Is The Spleen Part Of The Endocrine System
Juapaving
Apr 06, 2025 · 5 min read
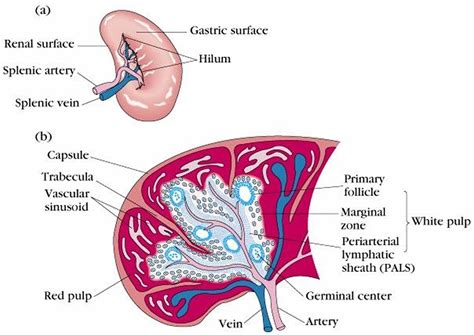
Table of Contents
Is the Spleen Part of the Endocrine System? Unraveling the Complexities of a Vital Organ
The spleen, a fist-sized organ nestled in the upper left quadrant of the abdomen, often gets overlooked in discussions of the body's intricate systems. While primarily known for its role in the lymphatic and immune systems, the question of whether the spleen belongs to the endocrine system is a fascinating one, demanding a deeper exploration of its multifaceted functions. The simple answer is no, the spleen is not considered a primary organ of the endocrine system. However, its contributions to endocrine function are more nuanced and significant than a simple "no" can adequately convey. This article delves into the spleen's complex relationship with the endocrine system, exploring its various roles and clarifying its position within the body's overall regulatory network.
Understanding the Endocrine System: A Brief Overview
Before we dissect the spleen's involvement, it's crucial to understand the endocrine system's core function. The endocrine system is a network of glands that produce and secrete hormones directly into the bloodstream. These hormones act as chemical messengers, regulating a vast array of bodily processes, including:
- Metabolism: Hormones control how the body uses and stores energy.
- Growth and Development: Hormones influence growth, maturation, and reproduction.
- Mood: Hormones significantly affect emotions and cognitive function.
- Tissue Function: Hormones regulate the activities of various tissues and organs.
- Sexual Function: Hormones are essential for sexual development and reproduction.
Classical endocrine glands include the pituitary, thyroid, parathyroid, adrenal, pineal glands, and the pancreas (islet cells). These glands produce well-defined hormones with specific, identifiable targets. The spleen, however, doesn't fit neatly into this classical definition.
The Spleen's Primary Roles: Immunity and Hematopoiesis
The spleen's primary functions reside within the immune and lymphatic systems. It acts as a crucial filter for the blood, removing old or damaged red blood cells, platelets, and bacteria. This process, known as erythrophagocytosis, is essential for maintaining healthy blood composition.
Furthermore, the spleen plays a significant role in hematopoiesis, particularly during fetal development. It produces red blood cells, white blood cells, and platelets. While this role diminishes after birth (hematopoiesis largely shifts to the bone marrow), the spleen retains its capacity to resume this function under certain circumstances, such as bone marrow failure.
The spleen also houses a significant population of lymphocytes, including B cells and T cells. These cells are vital components of the adaptive immune system, recognizing and eliminating specific pathogens. The spleen acts as a crucial site for antibody production and immune response initiation.
The Spleen's Indirect Influence on Endocrine Function
While not a classic endocrine gland, the spleen indirectly influences endocrine function in several ways:
1. Immune Regulation and Hormone Production: The immune system and endocrine system are intimately interconnected. Chronic inflammation, often managed by the immune system (in which the spleen plays a key role), can significantly affect hormone production and function. For instance, autoimmune diseases often lead to hormonal imbalances. The spleen’s involvement in immune regulation thus indirectly affects the endocrine milieu.
2. Erythrophagocytosis and Hormone Production: The spleen's removal of damaged red blood cells is vital for maintaining iron homeostasis. Iron is an essential component of hemoglobin, and its regulation is critical. Iron levels influence the production of erythropoietin (EPO), a hormone produced primarily by the kidneys that stimulates red blood cell production. Dysfunction in the spleen's erythrophagocytic activity can indirectly affect EPO production and red blood cell levels.
3. Cytokine Production and Endocrine Signaling: The spleen produces various cytokines, small proteins that act as signaling molecules within the immune system. Some cytokines also have endocrine effects, influencing hormone production and function in other organs. For example, certain cytokines can affect the hypothalamic-pituitary-adrenal (HPA) axis, which is a central component of the stress response system and regulates hormone production in the adrenal glands.
4. Interactions with Other Immune and Endocrine Organs: The spleen's intricate network of interactions with other organs further complicates the simple classification. It interacts extensively with the bone marrow (hematopoiesis), the thymus (T cell maturation), and the lymph nodes (lymphocyte circulation). These organs, in turn, have their own subtle influences on the endocrine system, making it difficult to isolate the spleen's specific contributions.
Splenectomy and Endocrine Function: Clinical Observations
Splenectomy, the surgical removal of the spleen, can provide indirect insights into its relationship with endocrine function. While splenectomy primarily affects immune function, some studies have suggested potential, albeit subtle, consequences on hormonal levels. However, these changes are typically overshadowed by the more significant impact on immune function and blood cell counts.
Conclusion: The Spleen's Complex Role in the Body's Regulatory Network
The question of whether the spleen is part of the endocrine system necessitates a careful consideration of its multifaceted roles. While the spleen doesn't directly produce hormones in the same way as classical endocrine glands, its contributions to immune regulation, hematopoiesis, and cytokine production exert significant indirect influences on endocrine function. Its intricate interplay with other immune and endocrine organs further complicates a simple categorization. Therefore, while not a primary endocrine organ, the spleen's influence on endocrine balance cannot be ignored. Its activities are intricately woven into the body's complex regulatory network, highlighting the importance of holistic understanding of physiological processes.
Further research focusing on the specific cytokines produced by the spleen and their endocrine effects, alongside detailed studies on the long-term hormonal changes following splenectomy, could provide deeper insights into this fascinating interplay. Understanding this complex relationship is essential for advancing our understanding of health and disease, particularly in conditions where both the immune and endocrine systems are affected. The spleen, often relegated to a supporting role, plays a far more significant and nuanced part in the body's intricate symphony of regulatory functions than previously recognized.
Latest Posts
Latest Posts
-
How Many Cups Is 6 Quarts Of Water
Apr 07, 2025
-
System Of Linear Equations Practice Problems
Apr 07, 2025
-
Lcm Of 6 7 And 8
Apr 07, 2025
-
What Organisms Need To Be The Fittest To Survive
Apr 07, 2025
-
How Many Angles In A Triangle
Apr 07, 2025
Related Post
Thank you for visiting our website which covers about Is The Spleen Part Of The Endocrine System . We hope the information provided has been useful to you. Feel free to contact us if you have any questions or need further assistance. See you next time and don't miss to bookmark.