Is Nh4oh An Acid Or Base
Juapaving
Mar 18, 2025 · 5 min read
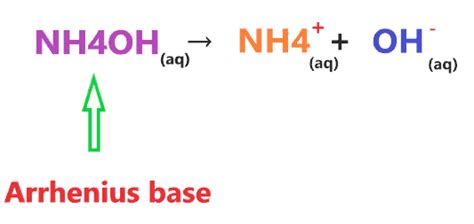
Table of Contents
Is NH₄OH an Acid or a Base? Understanding Ammonium Hydroxide
Ammonium hydroxide, often represented as NH₄OH, is a common chemical compound that sparks curiosity among students and chemistry enthusiasts alike. The question of whether it's an acid or a base often arises due to its unique properties and the way it behaves in aqueous solutions. This comprehensive article will delve deep into the nature of NH₄OH, exploring its chemical structure, its behavior in water, and the factors that contribute to its classification as a base. We'll also examine related concepts and dispel common misconceptions.
Understanding Acids and Bases
Before we classify NH₄OH, let's refresh our understanding of acids and bases. Several theories help us define these fundamental chemical entities.
Arrhenius Theory
The Arrhenius theory, one of the earliest definitions, states that an acid is a substance that increases the concentration of hydrogen ions (H⁺) in an aqueous solution, while a base increases the concentration of hydroxide ions (OH⁻). While simple, this theory has limitations, as it only applies to aqueous solutions.
Brønsted-Lowry Theory
A more comprehensive approach is the Brønsted-Lowry theory. This theory defines an acid as a proton (H⁺) donor and a base as a proton acceptor. This definition extends beyond aqueous solutions and allows for a broader understanding of acid-base reactions.
Lewis Theory
The most general theory is the Lewis theory, which defines an acid as an electron-pair acceptor and a base as an electron-pair donor. This encompasses a wider range of reactions than the previous theories.
The Chemical Structure of NH₄OH
Ammonium hydroxide, despite its formula, doesn't exist as a distinct molecule in the way we might think of water (H₂O) or ammonia (NH₃). It's more accurately described as an aqueous solution of ammonia (NH₃) in water (H₂O). When ammonia dissolves in water, it reacts with water molecules to form ammonium ions (NH₄⁺) and hydroxide ions (OH⁻):
NH₃(g) + H₂O(l) ⇌ NH₄⁺(aq) + OH⁻(aq)
This equilibrium reaction is crucial to understanding NH₄OH's properties. The presence of hydroxide ions (OH⁻) is the key to its classification.
Why NH₄OH is Considered a Base
The presence of hydroxide ions (OH⁻) in the aqueous solution of ammonia directly dictates its classification as a base. According to both the Arrhenius and Brønsted-Lowry theories, NH₄OH acts as a base because it increases the concentration of hydroxide ions (OH⁻) in the solution. The equilibrium reaction shows that while the reaction is reversible, a significant amount of OH⁻ ions are produced.
Evidence from its Reactions
Further supporting the base classification are the reactions NH₄OH undergoes:
-
Neutralization reactions: NH₄OH readily reacts with acids to form salts and water. This is a hallmark characteristic of bases. For example, its reaction with hydrochloric acid (HCl):
NH₄OH(aq) + HCl(aq) → NH₄Cl(aq) + H₂O(l)
-
pH measurements: Aqueous solutions of NH₄OH exhibit a pH greater than 7, which is indicative of a basic solution. The pH value depends on the concentration of NH₄OH.
-
Reactions with indicators: NH₄OH changes the color of acid-base indicators like litmus paper (turning it blue) and phenolphthalein (turning it pink), further demonstrating its basic nature.
Weak Base Nature of NH₄OH
It's important to note that NH₄OH is a weak base. This means that it only partially dissociates in water, unlike strong bases like sodium hydroxide (NaOH) which fully dissociate. The equilibrium reaction shown earlier highlights this partial dissociation. The equilibrium lies to the left, meaning a significant portion of the ammonia remains unreacted in its NH₃ form. This partial dissociation leads to a lower concentration of OH⁻ ions compared to what a strong base would produce at the same concentration.
Misconceptions about NH₄OH
There are some common misconceptions about ammonium hydroxide that should be clarified:
-
NH₄OH as a distinct molecule: It's crucial to reiterate that NH₄OH doesn't exist as a separate molecule. It is an aqueous solution of ammonia.
-
Confusing it with ammonium salts: Ammonium salts, like ammonium chloride (NH₄Cl), are acidic, while NH₄OH is basic. This difference stems from the presence of the hydroxide ion (OH⁻) in the latter.
-
Overestimating its strength: NH₄OH is a weak base, not a strong one. It's crucial not to treat it as a strong base in calculations or reactions, as this can lead to inaccurate results.
Practical Applications of NH₄OH
Despite its weak nature, NH₄OH finds several applications due to its basic properties:
-
Cleaning products: It's a component in many household cleaning agents due to its ability to dissolve grease and grime.
-
Fertilizers: Ammonia is a crucial component in fertilizers, and NH₄OH can be used in their production.
-
Textile industry: It plays a role in some textile processes, such as dyeing and finishing.
-
Food industry: In some instances, it's used as a food additive, acting as a leavening agent in certain baked goods.
-
Laboratory reagent: It's commonly used in laboratories as a base in various experiments and chemical reactions.
Conclusion: Understanding the nuances of NH₄OH
In conclusion, ammonium hydroxide, while often represented as NH₄OH, is more accurately described as an aqueous solution of ammonia (NH₃) in water. Its interaction with water leads to the formation of ammonium ions (NH₄⁺) and hydroxide ions (OH⁻). The presence of hydroxide ions unequivocally classifies NH₄OH as a base, specifically a weak base due to its partial dissociation in water. Understanding this distinction, alongside its weak base nature and its common applications, is crucial for anyone working with or studying this important chemical compound. Avoiding common misconceptions about its molecular structure and strength is vital for accurate scientific interpretations and safe handling. The chemical behaviour of NH₄OH provides a practical and illustrative example of the complexities and subtleties inherent in the chemistry of acids and bases. Remember, accurate classification and understanding of its properties are essential in its various applications.
Latest Posts
Latest Posts
-
How Many Faces On A Dice
Mar 19, 2025
-
Which Kingdom Does Not Contain Any Eukaryotes
Mar 19, 2025
-
Database Is A Collection Of Related Data
Mar 19, 2025
-
Is Distilled Water An Acid Or A Base
Mar 19, 2025
-
How Do You Calculate Absolute Pressure
Mar 19, 2025
Related Post
Thank you for visiting our website which covers about Is Nh4oh An Acid Or Base . We hope the information provided has been useful to you. Feel free to contact us if you have any questions or need further assistance. See you next time and don't miss to bookmark.
