Is Na2co3 Acidic Basic Or Neutral
Juapaving
Mar 31, 2025 · 5 min read
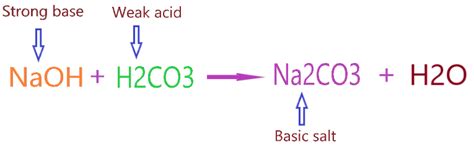
Table of Contents
Is Na₂CO₃ Acidic, Basic, or Neutral? A Deep Dive into Sodium Carbonate's Properties
Sodium carbonate (Na₂CO₃), also known as washing soda or soda ash, is a widely used chemical compound with numerous industrial and household applications. Understanding its acid-base properties is crucial for its safe and effective use. This article will delve deep into the chemical properties of Na₂CO₃, explaining why it's considered basic and exploring its reactions in various contexts. We'll also examine its practical implications and safety considerations.
Understanding pH and Acid-Base Chemistry
Before diving into the specifics of sodium carbonate, let's establish a fundamental understanding of pH and acid-base chemistry. The pH scale measures the acidity or basicity of a solution, ranging from 0 to 14. A pH of 7 is considered neutral, while values below 7 are acidic and values above 7 are basic (or alkaline).
Acids are substances that donate protons (H⁺ ions) in a solution, while bases are substances that accept protons or donate hydroxide ions (OH⁻ ions). The strength of an acid or base is determined by its ability to donate or accept protons. Strong acids and bases completely dissociate in water, while weak acids and bases only partially dissociate.
The Chemistry of Sodium Carbonate: Why It's Basic
Sodium carbonate is a salt, formed from the neutralization reaction between a strong base (sodium hydroxide, NaOH) and a weak acid (carbonic acid, H₂CO₃). This is key to understanding its basic nature.
The reaction can be represented as:
2NaOH (aq) + H₂CO₃ (aq) → Na₂CO₃ (aq) + 2H₂O (l)
When sodium carbonate dissolves in water, it undergoes hydrolysis. This means it reacts with water molecules, leading to the formation of hydroxide ions (OH⁻):
Na₂CO₃ (aq) + H₂O (l) ⇌ 2Na⁺ (aq) + HCO₃⁻ (aq) + OH⁻ (aq)
The bicarbonate ion (HCO₃⁻) can further react with water, though to a lesser extent:
HCO₃⁻ (aq) + H₂O (l) ⇌ H₂CO₃ (aq) + OH⁻ (aq)
These reactions generate an excess of hydroxide ions (OH⁻) in the solution, which directly contributes to its alkaline pH. The presence of these hydroxide ions is what makes sodium carbonate a basic substance. A solution of sodium carbonate will typically have a pH significantly above 7, indicating its alkaline nature.
Factors Influencing the pH of Sodium Carbonate Solutions
The pH of a sodium carbonate solution isn't a fixed value. Several factors influence the precise pH:
-
Concentration: A more concentrated solution of sodium carbonate will generally have a higher pH than a dilute solution. This is because a higher concentration of Na₂CO₃ leads to a greater production of hydroxide ions through hydrolysis.
-
Temperature: Temperature can also affect the pH. Generally, increasing the temperature can slightly increase the pH, although this effect is often less pronounced than the concentration effect.
-
Presence of other ions: The presence of other ions in the solution can influence the pH through various interactions and complex equilibria. For example, the presence of certain metal ions might lead to the formation of insoluble precipitates, which in turn can affect the concentration of hydroxide ions.
-
Purity of the sodium carbonate: Impurities in the sodium carbonate sample can also affect the pH. Contaminants might be acidic or basic, thus influencing the overall pH of the solution.
Practical Applications of Sodium Carbonate's Basicity
The basic nature of sodium carbonate is exploited in numerous applications:
1. Water Softening:
Sodium carbonate's ability to react with calcium and magnesium ions (which cause water hardness) makes it an effective water softener. It precipitates these ions as insoluble carbonates, thereby removing them from the solution.
2. Cleaning Agent:
Its alkalinity makes it a powerful cleaning agent. It helps to emulsify grease and oils, removing dirt and grime effectively. This is why it's a common ingredient in many cleaning products.
3. pH Control in Industrial Processes:
In various industrial processes, maintaining a specific pH range is critical. Sodium carbonate is often used as a pH buffer or adjusting agent to achieve the desired alkalinity.
4. Food Industry:
Sodium carbonate is used in the food industry as a pH regulator, leavening agent (in baking), and even as a meat tenderizer.
5. Photography:
Historically, sodium carbonate has been used in photographic developing solutions.
6. Glass Manufacturing:
It's a crucial component in the manufacture of glass.
Safety Considerations When Handling Sodium Carbonate
While sodium carbonate is generally considered safe for many applications, certain precautions are necessary:
-
Eye and Skin Irritation: Direct contact with concentrated solutions can cause irritation to eyes and skin. Always wear appropriate personal protective equipment (PPE) such as gloves and eye protection when handling sodium carbonate.
-
Inhalation Hazards: Inhalation of dust can irritate the respiratory system. Proper ventilation should be ensured when working with powdered sodium carbonate.
-
Ingestion: Ingestion of significant amounts can cause gastrointestinal upset. Keep it away from children and pets.
Distinguishing Sodium Carbonate from Other Compounds
It's crucial to distinguish sodium carbonate from other related compounds, especially sodium bicarbonate (NaHCO₃), also known as baking soda. While both are alkaline, sodium carbonate is significantly more basic than sodium bicarbonate. Sodium bicarbonate is a weaker base and has different applications.
Conclusion: Sodium Carbonate – A Versatile Basic Compound
Sodium carbonate's basic nature is a defining characteristic that dictates its wide range of applications. Its ability to readily react with water to produce hydroxide ions underpins its efficacy in water softening, cleaning, and various industrial processes. Understanding the factors that influence its pH and taking appropriate safety precautions are essential for its safe and effective utilization. The knowledge of its chemical properties enables its proper application in diverse fields, highlighting the importance of understanding fundamental chemistry in practical applications. Always remember to consult the Safety Data Sheet (SDS) for detailed safety information before handling any chemical, including sodium carbonate.
Latest Posts
Latest Posts
-
What Is The Lowest Common Multiple Of 3 And 7
Apr 02, 2025
-
How To Find A Supplementary Angle
Apr 02, 2025
-
How Can The Strength Of An Electromagnet Be Increased
Apr 02, 2025
-
If Qt Is Perpendicular To Pr
Apr 02, 2025
-
Which Base Is Not Present In Rna
Apr 02, 2025
Related Post
Thank you for visiting our website which covers about Is Na2co3 Acidic Basic Or Neutral . We hope the information provided has been useful to you. Feel free to contact us if you have any questions or need further assistance. See you next time and don't miss to bookmark.
