Is Concave Mirror Converging Or Diverging
Juapaving
Mar 25, 2025 · 6 min read
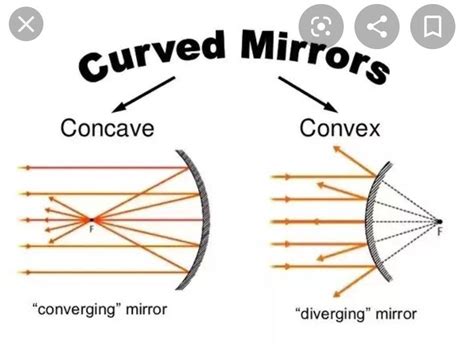
Table of Contents
Is a Concave Mirror Converging or Diverging? Understanding Mirror Types and Their Applications
The question of whether a concave mirror is converging or diverging is fundamental to understanding geometric optics. The answer, simply put, is that a concave mirror is converging. However, a deeper understanding requires exploring the principles of reflection, focal points, and image formation. This article delves into the properties of concave mirrors, contrasting them with convex mirrors, and illustrating their diverse applications.
Understanding Reflection and Image Formation
Before diving into the specifics of concave mirrors, let's establish the basic principles of reflection. Reflection is the bouncing back of light rays when they strike a surface. The angle of incidence (the angle between the incident ray and the normal to the surface) is equal to the angle of reflection (the angle between the reflected ray and the normal). This fundamental law governs how light interacts with mirrors, leading to image formation.
Types of Mirrors: Concave vs. Convex
Mirrors are categorized into two primary types based on their shape:
-
Concave Mirrors: These mirrors have a reflecting surface that curves inward, like the inside of a sphere. The inward curvature is crucial to their converging properties.
-
Convex Mirrors: These mirrors have a reflecting surface that curves outward, like the outside of a sphere. This outward curvature causes them to diverge light rays.
Why Concave Mirrors are Converging
The converging nature of a concave mirror stems directly from its inward curvature. When parallel rays of light strike a concave mirror, they reflect and converge at a single point called the focal point (F). The distance between the mirror's surface and the focal point is known as the focal length (f). This convergence is what makes concave mirrors so useful in a variety of applications.
Ray Diagrams: Visualizing Convergence
Ray diagrams are essential tools for visualizing how light interacts with mirrors and lenses. For a concave mirror, three key rays are typically used:
-
Parallel Ray: A ray parallel to the principal axis reflects through the focal point.
-
Focal Ray: A ray passing through the focal point reflects parallel to the principal axis.
-
Central Ray: A ray passing through the center of curvature (C) reflects back on itself.
By drawing these three rays, one can accurately determine the location, size, and orientation of the image formed by a concave mirror.
Image Formation in Concave Mirrors: A Detailed Look
The type of image formed by a concave mirror depends on the position of the object relative to the focal point and the center of curvature. Several scenarios exist:
-
Object beyond the center of curvature (C): The image formed is real, inverted, and diminished. This is the principle behind many astronomical telescopes.
-
Object at the center of curvature (C): The image formed is real, inverted, and the same size as the object.
-
Object between the center of curvature (C) and the focal point (F): The image formed is real, inverted, and magnified. This principle is employed in slide projectors.
-
Object at the focal point (F): No image is formed; the reflected rays are parallel.
-
Object between the focal point (F) and the mirror: The image formed is virtual, upright, and magnified. This is the type of image you see when using a concave mirror as a shaving or makeup mirror.
The terms "real" and "virtual" refer to the nature of the image. A real image can be projected onto a screen, while a virtual image cannot.
Contrasting Concave and Convex Mirrors
While concave mirrors converge light, convex mirrors diverge light. This fundamental difference leads to distinct image characteristics:
| Feature | Concave Mirror | Convex Mirror |
|---|---|---|
| Shape | Curves inward | Curves outward |
| Image Type | Real or virtual, depending on object position | Always virtual |
| Image Orientation | Real images are inverted; virtual images are upright | Always upright |
| Image Size | Can be magnified, diminished, or same size | Always diminished |
| Focal Length | Positive | Negative |
| Applications | Telescopes, projectors, shaving mirrors | Security mirrors, car side mirrors |
The diverging nature of a convex mirror means that parallel rays of light, after reflection, appear to originate from a virtual focal point behind the mirror. This results in images that are always virtual, upright, and diminished.
Applications of Concave Mirrors: A Diverse Range
Concave mirrors find widespread applications due to their ability to converge light:
1. Astronomical Telescopes: Capturing Distant Light
Large concave mirrors in reflecting telescopes collect and focus faint light from distant celestial objects, enabling astronomers to observe stars, galaxies, and other astronomical phenomena. The converging property allows the telescope to gather much more light than a refracting telescope of the same size.
2. Projectors: Magnifying Images onto a Screen
Projectors use concave mirrors to magnify images projected from a light source onto a screen. The mirror's converging ability creates a larger, clearer image suitable for presentations and entertainment.
3. Shaving and Makeup Mirrors: Close-up Views
The magnified virtual image produced by a concave mirror when the object is placed close to the focal point is ideal for detailed tasks like shaving or applying makeup. The magnification helps users see finer details.
4. Solar Furnaces: Concentrating Solar Energy
Concave mirrors can be used to concentrate sunlight onto a small area, creating intense heat. This principle is used in solar furnaces, which can reach extremely high temperatures for various industrial applications.
5. Headlights and Reflectors: Directing Light
Concave reflectors in headlights and flashlights help to focus light into a beam, increasing the intensity and distance of illumination. The concentrated beam improves visibility.
6. Satellite Dishes: Receiving Signals
Parabolic concave mirrors, commonly used in satellite dishes, focus incoming radio waves onto a receiver. This concentration enhances signal reception, making it possible to receive weak signals from distant satellites.
Applications of Convex Mirrors: Expanding the View
While not as widely used as concave mirrors for image magnification, convex mirrors offer unique benefits:
1. Security Mirrors: Wide-Angle Views
Convex mirrors provide a wider field of view than flat mirrors, making them ideal for security applications. They allow security personnel to monitor a larger area.
2. Car Side Mirrors: Reducing Blind Spots
Convex mirrors on cars minimize blind spots by providing a wider view of the surrounding area. However, the resulting diminished image needs to be interpreted accordingly. The warning "Objects in mirror are closer than they appear" is a crucial reminder of this image characteristic.
3. Store Security Mirrors: Enhancing Surveillance
Similar to security mirrors, convex mirrors in stores provide a wide-angle view of the sales floor, allowing store staff to monitor customers and deter shoplifting.
Conclusion: Understanding the Convergence and Divergence of Mirrors
The converging nature of concave mirrors and the diverging nature of convex mirrors are fundamental properties that dictate their diverse applications. Understanding the principles of reflection, image formation, and the differences between these mirror types is crucial in various fields, including astronomy, optics, engineering, and everyday life. Whether it's magnifying distant stars, projecting images onto a screen, or enhancing security, these mirrors play significant roles in shaping our technological landscape. The ability to visualize the path of light rays through ray diagrams provides a powerful tool for understanding and predicting how these mirrors interact with light and form images. This knowledge facilitates the design and use of mirrors in a multitude of innovative applications.
Latest Posts
Latest Posts
-
5 Letter Words Ending In An
Mar 26, 2025
-
Is The Number 11 A Prime Number
Mar 26, 2025
-
Difference Between Violet And Purple Colour
Mar 26, 2025
-
Whats The Square Root Of 29
Mar 26, 2025
-
How Many Mm Is 8 Cm
Mar 26, 2025
Related Post
Thank you for visiting our website which covers about Is Concave Mirror Converging Or Diverging . We hope the information provided has been useful to you. Feel free to contact us if you have any questions or need further assistance. See you next time and don't miss to bookmark.
