Is Air A Compound Or An Element
Juapaving
Mar 20, 2025 · 6 min read
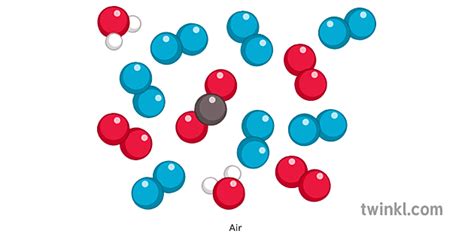
Table of Contents
Is Air a Compound or an Element? Understanding the Composition of Our Atmosphere
The simple question, "Is air a compound or an element?" belies a surprisingly complex answer. While it might seem like a straightforward classification, understanding the nature of air requires delving into the fundamental concepts of chemistry, specifically the distinctions between elements, compounds, and mixtures. This article will explore the composition of air, explaining why it's classified as a mixture and detailing the different elements and compounds that comprise it. We'll also discuss the implications of air's composition on our planet and its life-sustaining properties.
The Fundamentals: Elements, Compounds, and Mixtures
Before we dive into the specifics of air, let's establish a clear understanding of the key terms:
-
Element: An element is a pure substance consisting only of atoms that all have the same number of protons in their atomic nuclei. Elements cannot be broken down into simpler substances by chemical means. Examples include oxygen (O), nitrogen (N), and hydrogen (H).
-
Compound: A compound is a pure substance formed when two or more different chemical elements are chemically bonded together. These bonds create a distinct substance with properties different from its constituent elements. Water (H₂O), a compound of hydrogen and oxygen, is a classic example. Compounds can be broken down into their constituent elements through chemical reactions.
-
Mixture: A mixture is a substance comprising two or more components not chemically bonded. A mixture's components retain their individual chemical properties, and the proportions of each component can vary. Air is a prime example of a mixture.
The Composition of Air: A Mixture of Gases
Air is not a compound; it's a homogeneous mixture of various gases. This means the gases are evenly distributed throughout, making the air appear uniform in composition. However, the exact proportions of these gases can vary depending on location, altitude, and other environmental factors.
The major components of air are:
1. Nitrogen (N₂): The Predominant Gas
Nitrogen constitutes approximately 78% of the Earth's atmosphere by volume. It's a diatomic gas, meaning two nitrogen atoms are bonded together to form a molecule (N₂). While nitrogen is essential for life, in its gaseous form, it's largely inert, meaning it doesn't readily react with other substances. This inertness is crucial; otherwise, nitrogen would react with many other atmospheric components, drastically altering the composition and properties of air.
2. Oxygen (O₂): Essential for Life
Oxygen makes up about 21% of the atmosphere's volume. Unlike nitrogen, oxygen is highly reactive. It plays a vital role in respiration, the process by which living organisms obtain energy from food. Oxygen's reactivity also makes it essential for combustion, the process of burning. The presence of oxygen in sufficient quantities is critical for the survival of most life forms on Earth.
3. Argon (Ar): An Inert Noble Gas
Argon accounts for approximately 0.93% of the atmosphere. It's a noble gas, meaning it's chemically inert and doesn't readily react with other substances. This inertness makes argon useful in various industrial applications where preventing unwanted chemical reactions is necessary.
4. Other Gases: Trace Components with Significant Impacts
Besides nitrogen, oxygen, and argon, air contains small amounts of other gases. These include:
-
Carbon Dioxide (CO₂): Although present in relatively small quantities (around 0.04%), carbon dioxide plays a crucial role in the Earth's climate. It's a greenhouse gas, trapping heat and contributing to the greenhouse effect. Human activities, particularly the burning of fossil fuels, have significantly increased atmospheric CO₂ levels, leading to concerns about climate change.
-
Neon (Ne), Helium (He), Krypton (Kr), Xenon (Xe): These are all noble gases present in trace amounts. They are chemically inert and have limited biological significance.
-
Water Vapor (H₂O): The concentration of water vapor is highly variable, depending on factors such as temperature, humidity, and location. Water vapor is essential for the water cycle and plays a significant role in weather patterns.
-
Ozone (O₃): Ozone is a triatomic molecule of oxygen. While it's a significant pollutant at ground level, it plays a critical role in the stratosphere, forming the ozone layer that protects life on Earth from harmful ultraviolet radiation from the sun.
Why Air is a Mixture, Not a Compound
The key reason air is classified as a mixture, and not a compound, is the absence of chemical bonding between its constituent components. In a compound, the atoms of different elements are chemically linked through strong bonds, forming a distinct molecule with unique properties. In air, nitrogen, oxygen, and other gases exist as individual molecules, simply mixed together. They aren't chemically bonded to each other. This lack of chemical bonding allows the proportions of each component in air to vary. If air were a compound, the ratio of its components would be fixed and constant, as is the case with water (H₂O) always having a 2:1 ratio of hydrogen to oxygen.
The Importance of Air's Composition
The composition of air is crucial for supporting life on Earth. The balance of nitrogen and oxygen is particularly significant. Nitrogen's inertness prevents it from interfering with other chemical processes, while oxygen provides the necessary reactant for respiration and combustion. The presence of trace gases like carbon dioxide, while crucial for plant life through photosynthesis, also plays a significant role in regulating the Earth's temperature. The ozone layer, high in the stratosphere, provides essential protection from harmful UV radiation.
Variations in Air Composition: Factors to Consider
The composition of air is not uniform across the globe. Several factors can influence the proportions of different gases:
-
Altitude: The composition of air changes with altitude. The concentration of oxygen, for instance, decreases with increasing altitude, making it challenging to breathe at high elevations.
-
Location: Urban areas typically have higher concentrations of pollutants, such as carbon monoxide and nitrogen oxides, than rural areas.
-
Weather patterns: Weather systems can impact air composition, leading to variations in humidity and the concentration of various gases.
-
Industrial activity: Industrial emissions can release significant amounts of pollutants into the atmosphere, affecting air quality locally and sometimes regionally.
Conclusion: Air - A Vital Mixture
In conclusion, air is unequivocally a mixture, not a compound. It's a complex mixture of gases, primarily nitrogen and oxygen, with various other trace components. The proportions of these gases can vary, but the overall composition plays a crucial role in supporting life and shaping our planet's climate. Understanding the composition of air is essential for addressing environmental challenges such as air pollution and climate change, ensuring the continued health of our atmosphere and the life it supports. Further research into the intricacies of atmospheric composition is crucial for a deeper understanding of our planet's dynamics and for developing strategies to protect its delicate ecological balance. The seemingly simple question of whether air is a compound or an element opens up a fascinating world of chemistry, environmental science, and the intricate relationship between the atmosphere and all living things.
Latest Posts
Latest Posts
-
Is Sales And Revenue The Same
Mar 21, 2025
-
What Is The Lcm Of 3 And 8
Mar 21, 2025
-
68 F Is What In Celsius
Mar 21, 2025
-
Africa Is Separated From Europe By The
Mar 21, 2025
-
What Is Least Common Multiple Of 8 And 12
Mar 21, 2025
Related Post
Thank you for visiting our website which covers about Is Air A Compound Or An Element . We hope the information provided has been useful to you. Feel free to contact us if you have any questions or need further assistance. See you next time and don't miss to bookmark.
