Africa Is Separated From Europe By The
Juapaving
Mar 21, 2025 · 6 min read
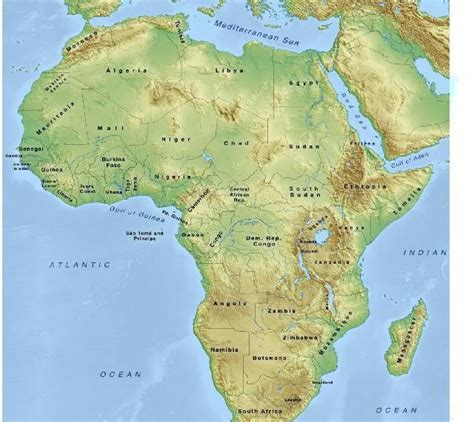
Table of Contents
Africa is Separated from Europe by the Mediterranean Sea: A Deep Dive into Geography, History, and Culture
Africa and Europe, two continents rich in diverse cultures, histories, and landscapes, are geographically separated by a significant body of water: the Mediterranean Sea. This seemingly simple statement belies a complex interplay of geographical features, historical interactions, and cultural exchanges that have shaped the destinies of both continents for millennia. This article will explore the Mediterranean Sea's role as a geographical divider and connector, examining its impact on the relationship between Africa and Europe.
The Mediterranean Sea: A Geographical Divide
The Mediterranean Sea is a vast expanse of water, approximately 2.5 million square kilometers, nestled between three continents: Europe, Africa, and Asia. Its roughly horseshoe shape, bounded by diverse coastlines, creates a distinct geographical boundary between Africa and Europe. The Strait of Gibraltar, a narrow passage between Spain and Morocco, is the only natural oceanic connection between the Mediterranean and the Atlantic Ocean, making the Mediterranean a relatively enclosed sea. This semi-enclosed nature contributes to its unique hydrological characteristics, including its higher salinity and distinct marine ecosystem compared to the Atlantic.
Key Geographical Features Defining the Boundary:
-
The Strait of Gibraltar: This crucial strait acts as the gateway between the Atlantic and Mediterranean, significantly influencing the water flow and salinity levels within the Mediterranean Sea. Its narrow width has historically held strategic importance, controlling maritime access between the two continents.
-
The Northern Coastline (Europe): This coastline boasts varied topography, ranging from the rugged cliffs of Greece and Italy to the more gently sloping beaches of Spain and France. The diverse landscapes have profoundly influenced the development of human settlements and economic activities throughout history.
-
The Southern Coastline (Africa): The African coastline of the Mediterranean is characterized by diverse coastal plains, mountains, and deltas. The geography has influenced the development of distinct regional cultures and economies along the North African littoral.
Historical Interactions: A Bridge Despite the Divide
Despite the geographical separation, the Mediterranean Sea has acted as a vital conduit for interaction between Africa and Europe throughout history. Rather than a barrier, the sea became a highway for trade, migration, cultural exchange, and conflict.
Ancient Civilizations and the Mediterranean:
-
Phoenician Expansion: The Phoenicians, originating from modern-day Lebanon, established extensive trading networks throughout the Mediterranean, connecting Africa and Europe. Their maritime prowess facilitated cultural exchange and the spread of ideas and technologies.
-
Greek Colonization: Ancient Greeks established numerous colonies along the Mediterranean coast of Africa, leading to the fusion of Greek and African cultures. This interaction significantly shaped the development of North African societies.
-
Roman Empire: The Roman Empire's vast reach encompassed both sides of the Mediterranean, creating a period of extensive interaction and cultural exchange. Roman infrastructure, laws, and language left a lasting legacy across both continents.
The Middle Ages and Beyond:
-
Islamic Expansion: The expansion of the Islamic Empire across North Africa and parts of Europe led to renewed connections between the two continents. The exchange of knowledge, art, and culture during this period was substantial.
-
The Crusades: The Crusades, a series of religious wars between Christians and Muslims, further intensified interactions between Europe and North Africa, albeit often marked by conflict and conquest.
-
Colonial Era: The Age of Exploration and colonialism brought a new era of interaction, largely characterized by European dominance over North Africa and other parts of the continent. This era had a profound and often negative impact on the political and social landscapes of Africa.
Cultural Exchanges Across the Waters:
The Mediterranean Sea hasn't merely facilitated political and economic interactions; it has also been instrumental in shaping the rich tapestry of cultures found on both continents. The proximity and historical interactions have led to a complex interplay of influences.
Linguistic Influences:
The Mediterranean's role as a conduit for migration and trade is reflected in the languages spoken on both sides. The spread of Latin, Greek, Arabic, and other languages through migration, colonization, and trade reflects the historical connections across the sea. Many languages in North Africa retain traces of Arabic and Berber influences, while European languages have been shaped by interactions with languages from North Africa and the wider Mediterranean world.
Architectural and Artistic Influences:
Architectural styles in North Africa and parts of Southern Europe reflect centuries of interaction and exchange. Roman, Byzantine, Islamic, and European architectural styles have intertwined, resulting in unique architectural blends specific to the Mediterranean region. Similar influences are seen in artistic expressions across the region, indicating the extent of cultural fusion and exchange across the Mediterranean.
Culinary Influences:
The Mediterranean diet, a cornerstone of healthy eating, is a testament to the culinary exchange fostered by the sea. Shared ingredients, cooking techniques, and culinary traditions reveal the long history of interaction between North African and European cuisines. Shared ingredients like olives, wheat, and spices are evidence of this deep culinary connection.
The Mediterranean Today: Challenges and Opportunities
The Mediterranean Sea continues to be a significant factor in the relationship between Africa and Europe. While historical connections are undeniable, current challenges and opportunities also highlight the ongoing importance of the sea.
Migration:
The Mediterranean Sea has become a prominent route for migration, with many individuals from Africa seeking opportunities or refuge in Europe. This migration has sparked complex debates concerning immigration policies, humanitarian concerns, and economic integration.
Trade and Economics:
The Mediterranean remains a vital trade route, connecting European and African economies. Trade across the sea continues to be important for both continents, driving economic growth and fostering business relations.
Environmental Concerns:
The Mediterranean Sea faces numerous environmental challenges, including pollution, overfishing, and climate change. Addressing these concerns requires collaboration between European and African nations to protect this shared natural resource.
Political Relations:
Political relations between European and African nations bordering the Mediterranean are complex and varied, ranging from cooperation on economic and environmental issues to tensions related to migration and security concerns.
Conclusion: A Sea of Connections
The Mediterranean Sea, though geographically separating Africa and Europe, has historically served as a vital connector. Its waters have borne witness to millennia of trade, migration, conflict, and cultural exchange, shaping the destinies of both continents. Understanding the Mediterranean's role in this dynamic interplay is crucial to grasping the complex relationship between Africa and Europe, and appreciating the richness of their intertwined histories and cultures. The challenges and opportunities presented by the sea today underscore the continued importance of collaboration and understanding between these two continents as they navigate a shared future. Further research into specific historical periods, cultural interactions, and contemporary challenges will reveal the enduring significance of the Mediterranean Sea in the relationship between Africa and Europe.
Latest Posts
Latest Posts
-
What Percent Is 5 Of 20
Mar 21, 2025
-
What Is 62 Inches In Feet
Mar 21, 2025
-
Lowest Common Multiple Of 16 And 24
Mar 21, 2025
-
Common Multiples Of 10 And 12
Mar 21, 2025
-
The Division Of Cytoplasm Is Called
Mar 21, 2025
Related Post
Thank you for visiting our website which covers about Africa Is Separated From Europe By The . We hope the information provided has been useful to you. Feel free to contact us if you have any questions or need further assistance. See you next time and don't miss to bookmark.
