How To Find Orthocentre Of A Triangle
Juapaving
Mar 25, 2025 · 5 min read
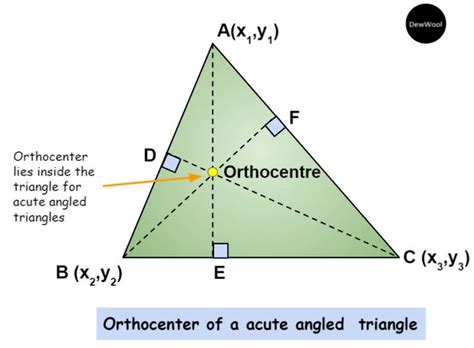
Table of Contents
How to Find the Orthocenter of a Triangle: A Comprehensive Guide
The orthocenter, a fascinating point within a triangle, holds a significant place in geometry. Understanding how to locate this point is crucial for various geometric proofs and applications. This comprehensive guide will delve into multiple methods for finding the orthocenter, catering to different levels of mathematical understanding. We'll explore the underlying principles, provide step-by-step instructions, and offer practical examples to solidify your grasp of this concept.
Understanding the Orthocenter
Before we delve into the methods, let's establish a solid foundation. The orthocenter of a triangle is the point where the three altitudes of the triangle intersect. An altitude is a line segment drawn from a vertex of the triangle perpendicular to the opposite side (or its extension). Crucially, these three altitudes always concur (meet at a single point) – that point is the orthocenter.
Key Properties of the Orthocenter:
- Intersection of Altitudes: As mentioned, the orthocenter is the intersection point of the three altitudes.
- Type of Triangle: The orthocenter's location varies depending on the type of triangle:
- Acute Triangle: The orthocenter lies inside the triangle.
- Right-Angled Triangle: The orthocenter coincides with the right-angled vertex.
- Obtuse Triangle: The orthocenter lies outside the triangle.
- Geometric Significance: The orthocenter is a central point in many geometric theorems and constructions.
Method 1: Using Coordinate Geometry
This method is particularly useful when the coordinates of the triangle's vertices are known. It leverages the concept of slopes and perpendicular lines.
Steps:
-
Assign Coordinates: Let the vertices of the triangle be A(x₁, y₁), B(x₂, y₂), and C(x₃, y₃).
-
Find Slopes: Calculate the slopes of the sides of the triangle:
- m(AB) = (y₂ - y₁) / (x₂ - x₁)
- m(BC) = (y₃ - y₂) / (x₃ - x₂)
- m(AC) = (y₃ - y₁) / (x₃ - x₁)
-
Find Slopes of Altitudes: Since altitudes are perpendicular to the sides, their slopes are the negative reciprocals of the sides' slopes:
- m(altitude from C) = -1 / m(AB)
- m(altitude from A) = -1 / m(BC)
- m(altitude from B) = -1 / m(AC)
-
Find Equations of Altitudes: Use the point-slope form of a line (y - y₁ = m(x - x₁)) to find the equations of at least two altitudes. For example:
- Equation of altitude from C: y - y₃ = m(altitude from C)(x - x₃)
- Equation of altitude from A: y - y₁ = m(altitude from A)(x - x₁)
-
Solve the System of Equations: Solve the system of equations formed by the two altitude equations simultaneously. The solution (x, y) represents the coordinates of the orthocenter.
Example:
Let's find the orthocenter of a triangle with vertices A(1, 2), B(4, 6), and C(7, 2).
-
Slopes of Sides:
- m(AB) = (6 - 2) / (4 - 1) = 4/3
- m(BC) = (2 - 6) / (7 - 4) = -4/3
- m(AC) = (2 - 2) / (7 - 1) = 0
-
Slopes of Altitudes:
- m(altitude from C) = -3/4
- m(altitude from A) = 3/4
- m(altitude from B) is undefined (since m(AC) = 0, the altitude from B is a vertical line).
-
Equations of Altitudes:
- Altitude from C: y - 2 = (-3/4)(x - 7)
- Altitude from B: x = 4 (vertical line passing through B)
-
Solving the System: Substitute x = 4 into the equation of the altitude from C:
- y - 2 = (-3/4)(4 - 7)
- y - 2 = 9/4
- y = 17/4
Therefore, the orthocenter is (4, 17/4).
Method 2: Using Geometric Construction
This method utilizes a compass and straightedge to construct the altitudes and locate their intersection.
Steps:
-
Construct Altitudes: For each vertex, construct a line perpendicular to the opposite side. This can be done using a compass to create perpendicular bisectors or by utilizing other geometric construction techniques. Only two altitudes are needed to find the orthocenter.
-
Locate Intersection: The point where the two altitudes intersect is the orthocenter.
Method 3: Using Vectors
This method employs vector algebra to determine the orthocenter's position.
Steps:
-
Define Vectors: Represent the sides of the triangle as vectors: AB, BC, CA.
-
Find Perpendicular Vectors: Determine vectors perpendicular to each side using the dot product. For instance, a vector perpendicular to AB would satisfy the dot product condition AB • v = 0.
-
Express Altitudes: Express the equations of the altitudes in vector form using a suitable parameter.
-
Solve System: Solve the resulting system of equations to find the position vector of the orthocenter.
This method requires a more advanced understanding of vector algebra and is omitted from the detailed step-by-step instructions due to space constraints. However, it's a powerful method for those familiar with vector mathematics.
Method 4: Using Trigonometry (for specific cases)
While not a direct method for finding coordinates, trigonometry can be highly useful in specific scenarios, particularly when dealing with angles and side lengths. Knowing the angles of the triangle can allow you to determine the slopes of the altitudes and indirectly find the orthocenter's location using coordinate geometry. Similarly, knowing the side lengths, in combination with trigonometric ratios, can aid in finding the location of the orthocenter in specific triangle configurations.
Applications of the Orthocenter
The orthocenter isn't just a theoretical point; it has practical applications in various fields:
-
Computer Graphics: In computer-aided design (CAD) and computer graphics, the orthocenter's properties are utilized in algorithms for geometric calculations and transformations.
-
Engineering: Understanding the orthocenter is helpful in structural engineering and other disciplines where geometric relationships are crucial for design and analysis.
-
Physics: The orthocenter plays a role in certain physical problems involving forces and vectors.
Conclusion
Finding the orthocenter of a triangle offers a rewarding exploration into the intricacies of geometry. The methods described here—coordinate geometry, geometric construction, vector algebra, and indirect trigonometric approaches—provide versatile tools for tackling various problems and contexts. Mastering these techniques opens doors to a deeper understanding of geometric principles and their applications in diverse fields. Remember to choose the method best suited to the given information and your mathematical comfort level. With practice, locating the orthocenter will become second nature!
Latest Posts
Latest Posts
-
How To Find The Natural Abundance Of Isotopes
Mar 28, 2025
-
What Is The Lcm Of 4 8 10
Mar 28, 2025
-
What Triangle Has 2 Equal Sides
Mar 28, 2025
-
Metal Which Is Poor Conductor Of Heat
Mar 28, 2025
-
Nouns That Start With A V
Mar 28, 2025
Related Post
Thank you for visiting our website which covers about How To Find Orthocentre Of A Triangle . We hope the information provided has been useful to you. Feel free to contact us if you have any questions or need further assistance. See you next time and don't miss to bookmark.
