In What Organelle Does Cellular Respiration Occur In
Juapaving
Mar 21, 2025 · 5 min read
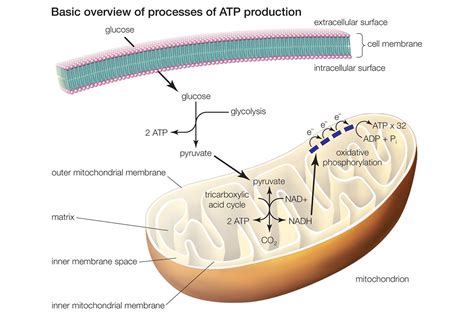
Table of Contents
In What Organelle Does Cellular Respiration Occur? A Deep Dive into the Mitochondria
Cellular respiration, the process that powers our cells and sustains life, is a complex series of biochemical reactions. Understanding where these reactions take place is crucial to grasping the intricate machinery of life. The simple answer is: cellular respiration primarily occurs in the mitochondria, often referred to as the "powerhouses" of the cell. However, this seemingly straightforward answer belies a much richer and more fascinating story. Let's delve deeper into the role of the mitochondria and explore the nuanced details of this vital process.
The Mitochondria: The Powerhouse of the Cell
The mitochondria are double-membrane-bound organelles found in almost all eukaryotic cells. Their unique structure is intimately linked to their function in cellular respiration. This structure facilitates the compartmentalization of different stages of respiration, enhancing efficiency and control.
The Double Membrane: A Key Feature
The double membrane system of the mitochondria consists of:
- Outer Mitochondrial Membrane (OMM): This relatively permeable membrane allows the passage of small molecules.
- Inner Mitochondrial Membrane (IMM): This highly folded membrane is impermeable to most molecules, except through specific transport proteins. The folds, called cristae, significantly increase the surface area available for the electron transport chain—a crucial component of cellular respiration.
- Intermembrane Space: The space between the OMM and IMM. This compartment plays a critical role in chemiosmosis, a key step in ATP production.
- Mitochondrial Matrix: The space enclosed by the IMM. This is where the Krebs cycle (citric acid cycle) takes place.
Key Mitochondrial Components for Cellular Respiration
Beyond the double membrane, several other components within the mitochondria are essential for the smooth operation of cellular respiration:
- Mitochondrial DNA (mtDNA): Mitochondria possess their own DNA, separate from the nuclear DNA. This mtDNA encodes several proteins vital for mitochondrial function, particularly those involved in the electron transport chain.
- Ribosomes: Mitochondria contain their own ribosomes, allowing them to synthesize some of their own proteins.
- Enzymes: A plethora of enzymes are embedded within the mitochondrial membranes and located in the matrix, catalyzing the various steps of cellular respiration.
The Stages of Cellular Respiration: A Location-Specific Breakdown
Cellular respiration is a multi-stage process, and each stage occurs in a specific location within the mitochondrion (or sometimes outside, in the cytoplasm, for the first stage):
1. Glycolysis: The Initial Steps in the Cytoplasm
Glycolysis, the first stage, takes place in the cytoplasm, not within the mitochondria. It involves the breakdown of glucose into pyruvate, generating a small amount of ATP and NADH. While not directly in the mitochondrion, glycolysis is crucial as it provides the pyruvate that fuels the subsequent mitochondrial stages.
2. Pyruvate Oxidation: Preparing for the Krebs Cycle
Once pyruvate is formed in the cytoplasm, it's transported into the mitochondrial matrix. Here, pyruvate undergoes oxidative decarboxylation, converting it into acetyl-CoA. This step also produces NADH and releases carbon dioxide.
3. The Krebs Cycle (Citric Acid Cycle): Generating Energy Carriers
The Krebs cycle takes place entirely within the mitochondrial matrix. Acetyl-CoA enters the cycle, undergoing a series of reactions that release carbon dioxide and generate ATP, NADH, and FADH2 – molecules that carry high-energy electrons to the next stage.
4. Oxidative Phosphorylation: The Electron Transport Chain and Chemiosmosis
This final and most significant stage occurs in the inner mitochondrial membrane (IMM). It involves two coupled processes:
-
Electron Transport Chain (ETC): Electrons from NADH and FADH2 are passed along a series of protein complexes embedded in the IMM. This electron flow releases energy, used to pump protons (H+) from the matrix into the intermembrane space, creating a proton gradient.
-
Chemiosmosis: The proton gradient created by the ETC drives protons back into the matrix through ATP synthase, an enzyme that uses the energy of this proton flow to synthesize ATP – the cell's primary energy currency. This process, occurring across the IMM, is responsible for the vast majority of ATP production during cellular respiration.
The Importance of Mitochondrial Function in Health and Disease
The efficiency of mitochondrial function is paramount for cellular health and overall well-being. Mitochondrial dysfunction has been implicated in a wide range of diseases, including:
- Neurodegenerative diseases: Alzheimer's disease, Parkinson's disease, and Huntington's disease are all associated with impaired mitochondrial function. The high energy demands of neurons make them particularly vulnerable to mitochondrial defects.
- Metabolic disorders: Conditions like diabetes and obesity are often linked to mitochondrial dysfunction, affecting glucose metabolism and energy production.
- Cardiovascular diseases: Mitochondrial dysfunction contributes to heart failure and other cardiovascular problems by impairing the energy supply to the heart muscle.
- Cancer: Cancer cells often exhibit altered mitochondrial metabolism, which supports their rapid growth and proliferation.
Beyond the Mitochondria: Other Cellular Respiration Players
While the mitochondria are the primary site of cellular respiration, other cellular components also play important roles:
- Cytoplasm: As mentioned earlier, glycolysis takes place in the cytoplasm, providing the starting material for the mitochondrial stages.
- Nucleus: The nucleus houses the genes that code for many of the proteins involved in cellular respiration, including those involved in mitochondrial biogenesis (the creation of new mitochondria).
Conclusion: A Symphony of Cellular Processes
Cellular respiration is a highly coordinated and efficient process, a testament to the sophistication of cellular machinery. The mitochondria, with their intricate structure and specialized components, are central to this process, acting as the primary site for energy production. Understanding the precise location of each stage, and the crucial roles of various organelles, is fundamental to appreciating the complexity and beauty of life's fundamental energy-generating mechanisms. The continued research into mitochondrial biology and cellular respiration holds the key to advancing our understanding of health, disease, and the intricate workings of life itself. Furthermore, exploring the intricacies of mitochondrial function opens doors to developing novel therapeutic strategies for a wide range of diseases linked to mitochondrial dysfunction. The powerhouse of the cell is, indeed, a powerhouse of research and future discoveries.
Latest Posts
Latest Posts
-
Is 6 A Factor Of 84
Mar 28, 2025
-
What Is The Lcm Of 2 And 11
Mar 28, 2025
-
In The Burning Of Methane What Are The Reactants
Mar 28, 2025
-
What Is The Difference Between Methanol And Ethanol Fuels
Mar 28, 2025
-
If A Circle Is One How Many Is An Octagon
Mar 28, 2025
Related Post
Thank you for visiting our website which covers about In What Organelle Does Cellular Respiration Occur In . We hope the information provided has been useful to you. Feel free to contact us if you have any questions or need further assistance. See you next time and don't miss to bookmark.
