. We'll also touch upon related shapes and concepts to provide a comprehensive understanding of this geometric property.
Understanding Symmetry: A Foundation
Before we tackle the rectangle, let's establish a clear understanding of symmetry. In its simplest form, symmetry refers to a balanced and proportionate arrangement of parts. In geometry, we focus on two main types of symmetry:
1. Line Symmetry (Reflectional Symmetry)
Line symmetry, also known as reflectional symmetry, occurs when a shape can be folded along a line, creating two identical halves that mirror each other. This line of folding is called the line of symmetry or axis of symmetry. If you were to place a mirror along the line of symmetry, the reflection in the mirror would perfectly overlap the other half of the shape.
2. Rotational Symmetry
Rotational symmetry, on the other hand, involves rotating a shape around a central point. If the shape looks identical after a rotation of less than 360 degrees, it possesses rotational symmetry. The number of times the shape looks identical during a full 360-degree rotation determines its order of rotational symmetry. For example, a square has rotational symmetry of order 4 because it looks identical four times during a 360-degree rotation (at 90°, 180°, 270°, and 360°).
Exploring the Rectangle's Symmetry
Now, let's address the central question: how many lines of symmetry does a rectangle possess?
A rectangle is a quadrilateral (a four-sided polygon) with four right angles. Crucially, opposite sides of a rectangle are equal in length and parallel. This seemingly simple definition holds the key to understanding its symmetry.
To determine the lines of symmetry, imagine folding a rectangle. A rectangle can be folded in two ways to produce two identical halves:
-
Folding along the line connecting the midpoints of opposite sides: This creates two congruent (identical) rectangles. This line of symmetry is vertical if the rectangle is oriented in a landscape position, and horizontal if the rectangle is oriented in a portrait position.
-
Folding along the other line connecting the midpoints of opposite sides: This creates two congruent rectangles, and this line of symmetry is perpendicular to the first line of symmetry.
Therefore, a rectangle has two lines of symmetry. No other lines of symmetry exist. Attempting to fold a rectangle along any other line will not result in two identical halves. This demonstrates that the number of lines of symmetry is directly tied to the properties of the shape.
Comparing Rectangles to Other Shapes
Let's compare the rectangle's symmetry to other related shapes to further solidify our understanding:
Square
A square is a special type of rectangle where all four sides are equal in length. This additional property grants it more symmetry. A square has four lines of symmetry: two that connect the midpoints of opposite sides, and two that connect opposite corners (diagonals).
Rhombus
A rhombus is a quadrilateral with all four sides equal in length. However, unlike a square, its angles are not necessarily right angles. A rhombus has two lines of symmetry: the diagonals.
Parallelogram
A parallelogram is a quadrilateral with opposite sides parallel and equal in length. Unlike a rectangle, its angles are not necessarily right angles. A parallelogram has no lines of symmetry, although it does possess rotational symmetry of order 2 (180° rotation).
Irregular Quadrilaterals
Irregular quadrilaterals, which have no equal sides or angles, typically possess no lines of symmetry.
The Significance of Symmetry in Various Fields
The concept of symmetry extends far beyond the realm of pure geometry. It plays a crucial role in numerous fields:
-
Art and Design: Symmetry is a fundamental principle in art and design, creating visually appealing and balanced compositions. From architecture to painting, symmetry contributes to harmony and aesthetic pleasure.
-
Nature: Symmetry is prevalent in nature, evident in the patterns of snowflakes, flowers, and animal bodies. Its presence suggests underlying principles of efficiency and optimal growth.
-
Physics and Chemistry: Symmetry plays a crucial role in physics and chemistry, influencing properties of molecules and physical phenomena. For example, the symmetry of a molecule can determine its reactivity and other chemical properties.
-
Mathematics: Symmetry forms the basis of many mathematical concepts and theorems, serving as a powerful tool in solving complex problems. Group theory, a branch of abstract algebra, is deeply connected to the concept of symmetry.
Exploring Further: Advanced Concepts Related to Symmetry
For those interested in a more in-depth exploration, several advanced concepts are worth investigating:
-
Point Symmetry: A shape has point symmetry if it looks the same when rotated 180 degrees about a central point. Both rectangles and squares have point symmetry.
-
Crystallography: The study of crystals heavily relies on understanding different types of symmetry. Crystals exhibit various symmetry operations, including rotations, reflections, and inversions.
-
Frieze Patterns and Wallpaper Groups: These are mathematical classifications of repeating patterns, categorizing them based on their symmetry properties.
Conclusion: The Rectangle's Two Lines of Symmetry
In conclusion, a rectangle possesses two lines of symmetry, each connecting the midpoints of opposite sides. Understanding this seemingly simple geometric property provides a foundational understanding of symmetry and its broader significance across numerous disciplines. By comparing rectangles to other shapes, we gain a clearer appreciation for the relationship between a shape's properties and its symmetry. The concept of symmetry, explored through the lens of the rectangle, opens doors to deeper exploration of mathematical beauty and its influence on the world around us. The seemingly simple question of a rectangle's lines of symmetry unveils a rich and multifaceted world of geometric principles and their wide-ranging applications.
Latest Posts
Latest Posts
-
Drops Collected From In Column Chromatography
Mar 25, 2025
-
What Is 1 25 In Fraction Form
Mar 25, 2025
-
How Many Sides Does A Trapezoid Has
Mar 25, 2025
-
How Many Seconds In 45 Minutes
Mar 25, 2025
-
What Do The Arrows In A Food Chain Mean
Mar 25, 2025
Related Post
Thank you for visiting our website which covers about How Many Lines Of Symmetry Does A Rectangle Has . We hope the information provided has been useful to you. Feel free to contact us if you have any questions or need further assistance. See you next time and don't miss to bookmark.
