Is 12 Prime Or Composite Number
Juapaving
Mar 13, 2025 · 5 min read
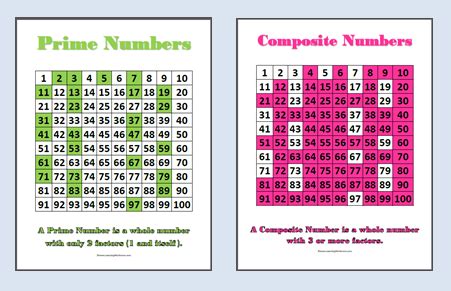
Table of Contents
Is 12 a Prime or Composite Number? A Deep Dive into Number Theory
The question, "Is 12 a prime or composite number?" might seem simple at first glance. However, understanding the answer requires a deeper dive into the fundamentals of number theory, exploring the definitions of prime and composite numbers, and examining the properties that distinguish them. This comprehensive guide will not only answer this specific question but also equip you with a solid understanding of prime and composite numbers, their significance in mathematics, and how to identify them.
Understanding Prime and Composite Numbers
Before we determine whether 12 is prime or composite, let's solidify our understanding of these crucial number classifications.
Prime Numbers: The Building Blocks of Arithmetic
A prime number is a natural number greater than 1 that has only two distinct positive divisors: 1 and itself. This means it's not divisible by any other whole number without leaving a remainder. Think of prime numbers as the fundamental building blocks of all other whole numbers, as every whole number greater than 1 can be expressed as a unique product of prime numbers (this is known as the Fundamental Theorem of Arithmetic).
Examples of prime numbers include: 2, 3, 5, 7, 11, 13, 17, and so on. Note that 2 is the only even prime number; all other even numbers are divisible by 2 and therefore have more than two divisors.
Composite Numbers: Products of Primes
A composite number is a natural number greater than 1 that is not a prime number. In other words, a composite number has more than two distinct positive divisors. Every composite number can be factored into a product of prime numbers. This factorization, while potentially complex for larger numbers, is unique according to the Fundamental Theorem of Arithmetic.
Examples of composite numbers include: 4 (2 x 2), 6 (2 x 3), 8 (2 x 2 x 2), 9 (3 x 3), 10 (2 x 5), and so on.
The Number 1: Neither Prime Nor Composite
It's crucial to note that the number 1 is neither prime nor composite. This is a specific definition, and understanding this exclusion is important for working with prime factorization and other number-theoretic concepts. The definition of prime numbers specifically requires two distinct divisors, and 1 only has one divisor (itself). Similarly, composite numbers, by definition, are not prime, and 1 doesn't fit this category either.
Determining if 12 is Prime or Composite
Now, let's address the question directly: Is 12 a prime or composite number?
The answer is definitively composite. Here's why:
-
Divisors of 12: 12 has several divisors other than 1 and itself. These include 2, 3, 4, and 6. Because 12 is divisible by 2, 3, 4, and 6, it violates the definition of a prime number which only allows for divisors of 1 and itself.
-
Prime Factorization of 12: We can express 12 as a product of prime numbers: 2 x 2 x 3 (or 2² x 3). This factorization demonstrates that 12 is built from prime numbers, a characteristic of all composite numbers.
Methods for Identifying Prime and Composite Numbers
Several methods can be used to determine whether a number is prime or composite. These methods range from simple observation to more sophisticated algorithms:
1. Trial Division:
This is the most straightforward method, particularly for smaller numbers. It involves testing for divisibility by all prime numbers less than or equal to the square root of the number in question. If the number is divisible by any of these primes, it's composite. If not, it's prime. For example, to test if 17 is prime, we only need to check for divisibility by 2, 3, and 5 because the square root of 17 is approximately 4.12. Since 17 is not divisible by 2, 3, or 5, it's a prime number.
However, this method becomes computationally expensive for very large numbers.
2. Sieve of Eratosthenes:
This ancient algorithm is an efficient method for finding all prime numbers up to a specified limit. It systematically eliminates multiples of each prime number, leaving only the prime numbers remaining. While not directly determining whether a single number is prime, it's a valuable tool for generating a list of primes within a given range.
3. Fermat's Little Theorem:
This theorem provides a probabilistic test for primality. It's not definitive, meaning it can sometimes incorrectly identify a composite number as prime (a false positive), but it's efficient for large numbers.
4. Miller-Rabin Primality Test:
This is a more sophisticated probabilistic primality test that significantly reduces the chance of false positives compared to Fermat's Little Theorem. It's widely used in cryptography and other applications requiring efficient primality testing.
The Significance of Prime and Composite Numbers
Prime and composite numbers are fundamental concepts in number theory with far-reaching applications across mathematics and computer science. Here are some key areas where they play a critical role:
-
Cryptography: Prime numbers are essential in many encryption algorithms, providing the basis for secure communication and data protection. The difficulty of factoring large composite numbers into their prime factors is the cornerstone of many modern cryptographic systems.
-
Abstract Algebra: Prime numbers and their properties are fundamental concepts in abstract algebra, influencing the structure and behavior of algebraic systems.
-
Number Theory Research: The distribution of prime numbers, their properties, and related unsolved problems (like the Riemann Hypothesis) remain active areas of mathematical research.
-
Computer Science: Algorithms for finding and testing prime numbers are crucial in areas like cryptography, data compression, and random number generation.
-
Coding Theory: Prime numbers play a vital role in error-correcting codes, ensuring reliable data transmission and storage.
Conclusion: Understanding the Fundamentals
Determining whether 12 is prime or composite is a simple exercise once the definitions are understood. However, delving deeper reveals the fundamental importance of prime and composite numbers in mathematics and its various applications. By mastering the concepts discussed here, you gain a more robust understanding of number theory and its significant influence on many fields of study. The seemingly simple question of whether 12 is prime or composite serves as a gateway to exploring the fascinating world of prime numbers and their profound significance. Remember, the ability to quickly identify prime and composite numbers is a critical skill in various mathematical and computational contexts. Practice using different methods to strengthen your understanding and speed.
Latest Posts
Latest Posts
-
Differentiate Between Greenhouse Effect And Global Warming
May 09, 2025
-
Derive Stefans Law From Plancks Radiation Law
May 09, 2025
-
A Three Base Sequence Of Mrna Is Called
May 09, 2025
-
The Structural And Functional Unit Of The Kidney Is The
May 09, 2025
-
What Chemical Is Inside A Battery
May 09, 2025
Related Post
Thank you for visiting our website which covers about Is 12 Prime Or Composite Number . We hope the information provided has been useful to you. Feel free to contact us if you have any questions or need further assistance. See you next time and don't miss to bookmark.